
The Acari are a taxon of arachnids that contains mites and ticks. The diversity of the Acari is extraordinary and their fossil history goes back to at least the early Devonian period. Acarologists have proposed a complex set of taxonomic ranks to classify mites. In most modern treatments, the Acari are considered a subclass of the Arachnida and are composed of two or three superorders or orders: Acariformes, Parasitiformes, and Opilioacariformes; the latter is often considered a subgroup within the Parasitiformes. The monophyly of the Acari is open to debate, and the relationships of the acarines to other arachnids is not at all clear. In older treatments, the subgroups of the Acarina were placed at order rank, but as their own subdivisions have become better understood, treating them at the superorder rank is more usual.

Colubridae is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest species of the family date back to the Oligocene epoch. Colubrid snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica.

Ranunculaceae is a family of over 2,000 known species of flowering plants in 43 genera, distributed worldwide.

Polypodiaceae is a family of ferns. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, the family includes around 65 genera and an estimated 1,650 species and is placed in the order Polypodiales, suborder Polypodiineae. A broader circumscription has also been used, in which the family includes other families kept separate in PPG I. Nearly all species are epiphytes, but some are terrestrial.
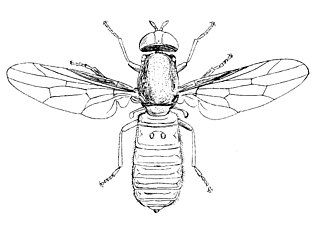
The Scenopinidae or window flies are a small family of flies (Diptera), distributed worldwide. In buildings, they are often taken at windows, hence the common name window flies.

The Viverrinae represent the largest subfamily within the Viverridae comprising five genera, which are subdivided into 22 species native to Africa and Southeast Asia. This subfamily was denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864.

Trichopezinae are a subfamily of empidoid flies. They are mainly predatory flies like most of their relatives, and generally small to medium-sized, long-legged and large-eyed.
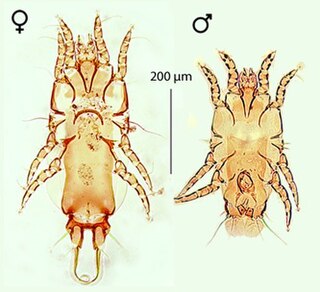
Proctophyllodes is a genus of feather mites, found on passerine birds.

Brachystomatinae is a subfamily of flies belonging to the family Empididae.

Nanorchestidae is a family of endeostigs in the order Endeostigmata. There are at least two genera and two described species in Nanorchestidae.
Echimyopodidae is a family of mites in the order Astigmata. There are at least two genera and two described species in Echimyopodidae.

Avenzoariidae is a family of feather mites in the order Astigmata. There are at least 15 genera in Avenzoariidae. They are found on the feathers of aquatic birds, and in the case of one species, birds of prey.

Chaetodactylidae is a family of mites in the order Sarcoptiformes. There are five genera: Sennertia, Chaetodactylus, Achaetodactylus, Centriacarus, and Roubikia.

Winterschmidtiidae is a family of mites in the order Astigmata. There are about six genera in Winterschmidtiidae.
Cyta is a genus of snout mites in the family Bdellidae. There are about 15 described species in Cyta.

Glycyphagus is a genus of astigs in the family Glycyphagidae. There are about five described species in Glycyphagus.

Glyphanoetus is a genus of astigs in the family Histiostomatidae.

Kiwalges haastii is a species of New Zealand feather mite in the superfamily Analgoidea, known only from the great spotted kiwi, from which it derives its name.















