
Amanoa is a genus from the family Phyllanthaceae first described as a genus in 1775. It is native to South America, Central America, the West Indies, and tropical Africa.

Glycydendron is a genus of plants, under the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1922. It is native to South America.
- Glycydendron amazonicumDucke - French Guinea, Suriname, Guyana, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, northwestern Brazil, possibly Colombia
- Glycydendron espiritosantenseKuhlm, - State of Espirito Santo in Brazil
Dendrothrix is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1996. It is native to southern Venezuela and northwestern Brazil.
- Dendrothrix multiglandulosaEsser - Amazonas State in Venezuela
- Dendrothrix wurdackiiEsser - Amazonas State in Brazil
- Dendrothrix yutajensis(Jabl.) Esser - Amazonas State in Brazil; Amazonas & Bolívar States in Venezuela

Mabea is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described in 1775. It is native to Central and South America as well as Mexico and Trinidad.
Pseudosenefeldera is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 2001. It contains only one known species, Pseudosenefeldera inclinata, native to Panama and to northern and west-central South America.
Discocarpus is a genus of the plant family Phyllanthaceae first described as a genus in 1841. It is native to northern South America. It is dioecious, with male and female flowers on separate plants.
- Discocarpus essequeboensisKlotzsch - Brazil, Venezuela (Amazonas), Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana
- Discocarpus gentryiS.M.Hayden - S Venezuela (Amazonas), Peru (Loreto), N Brazil
- Discocarpus pedicellatusFiaschi & Cordeiro - State of Bahia in Brazil
- Discocarpus spruceanusMüll.Arg. - Venezuela (Amazonas), Brazil, Suriname (Sipaliwini), Bolivia

Abolboda is a genus of flowering plants, traditionally and nowadays assigned to family Xyridaceae. It is native to South America and to the island of Trinidad, generally on marshy savanna.

Aspidosperma ulei is a timber tree native to Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, Guyana, and Suriname.
Imeria is a genus of South American flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.
Achnopogon is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, described as a genus in 1957.
Gongylolepis is a genus of South American flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. The following species are recognised by the Global Compositae Checklist:
Aechmea egleriana is a plant species in the genus Aechmea. This species is native to Venezuela, French Guiana and northern Brazil.
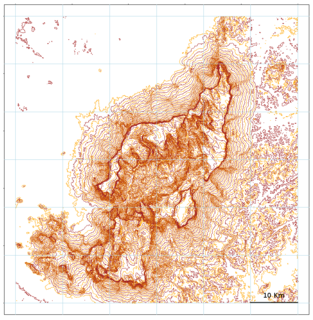
Cerro de la Neblina, also known as Serra da Neblina in Brazil and Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela, is a sandstone massif located in the northern Amazon Basin. It is a tilted, heavily eroded plateau, with a deep canyon in its central portion, drained by the Baria River.
Aciotis oliveriana is a plant species native to Colombia, Venezuela, Brazil, Ecuador and Perú. It occurs in disturbed habitats such as river banks, the edges of forests at elevations less than 1350 m.

Ischnosiphon is a genus of plants native to Central America, South America, Trinidad and the Lesser Antilles. It was first described as a genus in 1859.

Macradenia lutescens is a species of epiphytic orchid known by the common name longgland orchid. It is native to South America, the West Indies, and southern Florida.
Hylaeorchis is a genus of epiphytic orchids. There is only one known species, Hylaeorchis petiolaris, native to northwestern South America.
Achlyphila is a genus of plants in the Xyridaceae, first described as a genus in 1960. It contains only one known species, Achlyphila disticha, endemic to the Serranía de la Neblina National Park in the State of Amazonas in southern Venezuela, very close to the border with Brazil.
Tassadia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1844. It is native primarily to South America, with one species extending north into Central America, S Mexico, and Trinidad.
Pyrrorhiza is a genus of herbs in the family Haemodoraceae, first described as a genus in 1957. It contains only one known species, Pyrrorhiza neblinae, endemic to the Sierra de la Neblina in Amazonas State, Venezuela.







