
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At 508 million years old, it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints.

The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 485.4 Ma.
The PaleozoicEra is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six geologic periods, Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian.
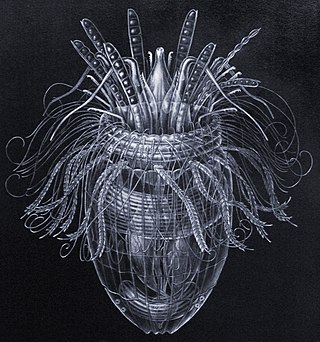
Loricifera is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals with 43 described species. and approximately 100 more that have been collected and not yet described. Their sizes range from 100 μm to ca. 1 mm.

Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

Dyfed is a preserved county in southwestern Wales. It is a mostly rural area with a coastline on the Irish Sea and the Bristol Channel.

The Maotianshan Shales (帽天山页岩) are a series of Early Cambrian sedimentary deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.

Panarthropoda is a proposed animal clade containing the extant phyla Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora. Panarthropods also include extinct marine legged worms known as lobopodians ("Lobopodia"), a paraphyletic group where the last common ancestor and basal members (stem-group) of each extant panarthropod phylum are thought to have risen. However the term "Lobopodia" is sometimes expanded to include tardigrades and onychophorans as well.

Sirius Passet is a Cambrian Lagerstätte in Peary Land, Greenland. The Sirius Passet Lagerstätte was named after the Sirius sledge patrol that operates in North Greenland. It comprises six places in Nansen Land, on the east shore of J.P. Koch Fjord in the far north of Greenland. It was discovered in 1984 by A. Higgins of the Geological Survey of Greenland. A preliminary account was published by Simon Conway Morris and others in 1987 and expeditions led by J. S. Peel and Conway Morris have returned to the site several times between 1989 and the present. A field collection of perhaps 10,000 fossil specimens has been amassed. It is a part of the Buen Formation.

The Orsten fauna are fossilized organisms preserved in the Orsten lagerstätte of Cambrian rocks, notably at Kinnekulle and on the island of Öland, all in Sweden.
The Burgess Shale of British Columbia is famous for its exceptional preservation of mid-Cambrian organisms. Around 69 other sites have been discovered of a similar age, with soft tissues preserved in a similar, though not identical, fashion. Additional sites with a similar form of preservation are known from the Ediacaran and Ordovician periods.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.
The Cambrian explosion is an interval of time beginning approximately 538.8 million years ago in the Cambrian period of the early Paleozoic, when a sudden radiation of complex life occurred and practically all major animal phyla started appearing in the fossil record. It lasted for about 13 to 25 million years and resulted in the divergence of most modern metazoan phyla. The event was accompanied by major diversification in other groups of organisms as well.

The Pioche Shale is an Early to Middle Cambrian Burgess shale-type Lagerstätte in Nevada. It spans the Early–Middle Cambrian boundary; fossils from the Early Cambrian are preserved in botryoidal hematite, whereas those from the Middle Cambrian are preserved in the more familiar carbon films, and very reminiscent of the Chengjiang County preservation.

Omnidens, meaning "all-tooth", is an extinct genus of large Cambrian animal known only from a series of large mouth apparatus and sclerotized talon-like structures, originally mistaken as the mouthparts of anomalocaridids. When first named, it was interpreted as a giant priapulid, but is now considered a panarthropod. Its mouth apparatus closely resembles that of the smaller gilled lobopodian Pambdelurion, indicating it is likely to have been a close relative of that species, potentially even synonymous. With a maximum estimated body length of 1.5 metres (4.9 ft), Omnidens is suggested to have been the largest known free-living Cambrian organism. Omnidens fossils are found in the Maotianshan Shales.

The Potosi Formation is a geologic formation in Missouri, Illinois and Indiana. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cambrian period.

Spinoloricus is a genus of nanaloricid loriciferans. Its type species is S. turbatio, described in 2007, and another species, native to completely anoxic environment, Spinoloricus cinziae, was described in 2014.
Orstenoloricus is a loriciferan larva, presumably from the stem group, preserved by early three-dimensional mineralization in an orsten-type setting in the mid-Cambrian of Australia. It somewhat resembles the larva of the unusual loriciferan Tenuiloricus.

Kutorginates (Kutorginata) are an extinct class of early rhynchonelliform ("articulate") brachiopods. The class contains only a single order, Kutorginida (kutorginides). Kutorginides were among the earliest rhynchonelliforms, restricted to the lower-middle part of the Cambrian Period.
Shergoldana is an extinct genus of fossil bilaterian worm-like organisms. It is described as having common features with Nemathelminthes, with a possible relation to an adult kinorhynch or to the larval stage of a palaeoscolecid worm. It has been described as the first occurrence of a free living Cycloneuralian from the Cambrian period.













