
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents. The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas, neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as "the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases.

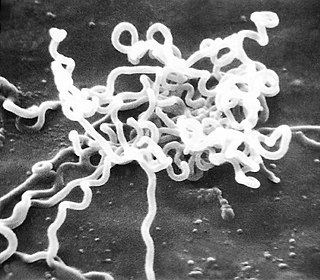
Treponema pallidum is a spirochaete bacterium with various subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel, and yaws. It is chiefly transmitted amongst humans, but it can also cause a condition found in cattle, bovine digital dermatitis. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. T. pallidum's lack of either a tricarboxylic acid cycle or oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. The treponemes have a cytoplasmic and an outer membrane. Using light microscopy, treponemes are visible only by using dark field illumination. Treponema pallidum consists of three subspecies, T. p. pallidum, T. p. endemicum, and T. p. pertenue, each of which has a distinct associated disease.
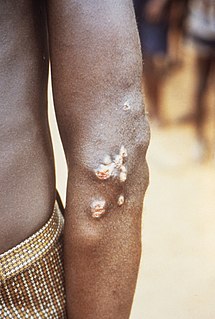
Yaws is a tropical infection of the skin, bones, and joints caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum pertenue. The disease begins with a round, hard swelling of the skin, 2 to 5 cm in diameter. The center may break open and form an ulcer. This initial skin lesion typically heals after 3–6 months. After weeks to years, joints and bones may become painful, fatigue may develop, and new skin lesions may appear. The skin of the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet may become thick and break open. The bones may become misshapen. After 5 years or more, large areas of skin may die, leaving scars.

Tabes dorsalis is a late consequence of neurosyphilis, characterized by the slow degeneration of the neural tracts primarily in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord. These patients have lancinating nerve root pain which is aggravated by coughing, and features of sensory ataxia with ocular involvement.
The rapid plasma reagin test is a type of rapid diagnostic test that looks for non-specific antibodies in the blood of the patient that may indicate an infection by syphilis or related non-venereal treponematoses. It is one of several nontreponemal tests for syphilis. The term reagin means that this test does not look for antibodies against the bacterium itself, Treponema pallidum, but rather for antibodies against substances released by cells when they are damaged by T. pallidum. Traditionally, syphilis serologic testing has been performed using a nontreponemal test (NTT) such as the RPR or VDRL test, with positive results then confirmed using a specific treponemal test (TT) such as TPPA or FTA-ABS. This algorithm is currently endorsed by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In addition to screening for syphilis, a titer can be used to track the progress of the disease over time and its response to therapy. The traditional algorithm using an NTT followed by a TT remains the standard in many parts of the world.

The Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test (VDRL) is a blood test for syphilis and related non-venereal treponematoses that was developed by the eponymous lab. The VDRL test is used to screen for syphilis, whereas other, more specific tests are used to diagnose the disease.

Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser was a German physician who discovered the causative agent (pathogen) of gonorrhea, a strain of bacteria that was named in his honour.
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection, against other foreign proteins, or to one's own proteins. In either case, the procedure is simple.
Pinta is a human skin disease caused by infection with the spirochete Treponema carateum, which is morphologically and serologically indistinguishable from the bacterium that causes syphilis. The disease is endemic to Mexico, Central America, and South America.

Bejel, or endemic syphilis, is a chronic skin and tissue disease caused by infection by the endemicum subspecies of the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Bejel is one of the "endemic treponematoses", a group that also includes yaws and pinta. Typically, endemic trepanematoses begin with localized lesions on the skin or mucous membranes. Pinta is limited to affecting the skin, whereas bejel and yaws are considered to be invasive because they can also cause disease in bone and other internal tissues.

Neurosyphilis refers to infection of the central nervous system in a patient with syphilis. In the era of modern antibiotics the majority of neurosyphilis cases have been reported in HIV-infected patients. Meningitis is the most common neurological presentation in early syphilis. Tertiary syphilis symptoms are exclusively neurosyphilis, though neurosyphilis may occur at any stage of infection.
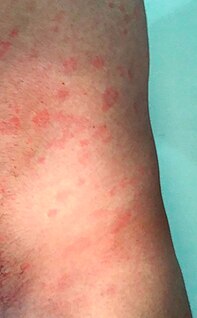
A Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction is a reaction to endotoxin-like products released by the death of harmful microorganisms within the body during antibiotic treatment. Efficacious antimicrobial therapy results in lysis (destruction) of bacterial cell membranes, and in the consequent release into the bloodstream of bacterial toxins, resulting in a systemic inflammatory response.
Treponema denticola is a Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic, motile and highly proteolytic spirochete bacterium. It is one of four species of oral spirochetes to be reliably cultured, the others being Treponema pectinovorum, Treponema socranskii and Treponema vincentii. T. denticola dwells in a complex and diverse microbial community within the oral cavity and is highly specialized to survive in this environment. T. denticola is associated with the incidence and severity of human periodontal disease. Treponema denticola is one of three bacteria that form the Red Complex, the other two being Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia. Together they form the major virulent pathogens that cause chronic periodontitis. Having elevated T. denticola levels in the mouth is considered one of the main etiological agents of periodontitis. T. denticola is related to the syphilis-causing obligate human pathogen, Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. It has also been isolated from women with bacterial vaginosis.

The mononuclear spot test or monospot test, a form of the heterophile antibody test, is a rapid test for infectious mononucleosis due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). It is an improvement on the Paul–Bunnell test. The test is specific for heterophile antibodies produced by the human immune system in response to EBV infection. Commercially available test kits are 70–92% sensitive and 96–100% specific, with a lower sensitivity in the first two weeks after clinical symptoms begin.
A nontreponemal test (NTT) is a blood test for diagnosis of infection with syphilis. Nontreponemal tests are an indirect method in that they detect biomarkers that are released during cellular damage that occurs from the syphilis spirochete. In contrast, treponemal tests look for antibodies that are a direct result of the infection thus, anti-treponeme IgG, IgM and to a lesser degree IgA. Nontreponemal tests are screening tests, very rapid and relatively simple, but need to be confirmed by treponemal tests. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-approved standard tests include the VDRL test, the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test, the unheated serum reagin (USR) test, and the toluidine red unheated serum test (TRUST). These have mostly replaced the first nontreponemal test, the Wassermann test.

The Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay is an indirect agglutination assay used for detection and titration of antibodies against the causative agent of syphilis, Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. It also detects other treponematoses.

The first recorded outbreak of syphilis in Europe occurred in 1494/1495 in Naples, Italy, during a French invasion. Because it was spread by returning French troops, the disease was known as "French disease", and it was not until 1530 that the term "syphilis" was first applied by the Italian physician and poet Girolamo Fracastoro. The causative organism, Treponema pallidum, was first identified by Fritz Schaudinn and Erich Hoffmann in 1905. The first effective treatment, Salvarsan, was developed in 1910 by Sahachirō Hata in the laboratory of Paul Ehrlich. It was followed by the introduction of penicillin in 1943.

Meningeal syphilis is a chronic form of syphilis infection that affects the central nervous system. Treponema pallidum, a spirochate bacterium, is the main cause of syphilis, which spreads drastically throughout the body and can infect all its systems if not treated appropriately. Treponema pallidum is the main cause of the onset of meningeal syphilis and other treponemal diseases, and it consists of a cytoplasmic and outer membrane that can cause a diverse array of diseases in the central nervous system and brain.
Spiral bacteria, bacteria of spiral (helical) shape, form the third major morphological category of prokaryotes along with the rod-shaped bacilli and round cocci. Spiral bacteria can be subclassified by the number of twists per cell, cell thickness, cell flexibility, and motility. The two types of spiral cells are spirillum and spirochete, with spirillum being rigid with external flagella, and spirochetes being with internal flagella.
Manfred Martin Mayer was a German-born, American microbiologist and immunologist. He is considered the founder of complement research.












