
Equisetum is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of vascular plants that reproduce by spores rather than seeds.

Osmundaceae is a family of ferns containing four to six extant genera and 18–25 known species. It is the only living family of the order Osmundales in the class Polypodiopsida (ferns) or in some classifications the only order in the class Osmundopsida. This is an ancient and fairly isolated group that is often known as the "flowering ferns" because of the striking aspect of the ripe sporangia in Claytosmunda, Osmunda, Osmundastrum, and Plensium. In these genera the sporangia are borne naked on non-laminar pinnules, while Todea and Leptopteris bear sporangia naked on laminar pinnules. Ferns in this family are larger than most other ferns.

Calamites is a genus of extinct arborescent (tree-like) horsetails to which the modern horsetails are closely related. Unlike their herbaceous modern cousins, these plants were medium-sized trees, growing to heights of 30-50 meters. They were components of the understories of coal swamps of the Carboniferous Period.

Equisetidae is one of the four subclasses of Polypodiopsida (ferns), a group of vascular plants with a fossil record going back to the Devonian. They are commonly known as horsetails. They typically grow in wet areas, with whorls of needle-like branches radiating at regular intervals from a single vertical stem.

A compression fossil is a fossil preserved in sedimentary rock that has undergone physical compression. While it is uncommon to find animals preserved as good compression fossils, it is very common to find plants preserved this way. The reason for this is that physical compression of the rock often leads to distortion of the fossil.

Oligochlora is an extinct genus of sweat bee in the Halictidae subfamily Halictinae. The genus currently contains six species, all of which are known from the early Miocene Burdigalian stage Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.

Equisetum scirpoides Michx., Fl. Bor.-Amer. 2: 281 (1803). 2 n = 216.The smallest of the currently occurring representatives of the genus Equisetum (horsetail).

Lutzomyia adiketis is an extinct species of sandfly in the moth fly subfamily Phlebotominae. L. adiketis is a vector of the extinct Paleoleishmania neotropicum and both species are solely known from early Miocene Burdigalian stage Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.

Araucaria mirabilis is an extinct species of coniferous tree from Patagonia, Argentina. It belongs to the genus Araucaria.
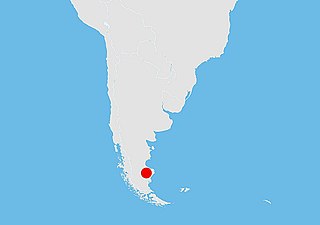
La Matilde Formation is a Jurassic geological formation in the Austral Basin of Santa Cruz Province, Patagonia, Argentina. It is dated to the Middle to Late Jurassic. From the Bathonian age to the Kimmeridgian age at the latest.
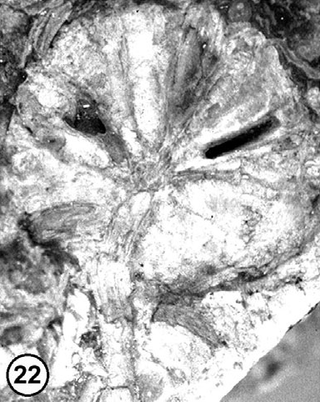
Araucarites sanctaecrucis is an extinct coniferous tree from Patagonia, Argentina. Its exact affinities are unknown and it is currently assigned to the form genus Araucarites of the family Araucariaceae. A. sanctaecrucis are known from petrified fossils of branches, foliage, and cones from the Cerro Cuadrado Petrified Forest.
Calocedrus huashanensis is an extinct incense-cedar species in the family Cupressaceae described from a group of isolated foliage fossils including stems and leaves. The species is known from Oligocene sediments exposed in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. It is one of a number of extinct species placed in the living genus Calocedrus.

Electrostephanus is an extinct genus of crown wasp in the hymenopteran family Stephanidae, and is the only genus placed in the subfamily Electrostephaninae. The genus contains four described species, E. brevicornis, E. neovenatus, E. janzeni, and E. petiolatus, placed in two subgenera E. (Electrostephanus) and E. (Electrostephanodes). Electrostephanus is known from several middle Eocene fossils which have been found in Europe.
Eoprephasma is an extinct genus of stick insect in the susumaniid subfamily Susumaniinae known from a group of Eocene fossils found in North America. When first described there was a single named species, Eoprephasma hichensi.
Liquidambar changii is an extinct species of sweetgum in the Altingiaceae genus Liquidambar. Liquidambar changii is known from Middle Miocene fossils found in Central Washington.

Quercus hiholensis is an extinct species of oak in the Fagaceae genus Quercus. The species is known from Middle Miocene fossils found in Central Washington.
Equisetum dimorphum is an extinct horsetail species of the family Equisetaceae, and one of the oldest records of the genus Equisetum. It was found in rocks from the Lower Jurassic of Chubut, Argentina, among other plants as ferns, conifers and pteridosperms. Their remains consist of stems, leaves, strobili, and pagoda structures, which are preserved as impressions and casts. The combination of fine grained sediment, and the probable silica deposits in the epidermis of the plant, have managed to conserve not only its gross morphology, but also epidermal details not often present in this kind of preservation. This species was described in 2015 in Ameghiniana by a team led by Andres Elgorriaga, that included investigators of the Museum of Paleontology Egidio Feruglio, the Swedish Museum of Natural History, and the Buenos Aires University.

Bombus trophonius is an extinct species of bumble bee known from a Miocene fossil found in Europe. It belongs to the Bombus subgenus Cullumanobombus and is considered most similar to the living species Bombus rufocinctus of North America.

Equisetites is an extinct genus of vascular plants within Equisetaceae, a family of vascular plants that reproduce by spores rather than seeds. The genus was named by Sternberg (1833) and contains at least 40 named species and two unnamed species, with the earliest known species being E. hemingwayi from the Westphalian of Yorkshire, England, though the affinity of this genus to modern Equistaceae is uncertain.

Equisetum similkamense is an extinct horsetail species in the family Equisetaceae described from a group of whole plant fossils including rhizomes, stems, and leaves. The species is known from Ypresian sediments exposed in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of several extinct species placed in the living genus Equisetum.














