
An auction is usually a process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bids, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder or buying the item from the lowest bidder. Some exceptions to this definition exist and are described in the section about different types. The branch of economic theory dealing with auction types and participants' behavior in auctions is called auction theory.

A Dutch auction is one of several similar types of auctions for buying or selling goods. Most commonly, it means an auction in which the auctioneer begins with a high asking price in the case of selling, and lowers it until some participant accepts the price, or it reaches a predetermined reserve price. This type of price auction is most commonly used for goods that are required to be sold quickly such as flowers, fresh produce, or tobacco. A Dutch auction has also been called a clock auction or open-outcry descending-price auction. This type of auction shows the advantage of speed since a sale never requires more than one bid. It is strategically similar to a first-price sealed-bid auction.

An online auction is an auction held over the internet and accessed by internet connected devices. Similar to in-person auctions, online auctions come in a variety of types, with different bidding and selling rules.

A Vickrey auction or sealed-bid second-price auction (SBSPA) is a type of sealed-bid auction. Bidders submit written bids without knowing the bid of the other people in the auction. The highest bidder wins but the price paid is the second-highest bid. This type of auction is strategically similar to an English auction and gives bidders an incentive to bid their true value. The auction was first described academically by Columbia University professor William Vickrey in 1961 though it had been used by stamp collectors since 1893. In 1797 Johann Wolfgang von Goethe sold a manuscript using a sealed-bid, second-price auction.

An English auction is an open-outcry ascending dynamic auction. It proceeds as follows.
In economics, a reservationprice is a limit on the price of a good or a service. On the demand side, it is the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay; on the supply side, it is the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a good or service.

A Japanese auction is a dynamic auction format. It proceeds in the following way.

A double auction is a process of buying and selling goods with multiple sellers and multiple buyers. Potential buyers submit their bids and potential sellers submit their ask prices to the market institution, and then the market institution chooses some price p that clears the market: all the sellers who asked less than p sell and all buyers who bid more than p buy at this price p. Buyers and sellers that bid or ask for exactly p are also included. A common example of a double auction is stock exchange.

Auction theory is an applied branch of economics which deals with how bidders act in auction markets and researches how the features of auction markets incentivise predictable outcomes. Auction theory is a tool used to inform the design of real-world auctions. Sellers use auction theory to raise higher revenues while allowing buyers to procure at a lower cost. The conference of the price between the buyer and seller is an economic equilibrium. Auction theorists design rules for auctions to address issues which can lead to market failure. The design of these rulesets encourages optimal bidding strategies among a variety of informational settings. The 2020 Nobel Prize for Economics was awarded to Paul R. Milgrom and Robert B. Wilson “for improvements to auction theory and inventions of new auction formats.”

A multiunit auction is an auction in which several homogeneous items are sold. The units can be sold each at the same price or at different prices.

A combinatorial auction is a type of smart market in which participants can place bids on combinations of discrete heterogeneous items, or “packages”, rather than individual items or continuous quantities. These packages can be also called lots and the whole auction a multi-lot auction. Combinatorial auctions are applicable when bidders have non-additive valuations on bundles of items, that is, they value combinations of items more or less than the sum of the valuations of individual elements of the combination.

The generalized second-price auction (GSP) is a non-truthful auction mechanism for multiple items. Each bidder places a bid. The highest bidder gets the first slot, the second-highest, the second slot and so on, but the highest bidder pays the price bid by the second-highest bidder, the second-highest pays the price bid by the third-highest, and so on. First conceived as a natural extension of the Vickrey auction, it conserves some of the desirable properties of the Vickrey auction. It is used mainly in the context of keyword auctions, where sponsored search slots are sold on an auction basis. The first analyses of GSP are in the economics literature by Edelman, Ostrovsky, and Schwarz and by Varian. It is used by Google's AdWords technology and Facebook.
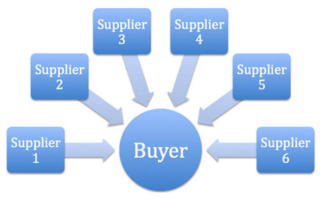
A reverse auction is a type of auction in which the traditional roles of buyer and seller are reversed. Thus, there is one buyer and many potential sellers. In an ordinary auction also known as a forward auction, buyers compete to obtain goods or services by offering increasingly higher prices. In contrast, in a reverse auction, the sellers compete to obtain business from the buyer and prices will typically decrease as the sellers underbid each other.
A Prior-independent mechanism (PIM) is a mechanism in which the designer knows that the agents' valuations are drawn from some probability distribution, but does not know the distribution.
Bayesian-optimal pricing is a kind of algorithmic pricing in which a seller determines the sell-prices based on probabilistic assumptions on the valuations of the buyers. It is a simple kind of a Bayesian-optimal mechanism, in which the price is determined in advance without collecting actual buyers' bids.
A sequential auction is an auction in which several items are sold, one after the other, to the same group of potential buyers. In a sequential first-price auction (SAFP), each individual item is sold using a first price auction, while in a sequential second-price auction (SASP), each individual item is sold using a second price auction.

The Price of Anarchy (PoA) is a concept in game theory and mechanism design that measures how the social welfare of a system degrades due to selfish behavior of its agents. It has been studied extensively in various contexts, particularly in auctions.
Regularity, sometimes called Myerson's regularity, is a property of probability distributions used in auction theory and revenue management. Examples of distributions that satisfy this condition include Gaussian, uniform, and exponential; some power law distributions also satisfy regularity. Distributions that satisfy the regularity condition are often referred to as "regular distributions".
Envy-free pricing is a kind of fair item allocation. There is a single seller that owns some items, and a set of buyers who are interested in these items. The buyers have different valuations to the items, and they have a quasilinear utility function; this means that the utility an agent gains from a bundle of items equals the agent's value for the bundle minus the total price of items in the bundle. The seller should determine a price for each item, and sell the items to some of the buyers, such that there is no envy. Two kinds of envy are considered:

In mechanism design, a branch of economics, a weakly-budget-balanced (WBB) mechanism is a mechanism in which the total payment made by the participants is at least 0. This means that the mechanism operator does not incur a deficit, i.e., does not have to subsidize the market. Weak budget balance is considered a necessary requirement for the economic feasibility of a mechanism. A strongly-budget-balanced (SBB) mechanism is a mechanism in which the total payment made by the participants is exactly 0. This means that all payments are made among the participants - the mechanism has neither a deficit nor a surplus. The term budget-balanced mechanism is sometimes used as a shorthand for WBB, and sometimes as a shorthand for SBB.




