ECMAScript is a standard for scripting languages, including JavaScript, JScript, and ActionScript. It is also best known as a JavaScript standard intended to ensure the interoperability of web pages across different web browsers. It is standardized by Ecma International in the document ECMA-262.

The Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing is an open-source middleware system for volunteer computing. Developed originally to support SETI@home, it became the platform for many other applications in areas as diverse as medicine, molecular biology, mathematics, linguistics, climatology, environmental science, and astrophysics, among others. The purpose of BOINC is to enable researchers to utilize processing resources of personal computers and other devices around the world.

Frozen Bubble is a free software clone of Puzzle Bobble for a variety of home and mobile systems.

Anjuta was an integrated development environment written for the GNOME project. It had support for C, C++, Java, JavaScript, Python and Vala programming language. In May 2022, the project was archived due a lack of maintainers. Since October 2022 the project's former homepage no longer exists and the domain is owned by an SBOBET, an Indonesian gambling website. It has been superseded by GNOME Builder.

Snort is a free open source network intrusion detection system (IDS) and intrusion prevention system (IPS) created in 1998 by Martin Roesch, founder and former CTO of Sourcefire. Snort is now developed by Cisco, which purchased Sourcefire in 2013.

DTrace is a comprehensive dynamic tracing framework originally created by Sun Microsystems for troubleshooting kernel and application problems on production systems in real time. Originally developed for Solaris, it has since been released under the free Common Development and Distribution License (CDDL) in OpenSolaris and its descendant illumos, and has been ported to several other Unix-like systems.
The actor model in computer science is a mathematical model of concurrent computation that treats an actor as the basic building block of concurrent computation. In response to a message it receives, an actor can: make local decisions, create more actors, send more messages, and determine how to respond to the next message received. Actors may modify their own private state, but can only affect each other indirectly through messaging.

diagrams.net is a cross-platform graph drawing software developed in HTML5 and JavaScript. Its interface can be used to create diagrams such as flowcharts, wireframes, UML diagrams, organizational charts, and network diagrams. Parts of its source code are provided under the Apache 2 open-source license.
This is a comparison of notable web frameworks, software used to build and deploy web applications.

Node.js is a cross-platform, open-source server environment that can run on Windows, Linux, Unix, macOS, and more. Node.js is a back-end JavaScript runtime environment, runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, and executes JavaScript code outside a web browser.

LightDM is a free and open-source X display manager that aims to be lightweight, fast, extensible and multi-desktop. It can use various front-ends to draw the user interface, also called Greeters. It also supports Wayland.

mpv is free and open-source media player software based on MPlayer, mplayer2 and FFmpeg. It runs on several operating systems, including Unix-like operating systems and Microsoft Windows, along with having an Android port called mpv-android. It is cross-platform, running on ARM, PowerPC, x86/IA-32, x86-64, and MIPS architecture.
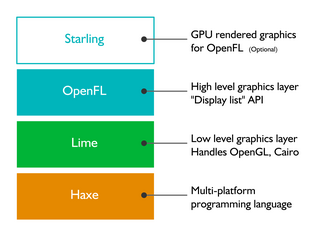
OpenFL is a free and open-source software framework and platform for the creation of multi-platform applications and video games. OpenFL applications can be written in Haxe, JavaScript, or TypeScript, and may be published as standalone applications for several targets including iOS, Android, HTML5, Windows, macOS, Linux, WebAssembly, Flash, AIR, PlayStation 4, PlayStation 3, PlayStation Vita, Xbox One, Wii U, TiVo, Raspberry Pi, and Node.js.

Snap is a software packaging and deployment system developed by Canonical for operating systems that use the Linux kernel and the systemd init system. The packages, called snaps, and the tool for using them, snapd, work across a range of Linux distributions and allow upstream software developers to distribute their applications directly to users. Snaps are self-contained applications running in a sandbox with mediated access to the host system. Snap was originally released for cloud applications but was later ported to also work for Internet of Things devices and desktop applications.

Searx is a free and open-source metasearch engine, available under the GNU Affero General Public License version 3, with the aim of protecting the privacy of its users. To this end, Searx does not share users' IP addresses or search history with the search engines from which it gathers results. Tracking cookies served by the search engines are blocked, preventing user-profiling-based results modification. By default, Searx queries are submitted via HTTP POST, to prevent users' query keywords from appearing in webserver logs. Searx was inspired by the Seeks project, though it does not implement Seeks' peer-to-peer user-sourced results ranking.













