Related Research Articles

Luitpold Coast is that portion of the coast of Coats Land extending from the vicinity of Hayes Glacier, at 27°54′W, to 36°W, which is regarded as the eastern limit of the Filchner Ice Shelf. It was discovered by Wilhelm Filchner, leader of the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, and named after Luitpold, Prince Regent of Bavaria.

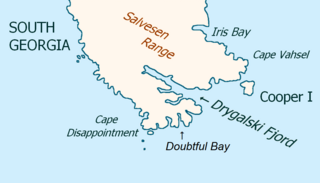
Drygalski Fjord is a bay 1 mile (1.6 km) wide which recedes northwestwards 7 miles (11 km), entered immediately north of Nattriss Head along the southeast coast of South Georgia. It was charted by the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Wilhelm Filchner, and named for Professor Erich von Drygalski, the leader of the First German Antarctica Expedition, 1901–03.
Goldcrest Point is the northwest point of Bird Island, South Georgia, with Payne Creek just south of it. It was charted by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery in the period 1926–30 and by the South Georgia Survey, 1951–57. The point is the site of a large colony of Macaroni penguins. The name, given by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963, refers to the golden crests of this species.
Gony Point is a high tussock-covered point 0.5 miles (0.8 km) southwest of Cardno Point, on the southeast side of Bird Island, South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963. Gony is an old sailors' name for the wandering albatross, which breeds on Bird Island.
Skua Island is an island immediately northeast of Prion Island in the entrance to the Bay of Isles, South Georgia. Charted in 1912-13 by Robert Cushman Murphy, American naturalist aboard the brig Daisy. Surveyed in 1929-30 by DI personnel and named in association with Albatross Island, Prion Island and other natural history names given in the Bay of Isles by Murphy in 1912–13.
Shoemaker Point is a point 0.5 miles (0.8 km) east of Jordan Cove on the south side of Bird Island, South Georgia, just south of Sooty Cove. Surveyed by the SGS in the period 1951-57 and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1963. "Shoemaker" is an old sailors' name for the Cape hen, a bird which breeds on Bird Island.
The Andrews Rocks are a small group of rocks 0.5 nautical miles (1 km) east of Cape Paryadin, South Georgia. The rocks are bare of vegetation and awash in heavy seas. The name "Andrews Islands" was probably given by Lieutenant Commander J.M. Chaplin, Royal Navy, of the RRS Discovery during his survey of the area in 1926. The South Georgia Survey, 1955–56, reported that "rocks" is a more suitable descriptive term for this group.
Bird Sound is a hazardous but navigable sound, 1 nautical mile (2 km) long and 0.5 nautical miles (1 km) wide, separating Bird Island from the west end of South Georgia. The names "La Roche Strait" and "Bird Sound" were used interchangeably for this feature on charts for many years. Bird Sound, which takes its name from nearby Bird Island, is approved on the basis of local usage.
The Cordall Stacks are two conspicuous rock stacks, the eastern one joined to Bird Island, South Georgia, by a low isthmus, lying on the northwest side of the island 0.3 nautical miles (0.6 km) northwest of Jordan Cove. They were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Peter A. Cordall, a member of the South Georgia Biological Expedition, 1958–59, who made a plane table survey of Bird Island.
Jordan Cove is a small cove which is the principal indentation in the south side of Bird Island, off the west end of South Georgia, near Antarctica.
Dixon Peak is a steep-sided peak rising to 420 metres (1,380 ft) at the southern end of Paryadin Ridge, 1 nautical mile (2 km) north of Cape Paryadin, South Georgia. It was roughly charted by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery in the period 1926–30, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963 for Lieutenant John B. Dixon, Royal Navy, surveying officer on HMS Owen, which surveyed the area in 1960–61.
Pio Point is a point forming the north side of the entrance to Johnson Cove at the west end of Bird Island, South Georgia. Roughly charted by DI personnel on the Discovery in the period 1926-30 and surveyed by HMS Owen in 1960–61. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1963. "Pio" is an old sailors' name for the light-mantled sooty albatross, a bird which breeds on Bird Island.
Elliott Rock is a rock lying in Stewart Strait, close west of Bird Island, off the west end of South Georgia. It was positioned by Discovery Investigations personnel under Lieutenant Commander J.M. Chaplin in the period 1926–30, and was named in 1957 by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Henry W. Elliott (1846–1930), an American naturalist who was a pioneer of fur seal studies in the North Pacific and a lifelong champion of fur seal protection. Fur seals breed on nearby Bird Island.
Evermann Cove is a cove 0.2 nautical miles (0.4 km) long, lying just southwest of Jordan Cove along the south side of Bird Island, South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Biological Expedition, 1958–59, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Barton W. Evermann, an American zoologist on the staff of the United States Fish Commission from 1891 to 1903 and its successor, the United States Bureau of Fisheries, from 1903 to 1914, and a specialist in administrative and legal problems relating to the fur seal.
Farewell Point is a point which forms the northeast extremity of Bird Island, off the west end of South Georgia. The name appears to have been applied by Discovery Investigations personnel who charted South Georgia in the period 1926–30.
Gazella Peak is a peak rising over 120 metres (390 ft) between Roche Peak and the Cordall Stacks on the north side of Bird Island, South Georgia. It was charted by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963 after the species name of the Antarctic fur seal, which breeds in considerable numbers on Bird Island.
Morris Point is a point 0.5 nautical miles (1 km) east of Pearson Point on the south side of Bird Island, South Georgia. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Lieutenant Roger O. Morris, hydrographic officer in HMS Owen during survey of Stewart Strait and approaches in 1960–61.
Square Rock is a rock lying 0.3 nautical miles (0.6 km) west of Cape Alexandra, at the west end of South Georgia. The name appears to be first used on a 1938 British Admiralty chart.
Hornaday Rock is a rock lying in Bird Sound, 0.6 nautical miles (1.1 km) west-southwest of Cape Alexandra at the west end of South Georgia. The feature appears on charts dating back to the 1930s. It was recharted by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for William T. Hornaday, an American zoologist who was Director of the New York Zoological Park, 1896–1926. From 1907 he was a leader in the fight to introduce protective legislation for fur seals; fur seals breed on nearby Bird Island.
References
- ↑ "Fantome Rock". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 15 March 2012.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Fantome Rock". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Fantome Rock". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.