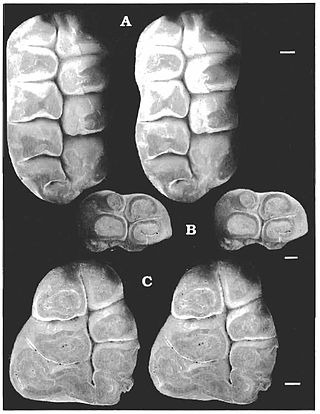
Catopsalis is a genus of extinct mammal from the Paleocene of North America. This animal was a relatively large member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. Most Multituberculates were much smaller.

Fonio, also sometimes called findi or acha, is the term for two cultivated grasses in the genus Digitaria that are notable crops in parts of West Africa. They are millets with small grains.

Fissidens adianthoides, the maidenhair pocketmoss, is a moss in the family Fissidentaceae. It was first collected by Hedwig in 1801.

The pygmy mammoth or Channel Islands mammoth is an extinct species of dwarf elephant native to the northern Channel Islands off the coast of California. It was descended from the Columbian mammoth of mainland North America.

Digitaria exilis, referred to as findi or fundi in areas of Africa, such as The Gambia, with English common names white fonio, fonio millet, and hungry rice or acha rice, is a grass species. It is the most important of a diverse group of wild and domesticated Digitaria species known as fonio that are harvested in the savannas of West Africa. The grains are very small. It has potential to improve nutrition, boost food security, foster rural development and support sustainable use of the land. Despite its valuable characteristics and widespread cultivation, fonio has generally received limited research and development attention, which is also why the species is sometimes referred to as an underutilized crop.

The western pygmy blue is one of the smallest butterflies in the world and the smallest in North America. It has reached Hawaii, as well as the Persian Gulf, including eastern Saudi Arabia, Bahrain and the United Arab Emirates.

The least honeyguide is a small species of bird in the family Indicatoridae. It is found in sub-Saharan Africa.
Fissidens hydropogon is a species of moss in the family Fissidentaceae. It is endemic to Ecuador. Its natural habitat is rivers. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Fissidens is a genus of haplolepideous mosses (Dicranidae) in the family Fissidentaceae.
Fissidens polypodioides is a species of moss first classified by Johannes Hedwig.
Astroblepus fissidens is a species of catfish of the family Astroblepidae. It can be found on Ecuador.

Microcoelia exilis, commonly known as the pinhead orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is a leafless epiphyte, a perennial herb that grows in a tangled cluster of roots and stems on the branch of a tree. This orchid is native to tropical central and eastern Africa and was first described in 1830 by the English botanist John Lindley.

Fissidens limbatus commonly known as Herzog's pocket-moss, is a moss in the family Fissidentaceae. This species is found growing in high elevations in tropical America in addition to the US, Mexico and Canada. Montagne first collected F. crispus in 1838.

Fissidens dubius is a species of moss belonging to the family Fissidentaceae.

Fissidens taxifolius is a species of moss in the Fissidentaceae family. It has a cosmopolitan distribution.
Fissidens celticus, also known by its common name Welsh pocket-moss, is a species of moss in the family Fissidentaceae. It was discovered in 1958 in Pembrokeshire by A.H. Norkett and was first described as a new species by Jean Paton in 1965.











