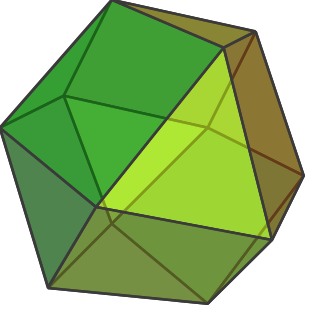
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it is a quasiregular polyhedron, i.e., an Archimedean solid that is not only vertex-transitive but also edge-transitive. It is radially equilateral. Its dual polyhedron is the rhombic dodecahedron.
In geometry, a dodecahedron or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid. There are also three regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry, order 120.

In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces, 36 edges, and 24 vertices.

In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron or great rhombicuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid, named by Kepler as a truncation of a cuboctahedron. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices, and 72 edges. Since each of its faces has point symmetry, the truncated cuboctahedron is a 9-zonohedron. The truncated cuboctahedron can tessellate with the octagonal prism.

In geometry, the rhombic dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with 12 congruent rhombic faces. It has 24 edges, and 14 vertices of 2 types. As a Catalan solid, it is the dual polyhedron of the cuboctahedron. As a parallelohedron, the rhombic dodecahedron can be used to tesselate its copies in space creating a rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb. There are some variations of the rhombic dodecahedron, one of which is the Bilinski dodecahedron. There are some stellations of the rhombic dodecahedron, one of which is the Escher's solid. The rhombic dodecahedron may also appear in the garnet crystal, the architectural philosophies, practical usages, and toys.
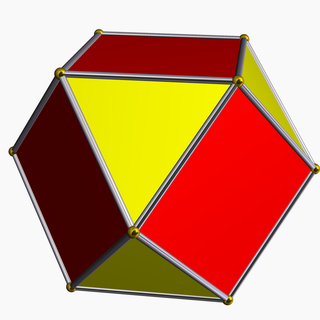
In Euclidean geometry, rectification, also known as critical truncation or complete-truncation, is the process of truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points. The resulting polytope will be bounded by vertex figure facets and the rectified facets of the original polytope.
In four-dimensional geometry, a runcinated 5-cell is a convex uniform 4-polytope, being a runcination of the regular 5-cell.

In four-dimensional geometry, a runcinated tesseract is a convex uniform 4-polytope, being a runcination of the regular tesseract.
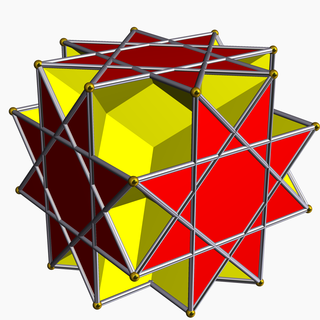
In geometry, the great rhombihexahedron (or great rhombicube) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U21. It has 18 faces (12 squares and 6 octagrams), 48 edges, and 24 vertices. Its dual is the great rhombihexacron. Its vertex figure is a crossed quadrilateral.

In geometry and topology, Conway polyhedron notation, invented by John Horton Conway and promoted by George W. Hart, is used to describe polyhedra based on a seed polyhedron modified by various prefix operations.

In geometry, the pentakis icosidodecahedron or subdivided icosahedron is a convex polyhedron with 80 triangular faces, 120 edges, and 42 vertices. It is a dual of the truncated rhombic triacontahedron.

In geometry, the tetrakis cuboctahedron is a convex polyhedron with 32 triangular faces, 48 edges, and 18 vertices. It is a dual of the truncated rhombic dodecahedron.
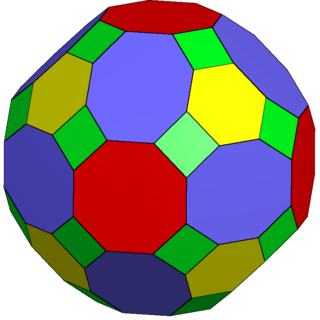
The truncated rhombicuboctahedron is a polyhedron, constructed as a truncation of the rhombicuboctahedron. It has 50 faces consisting of 18 octagons, 8 hexagons, and 24 squares. It can fill space with the truncated cube, truncated tetrahedron and triangular prism as a truncated runcic cubic honeycomb.

The expanded icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron, constructed as an expanded icosidodecahedron. It has 122 faces: 20 triangles, 60 squares, 12 pentagons, and 30 rhombs. The 120 vertices exist at two sets of 60, with a slightly different distance from its center.

In geometry, chamfering or edge-truncation is a topological operator that modifies one polyhedron into another. It is similar to expansion: it moves the faces apart (outward), and adds a new face between each two adjacent faces; but contrary to expansion, it maintains the original vertices. For a polyhedron, this operation adds a new hexagonal face in place of each original edge.

In geometry, an icosahedron is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes from Ancient Greek εἴκοσι (eíkosi) 'twenty' and ἕδρα (hédra) 'seat'. The plural can be either "icosahedra" or "icosahedrons".
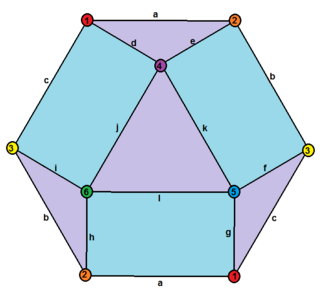
A hemi-cuboctahedron is an abstract polyhedron, containing half the faces of a semiregular cuboctahedron.

In geometry, a rectified prism is one of an infinite set of polyhedra, constructed as a rectification of an n-gonal prism, truncating the vertices down to the midpoint of the original edges. In Conway polyhedron notation, it is represented as aPn, an ambo-prism. The lateral squares or rectangular faces of the prism become squares or rhombic faces, and new isosceles triangle faces are truncations of the original vertices.































