
Leptocephalus is a genus that was used for species of larval eels, called leptocephali. Leptocephali larvae differ so much in appearance from their adults. When first discovered, leptocephali were thought to be a distinct type of fish, not an eel specie. Because of this, the genus designation of Leptocephalus was used for a while for an unidentified leptocephali. After it was known that these were eel larvae, it was identified to be part of a wastebasket taxon, but not anymore in the present classification system. Examples of marine congrid larvae, found in the western Indian Ocean and the Red Sea that were named this way are listed below. Only two species in two families are currently treated as having any validity, though the validity of L. bellottii is strongly in doubt.
Facciolella is a genus of eels in the duckbill eel family Nettastomatidae.
The rusty spaghetti eel, also known as the rusty worm eel, the slender worm eel, or the intermediate thrush-eel is an eel in the family Moringuidae. It was described by Richard Bliss Jr. in 1883. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific region, including East Africa, Easter Island, the Ryukyu Islands, Australia, and Micronesia. It leads a benthic lifestyle, burrowing into sandy regions in reefs at a depth range of 1–40 m. Males can reach a maximum total length of 140 cm.

The large-toothed conger is an eel belonging to the family Congridae. It was described by Léon Vaillant in 1888, originally as a species of the genus Uroconger.
Cynoponticus ferox, the Guinean pike conger, is an eel in the family Muraenesocidae. It was described by Oronzio Gabriele Costa in 1846. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Gibraltar, the western Mediterranean, and Angola. It dwells at a depth range of 10 to 100 metres ; larger individuals are usually found from 75 to 100 metres. It inhabits sand and mud substrates on the continental shelf. Males can reach a maximum total length of 200 centimetres (79 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 150 centimetres (59 in).
Facciolella castlei is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Nikolai Vasilyevich Parin and Emma Stanislavovna Karmovskaya in 1985. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from Chile, in the southeastern Pacific Ocean. The type specimen was retrieved from a depth of 230 metres.
The dogface witch eel is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1891. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Point Conception, California; Panama, Guadalupe, and the Galapagos Islands. The fish is known to dwell at an approximate depth of 734 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 90 centimetres.
Facciolella karreri is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Wolfgang Klausewitz in 1995. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern and western Indian Ocean and the western central Pacific Ocean, including the Red Sea, Egypt, Eritrea, Somalia, Saudi Arabia, Yemen and Sudan, and possibly northern Australia. It dwells at a depth range of 700–2000 metres, and is believed to inhabit holes in soft sediments on the sea-bottom. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36.1 centimetres.
Facciolella saurencheloides is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Umberto D'Ancona in 1928. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the northwestern and western Indian Ocean, including the Red Sea. It dwells at a depth range of 700–2,000 metres (2,300–6,560 ft).
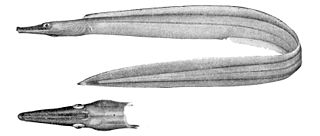
The duck-billed eel, also known as the shortsnouted sorcerer or the smallhead duckbill eel, is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1877. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel, which is known from the Indo-Pacific and the southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Japan, Hawaii, eastern Australia, southeastern Africa, and Chile. It dwells at a depth range of 60–1190 metres, and inhabits the continental shelf and slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 83 centimetres.
The slender sorcerer is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Wilhelm Peters in 1864. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic and Indian Ocean, including the River Congo and the Mediterranean. It dwells at a depth range of 185 to 700 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 65 centimetres (26 in).
The whipsnout sorcerer is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Léon Vaillant in 1888, originally under the genus Nettastoma. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from tropical, subtropical and temperate areas throughout the world. It dwells at a depth range of 385 to 2,200 metres, and inhabits the lower region of the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).
The Pacific worm eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1883. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including California, USA, Colombia, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Ecuador, Honduras, Mexico, Guatemala, Panama, Nicaragua, and Peru. It dwells at a depth range of 1 to 12 metres, and inhabits sand and mud sediments. Unlike many species of eel, it does not form burrows. Males can reach a maximum total length of 46 centimetres.
The shortfinned worm eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by William John Macleay in 1881, originally under the genus Muraenichthys. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling eel which is known from Australia, in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It forms large colonies which inhabit burrows in soft sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 40 centimetres (16 in).

The goldspotted eel, also known as the goldspotted snake eel or the dark-spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1825, originally under the genus Muraenophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, southern Florida, USA; the Bahamas, Santa Catarina, and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 15 metres (49 ft), and inhabits rocky and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 110 centimetres (3.6 ft).

The dark-shouldered snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Pieter Bleeker in 1864. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Pacific Ocean, including the East Indies, the Society Islands, the Mariana Islands, Queensland, the Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Japan, and India. It dwells at a depth range of 2–15 metres, and inhabits reefs. It forms burrows in mud and sand, and forages during the night. Males can reach a maximum total length of 115 centimetres.

The Marble-toothed snake-eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1898. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Colombia, Panama and Ecuador. It dwells in shallow waters at a maximum depth of 10 metres (33 ft), and inhabits sand and mud sediments and mangroves. Males can reach a maximum total length of 68 centimetres (27 in).

The Bean's sawtooth eel is an eel in the family Serrivomeridae. It was described by Theodore Gill and John Adam Ryder in 1883. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from throughout the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the Western Pacific Ocean, including Iceland, South Africa, Réunion, and Australia. It dwells at a depth range of 0–5,998 metres (0–19,680 ft), and leads a solitary lifestyle. It migrates vertically at night. Males can reach a maximum total length of 78-80 centimetres, making it the largest sawtooth eel.
Dysomma brevirostre, the pignosed arrowtooth eel or batnose eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Luigi Facciolà in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including Madeira Island, the Gulf of Guinea, the Ligurian Sea, Italy, and Florida and Hawaii, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 200 to 1,000 metres, and inhabits soft sediments on the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30 centimetres (12 in).

The Kaup's arrowtooth eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by James Yate Johnson in 1862. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Cape Verde, the Western Sahara, Nigeria, Namibia, South Africa, Greenland, France, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Philippines, Portugal, Spain, the Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Cuba, Japan, Australia, Mauritania, Morocco, and Hawaii. It dwells at a depth range of 120 to 4,800 metres, most often between 400 and 2,200 metres, and inhabits the upper abyssal zone on the continental slope. It is intolerant of the temperatures of higher waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).







