
Erechthias is a genus of the fungus moth family, Tineidae. Therein, it belongs to the subfamily Erechthiinae, of which it is the type genus. The exact circumscription of this genus is still disputed, but it may encompass more than 150 species.

Izatha prasophyta is a moth of the family Oecophoridae. It is endemic to New Zealand, where it is known from the North Island, except Hawkes Bay or the Wairarapa. Larvae likely feed on rotting wood although larvae of this species have been reared on the fruiting body of the bracket fungus Bjerkandera adusta. Adults are on the wing from November to February.

Erechthias chionodira is a species of moth of the family Tineidae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1880. This species is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed on both the North and South Islands. E. chionodira inhabits native forest. Larvae likely feed on dead plant debris or on the tough leaves of plants such as flax. Adults are on the wing from September until February. During the day they can be seen at rest on tree trunks or fences. Adults are attracted to light.
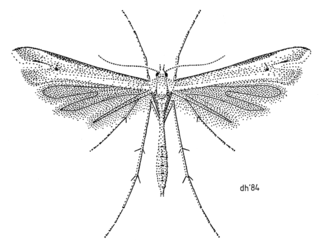
Amblyptilia lithoxesta is a moth of the family Pterophoridae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1885. This species inhabits rough herbage on mountain sides. Larvae feed on Veronica buchananii. Adults are on the wing in January.

Pyroderces aellotricha, also known as the Cosmet moth, is a moth of the family Cosmopterigidae. It is found in New Zealand, in Australia and the Cook Islands.

Erechthias lychnopa is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand and has only been collected in a karaka grove at Sinclair Head in Wellington in November. It has yet to be collected again. It has been hypothesised that the larvae inhabit dead wood. It is classified as "Data Deficient" by the Department of Conservation.

Erechthias acrodina is a species of moth of the family Tineidae. This species was first described by Edward Meyrick. It is endemic to New Zealand and is found in the North, South and the Chatham Islands. This species inhabits native forest often near Phormium species and have also been observed on dead Leptospermum scrub. Larvae has been reared from decaying Phormium leaves. Adults are on the wing from October to February.

Erechthias charadrota is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1880. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is found on both the North and South Islands. It inhabits native forest and the larvae likely feed on either deceased plant detritus or tough leaves of plants such as palms or flax. Adults are on the wing commonly from October to February and it is likely this species has two broods per year. Adults have been trapped via a blacklight.

Erechthias chasmatias is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1880. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is found in the North Island. This species inhabits native bush. Adults are on the wing from October to April and have been collected by beating small trees and foliage.

Erechthias crypsimima is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1920. This species is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in the North Island. This species inhabits native forest and has been observed in Nothofagus fusca forest. The larvae likely feed on either deceased plant detritus or tough leaves of plants such as palms or flax. Adults are on the wing commonly from January to March. During the day adults are known to rest of tree trunks where the moth's colouration helps provide protection by camouflaging the moth.

Erechthias decoranda is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1925. This species is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in the Chatham Islands. Larvae of species in the genus Erechthias feed on dead plant debris or the tough leaves of plants such as palms. Adults are on the wing in October, December and March.

Erechthias exospila is a species of moth of the family Tineidae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1901. It is endemic to New Zealand and can be found in the North Island as well as the Poor Knights and D'Urville Islands. This species inhabits native forest. Larvae of species in the genus Erechthias feed on dead plant debris or the tough leaves of plants such as palms. E. exospila frequents the dead leaves of Astelia. Adults have been observed in November and February. Specimens of this species have been collected via malaise trap and beating shrubs.

Erechthias hemiclistra is a species of moth of the family Tineidae. It was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1911. This species is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in both the North and South Islands. It inhabits native forest and has an affinity for species in the genera Phormium,Cortaderia and Cordyline, likely as a result of its larvae feeding on dead fibre sourced from plant species in these genera. Adults are on the wing from September to April but are most commonly observed in December and January. Adults are also attracted to light.

Erechthias macrozyga is a species of moth of the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1916. This species is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in the North and South Islands. This species inhabits lowland native forest. Adult moths are on the wing from October to February.

Erechthias terminella is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was first described by Francis Walker in 1863. This species is endemic to New Zealand and can be found throughout the North and in the upper parts of the South Islands. It inhabits native forest. The larvae of E. terminella feed under a web of silk and frass on the seeds as well as possibly the pods of Phormium tenax and are also known to feed on the fruits of plant species such as Meryta sinclairii. Larva are generally sluggish but can be very agile when disturbed. Adults are on the wing throughout the year and are attracted to light.

Tingena chloritis is a species of moth in the family Oecophoridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and has been found in the South Island. Larvae of this species feed on leaf litter. The adults of this species are light flyers and are attracted to light.

Tingena hemimochla is a species of moth in the family Oecophoridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in the North Island. Adults of this species are on the wing from December until March.

Tingena pronephela is a species of moth in the family Oecophoridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and is found in the southern parts of the South Island. The species inhabits the outskirts of scrub and native forest. The adults of this species are on the wing from October to February.

Orthenches chlorocoma is a moth of the family Plutellidae first described by Edward Meyrick in 1885. It is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in the North and South Islands. The larvae of this species feed on native broom species in the genus Carmichaelia including Carmichaelia australis. Adults are on the wing in September, October and February.



















