Related Research Articles

Corrugated fiberboard is a material consisting of a fluted corrugated sheet and one or two flat linerboards. It is made on "flute lamination machines" or "corrugators" and is used in the manufacture of shipping containers and corrugated boxes.

The art, science, and technology of papermaking addresses the methods, equipment, and materials used to make paper and cardboard, these being used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes and useful products. Today almost all paper is manufactured using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a specialized craft and a medium for artistic expression.

Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system. A closely related ISO system is used to describe the relationship between exposure and output image lightness in digital cameras.

The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measuring the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load compared to the penetration made by a preload. There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different loads or indenters. The result is a dimensionless number noted as HRA, HRB, HRC, etc., where the last letter is the respective Rockwell scale . When testing metals, indentation hardness correlates linearly with tensile strength.

The flash point of a volatile material is the lowest temperature at which its vapours ignite if given an ignition source.

Paperboard is a thick paper-based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker than paper and has certain superior attributes such as foldability and rigidity. According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a grammage above 250 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single- or multi-ply.
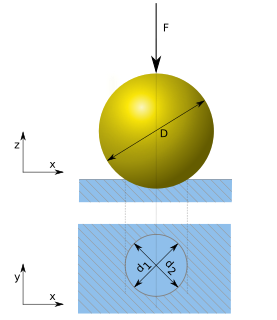
The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science.
In colorimetry, whiteness is the degree to which a surface is white. An example of its use might be to quantitatively compare two pieces of paper which appear white viewed individually, but not when juxtaposed.
The dropping point of a lubricating grease is an indication of the heat resistance of the grease and is the temperature at which it passes from a semi-solid to a liquid state under specific test conditions. It is dependent on the type of thickener used and the cohesiveness of the oil and thickener of a grease. The dropping point indicates the upper temperature limit at which a grease retains its structure though is not necessarily the maximum temperature at which a grease can be used.
APAO is an acronym that stands for Amorphous Poly Alpha Olefin(s). APAO is a commodity chemical used in multiple applications.
The Handle-o-Meter is a testing machine developed by Johnson & Johnson and now manufactured by Thwing-Albert that measures the "handle", i.e. a combination of surface friction and flexibility of sheeted materials.

Tracing paper is paper made to have low opacity, allowing light to pass through. It was originally developed for architects and design engineers to create drawings which could be copied precisely using the diazo copy process; it then found many other uses. The original use for drawing and tracing was largely superseded by technologies which do not require diazo copying or manual copying of drawings.
ISO/IEC 19752Information technology — Method for the determination of toner cartridge yield for monochromatic electrophotographic printers and multi-function devices that contain printer components is an ISO standard method for the determination of toner cartridge yield for monochrome laser printers, introduced in June 2004.
Refractoriness under load (RUL) is a measure of the deformation behavior of refractory ceramic products subjected to a constant load and increasing temperature. The temperature range in which the softening occurs is not identical with the melting range of the pure raw material, but it must be reliably determined with the RUL 421 to check the use of refractory products in high-temperature applications. Creep in compression (CIC) refers to the percent of shrinkage of a refractory test piece under a constant load and exposed to a constant high temperature over a long period of time. The creep in compression test is also carried out in the RUL 421 to a maximum temperature of 1700 °C. With its sturdy design, the RUL 421 is well suited for these long-running thermal and mechanical loads.
Abrasion is the process of scuffing, scratching, wearing down, marring, or rubbing away. It can be intentionally imposed in a controlled process using an abrasive. Abrasion can be an undesirable effect of exposure to normal use or exposure to the elements.

Package testing or packaging testing involves the measurement of a characteristic or property involved with packaging. This includes packaging materials, packaging components, primary packages, shipping containers, and unit loads, as well as the associated processes.
A roll hardness tester is a device to measure the roll hardness, hardness profile and hardness variation of paper rolls.

A double fold is a process of folding a paper sample first backwards and then forwards about the same line, i.e. one complete oscillation. The number of double folds that is required to make a test piece break is used to determine the material's folding endurance and fold number.
Fold number refers to how many double folds that are required to cause rupture of a paper test piece under standardized conditions. Fold number is defined in ISO 5626:1993 as the antilogarithm of the mean folding endurance:

Pressure-sensitive tape, known also in various countries as PSA tape, adhesive tape, self-stick tape, sticky tape, Sellotape, or just tape, is an adhesive tape that will stick with application of pressure, without the need for a solvent or heat for activation. It can be used in the home, office, industry, and institutions for a wide variety of purposes.
References
- ↑ ISO 5626:1993 Paper – Determination of folding endurance, 3.2.