An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.

A fusion gene is a hybrid gene formed from two previously independent genes. It can occur as a result of translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion. Fusion genes have been found to be prevalent in all main types of human neoplasia. The identification of these fusion genes play a prominent role in being a diagnostic and prognostic marker.

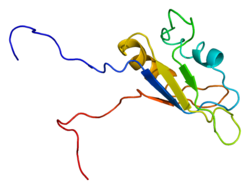
The PAX3 gene encodes a member of the paired box or PAX family of transcription factors. The PAX family consists of nine human (PAX1-PAX9) and nine mouse (Pax1-Pax9) members arranged into four subfamilies. Human PAX3 and mouse Pax3 are present in a subfamily along with the highly homologous human PAX7 and mouse Pax7 genes. The human PAX3 gene is located in the 2q36.1 chromosomal region, and contains 10 exons within a 100 kb region.

Ewing's sarcoma is a type of cancer that forms in bone or soft tissue. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture. The most common areas where it begins are the legs, pelvis, and chest wall. In about 25% of cases, the cancer has already spread to other parts of the body at the time of diagnosis. Complications may include a pleural effusion or paraplegia.

The neuron-derived orphan receptor 1 (NOR1) also known as NR4A3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A3 gene. NOR1 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors.

Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFATC2 gene.

Friend leukemia integration 1 transcription factor (FLI1), also known as transcription factor ERGB, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FLI1 gene, which is a proto-oncogene.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF1 gene.

ETS translocation variant 4 (ETV4), also known as polyoma enhancer activator 3 (PEA3), is a member of the PEA3 subfamily of Ets transcription factors.

The human DEKgene encodes the DEK protein.

ERG is an oncogene. ERG is a member of the ETS family of transcription factors. The ERG gene encodes for a protein, also called ERG, that functions as a transcriptional regulator. Genes in the ETS family regulate embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, inflammation, and apoptosis.

RNA-binding protein FUS/TLS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FUS gene.

Protein SSX2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSX2 gene.

Protein SSXT is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SS18 gene.

TATA-binding protein-associated factor 2N is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAF15 gene.
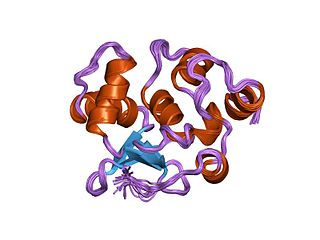
In the field of molecular biology, the ETSfamily is one of the largest families of transcription factors and is unique to animals. There are 29 genes in humans, 28 in the mouse, 10 in Caenorhabditis elegans and 9 in Drosophila. The founding member of this family was identified as a gene transduced by the leukemia virus, E26. The members of the family have been implicated in the development of different tissues as well as cancer progression.

A myxoid liposarcoma is a malignant adipose tissue neoplasm of myxoid appearance histologically.
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (EMC) is a rare low-grade malignant mesenchymal neoplasm of the soft tissues, that differs from other sarcomas by unique histology and characteristic chromosomal translocation. There is an uncertain differentiation and neuroendocrine differentiation is even possible.

CAMP responsive element binding protein 3 like 1 is a responsive element binding protein that in humans is encoded by the CREB3L1 gene.
EWS/FLI1 is an oncogenic protein that is pathognomonic for Ewing sarcoma. It is found in approximately 90% of all Ewing sarcoma tumors with the remaining 10% of fusions substituting one fusion partner with a closely related family member.