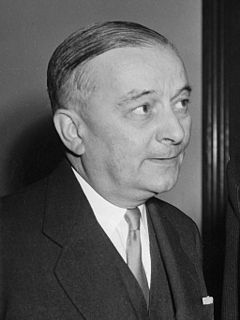The French Fourth Republic was the republican government of France between 1946 and 1958, governed by the fourth republican constitution. It was in many ways a revival of the Third Republic that was in place from 1870 during the Franco-Prussian War to 1940 during World War II, and suffered many of the same problems. France adopted the constitution of the Fourth Republic on 13 October 1946.
In France, the Gaullist Party is usually used to refer to the largest party professing to be Gaullist. Gaullism claim to transcend the left-right divide but in practice the current Gaullist party is the centre-right Republicans.

The Rally of the French People was a French political party, led by Charles de Gaulle.

Maurice Thorez was a French politician and longtime leader of the French Communist Party (PCF) from 1930 until his death. He also served as Deputy Prime Minister of France from 1946 to 1947.

The Popular Republican Movement was a Christian democratic political party in France during the Fourth Republic. Its base was the Catholic vote and its leaders included Georges Bidault, Robert Schuman, Paul Coste-Floret, Pierre-Henri Teitgen and Pierre Pflimlin. It played a major role in forming governing coalitions, in emphasizing compromise and the middle ground, and in protecting against a return to extremism and political violence. It played an even more central role in foreign policy, having charge of the Foreign Office for ten years and launching plans for the creation of the European Coal and Steel Community. which grew into the European Union. Its voter base gradually dwindled in the 1950s and it had little power by 1954.

The 1969 French presidential election took place on 1 June and 15 June 1969. It occurred due to the resignation of President Charles de Gaulle on 28 April 1969. De Gaulle had decided to consult the voters by referendum about regionalisation and the reform of the Senate, and he had announced he would resign if it resulted in a "no" vote. On 27 April, 53.5% of the voters had voted "no".

The 1965 French presidential election, held on 5 December and 19 December, was the first direct presidential election in the Fifth Republic and the first since the Second Republic in 1848. It had been widely expected that incumbent president Charles de Gaulle would be re-elected, but the election was notable for the unexpectedly strong performance of his left-wing challenger François Mitterrand.

The Provisional Government of the French Republic was an interim government of Free France between 1944 and 1946 following the liberation of continental France after Operations Overlord and Dragoon, and lasted until the establishment of the French Fourth Republic. Its establishment marked the official restoration and re-establishment of a provisional French Republic, assuring continuity with the defunct French Third Republic.

French legislative elections took place on 4 and 11 March 1973 to elect the fifth National Assembly of the Fifth Republic.
The Federation of the Democratic and Socialist Left was a conglomerate of French left-wing non-Communist forces. It was founded to support François Mitterrand's candidature at the 1965 presidential election and to counterbalance the Communist preponderance over the French left.

French legislative elections took place on 5 and 12 March 1967 to elect the third National Assembly of the Fifth Republic.
The Democratic and Socialist Union of the Resistance was a French political party founded after the liberation of France from German occupation and mainly active during the Fourth Republic (1947–58). It was a loosely organised "cadre party" without mass membership. Its ideology was vague, including a broad diversity of different political convictions with descriptions ranging from left-wing via centrist to conservative. It was decidedly anti-communist and linked with the Paix et Liberté movement. The UDSR was a founding member of the Liberal International in 1947.
Tripartisme was the mode of government in France from 1944 to 1947, when the country was ruled by a three-party alliance of communists, socialists and Christian democrats, represented by the French Communist Party (PCF), the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) and the Popular Republican Movement (MRP), respectively. The official charter of tripartisme was signed on 23 January 1946, following the resignation of Charles de Gaulle, who opposed the draft of the constitution. The draft envisioned a parliamentary system, whereas de Gaulle favored a presidential system.

Legislative election was held in France on 10 November 1946 to elect the first National Assembly of the Fourth Republic. The electoral system used was proportional representation.
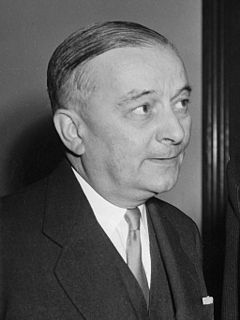
Legislative elections were held in France on 2 June 1946 to elect the second post-war Constituent Assembly designated to prepare a new constitution. The ballot system used was proportional representation.

Legislative elections were held in France on 17 June 1951 to elect the second National Assembly of the Fourth Republic.
The Third Force was a French coalition during the Fourth Republic (1947–1958) which gathered the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) party, the centre-right Democratic and Socialist Union of the Resistance (UDSR), the Radicals, the Christian democrat Popular Republican Movement (MRP) and other centrist politicians, opposed both to the French Communist Party (PCF) and the Gaullist movement. The Third Force governed France from 1947 to 1951, succeeding the tripartisme alliance between the SFIO, the MRP and the PCF. The Third Force was also supported by the conservative National Centre of Independents and Peasants (CNIP), which succeeded in having its most popular figure, Antoine Pinay, named Prime Minister in 1952, a year after the dissolving of the Third Force coalition.

A constitutional referendum was held in France on 5 May 1946. Voters were asked whether they approved of a new draft Constitution proposed by the Constituent Assembly elected in 1945.

The Left in France was represented at the beginning of the 20th century by two main political parties: the Republican, Radical and Radical-Socialist Party and the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO), created in 1905 as a merger of various Marxist parties. But in 1914, after the assassination of the leader of the SFIO, Jean Jaurès, who had upheld an internationalist and anti-militarist line, the SFIO accepted to join the Union sacrée national front. In the aftermaths of the Russian Revolution and the Spartacist uprising in Germany, the French Left divided itself in reformists and revolutionaries during the 1920 Tours Congress, which saw the majority of the SFIO spin-out to form the French Section of the Communist International (SFIC). The early French Left was often alienated into the Republican movements.

The French Communist Party (PCF) has been a part of the political scene in France since 1920, peaking in strength around the end of World War II. It originated when a majority of members resigned from the socialist French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) party to set up the French Section of the Communist International (SFIC). The SFIO had been divided over support for French participation in World War I and over whether to join the Communist International (Comintern). The new SFIC defined itself as revolutionary and democratic centralist. Ludovic-Oscar Frossard was its first secretary-general, and Ho Chi Minh was also among the founders. Frossard himself resigned in 1923, and the 1920s saw a number of splits within the party over relations with other left-wing parties and over adherence to the Communist International's dictates. The party gained representation in the French parliament in successive elections, but also promoted strike action and opposed colonialism. Pierre Sémard, leader from 1924 to 1928, sought party unity and alliances with other parties; but leaders including Maurice Thorez imposed a Stalinist line from the late 1920s, leading to loss of membership through splits and expulsions, and reduced electoral success. With the rise of Fascism this policy shifted after 1934, and the PCF supported the Popular Front, which came to power under Léon Blum in 1936. The party helped to secure French support for the Spanish Republicans during the Spanish Civil War, and opposed the 1938 Munich agreement with Hitler. During this period the PCF adopted a more patriotic image, and favoured an equal but distinct role for women in the communist movement.