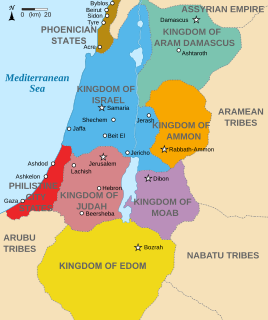
Ammon was an ancient Semitic-speaking nation occupying the east of the Jordan River, between the torrent valleys of Arnon and Jabbok, in present-day Jordan. The chief city of the country was Rabbah or Rabbath Ammon, site of the modern city of Amman, Jordan's capital. Milcom and Molech are named in the Hebrew Bible as the gods of Ammon. The people of this kingdom are called "Children of Ammon" or "Ammonites".

Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, and the last species either vanished in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, or shortly after during the Danian epoch of the Paleocene.

Moab is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territory is today located in the modern state of Jordan. The land is mountainous and lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by numerous archaeological findings, most notably the Mesha Stele, which describes the Moabite victory over an unnamed son of King Omri of Israel, an episode also noted in 2 Kings 3. The Moabite capital was Dibon. According to the Hebrew Bible, Moab was often in conflict with its Israelite neighbours to the west.

Hilda of Whitby was a Christian saint and the founding abbess of the monastery at Whitby, which was chosen as the venue for the Synod of Whitby in 664. An important figure in the Christianisation of Anglo-Saxon England, she was abbess at several monasteries and recognised for the wisdom that drew kings to her for advice.

Goniatids, informally goniatites, are ammonoid cephalopods that form the order Goniatitida, derived from the more primitive Agoniatitida during the Middle Devonian some 390 million years ago. Goniatites (goniatitids) survived the Late Devonian extinction to flourish during the Carboniferous and Permian only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 139 million years later.

Baculites is an extinct genus of cephalopods with a nearly straight shell, included in the heteromorph ammonites. The genus, which lived worldwide throughout most of the Late Cretaceous, and which briefly survived the K-Pg mass extinction event, was named by Lamarck in 1799.
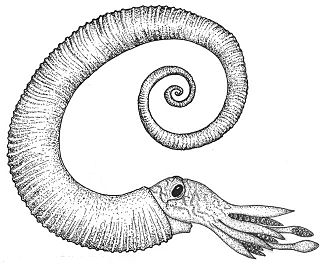
The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved during the Late Jurassic but were not very common until the Cretaceous period, when they rapidly diversified and became one of the most distinctive components of Cretaceous marine faunas. They have been recorded from every continent and many are used as zonal or index fossils. The most distinctive feature of the majority of the Ancyloceratina is the tendency for most of them to have shells that are not regular spirals like most other ammonites. These irregularly-coiled ammonites are called heteromorph ammonites, in contrast to regularly coiled ammonites, which are called homomorph ammonites.
The Toarcian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic. It spans the time between 182.7 Ma and 174.1 Ma. It follows the Pliensbachian and is followed by the Aalenian.
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 to 72.1 million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian.
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 201.3 ± 0.2 Ma and 199.3 ± 0.3 Ma. The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian and is followed by the Sinemurian.

In the geologic timescale, the Sinemurian is an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic Epoch or Series. It spans the time between 199.3 ± 2 Ma and 190.8 ± 1.5 Ma. The Sinemurian is preceded by the Hettangian and is followed by the Pliensbachian.
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age in the Late Jurassic Epoch and a stage in the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 157.3 ± 1.0 Ma and 152.1 ± 0.9 Ma. The Kimmeridgian follows the Oxfordian and precedes the Tithonian.

Ammonitina comprises a diverse suborder of ammonite cephalopods that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era. They are excellent index fossils, and it is often possible to link the rock layer in which they are found to specific geological time periods.

Ammolite is an opal-like organic gemstone found primarily along the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains of North America. It is made of the fossilized shells of ammonites, which in turn are composed primarily of aragonite, the same mineral contained in nacre, with a microstructure inherited from the shell. It is one of few biogenic gemstones; others include amber and pearl.1 In 1981, ammolite was given official gemstone status by the World Jewellery Confederation (CIBJO), the same year commercial mining of ammolite began. It was designated the official gemstone of the City of Lethbridge, Alberta in 2007.

Macroscaphites is an extinct cephalopod genus included in the Ammonoidea that lived during the Barremian and Aptian stages of the Early Cretaceous. Its fossils have been found throughout most of Europe and North Africa.

Cephalopod egg fossils are the fossilized remains of eggs laid by cephalopods. The fossil record of cephalopod eggs is scant since their soft, gelatinous eggs decompose quickly and have little chance to fossilize. Eggs laid by ammonoids are the best known and only a few putative examples of these have been discovered. The best preserved of these were discovered in the Jurassic Kimmeridge Clay of England. Currently no belemnoid egg fossils have ever been discovered although this may be because scientists have not properly searched for them rather than an actual absence from the fossil record.
Flickiidae is a family of dwarf ammonites with little ornament and very simples sutures known from small pyritic specimens found in middle Cretaceous deposits. Inclusion in the Acanthoceratoidea is tentative.

Leyvachelys is an extinct genus of turtles in the family Sandownidae from the Early Cretaceous of the present-day Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges, Colombian Andes. The genus is known only from its type species, Leyvachelys cipadi, described in 2015 by Colombian paleontologist Edwin Cadena. Fossils of Leyvachelys have been found in the fossiliferous Paja Formation, close to Villa de Leyva, Boyacá, after which the genus is named. The holotype specimen is the oldest and most complete sandownid turtle found to date.

Ammonite is a 2020 romantic drama film written and directed by Francis Lee. The film is loosely inspired by the life of British palaeontologist Mary Anning, played by Kate Winslet. The film centres on a speculative romantic relationship between Anning and Charlotte Murchison, played by Saoirse Ronan. Gemma Jones, James McArdle, Alec Secăreanu and Fiona Shaw also star.
Zolhafah is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered in the Western Desert of Egypt. The genus consists solely of type species Z. bella.












