
The forest raven, also commonly known as the Tasmanian raven, is a passerine bird in the family Corvidae native to Tasmania and parts of southern Victoria, such as Wilsons Promontory and Portland. Populations are also found in parts of New South Wales, including Dorrigo and Armidale. Measuring 50–53 cm (20–21 in) in length, it has all-black plumage, beak and legs. As with the other two species of raven in Australia, its black feathers have grey bases. Adults have white irises; younger birds have dark brown and then hazel irises with an inner blue rim. New South Wales populations are recognised as a separate subspecies C. tasmanicus boreus, but appear to be nested within the Tasmanian subspecies genetically.

The tiger quoll, also known as the spotted-tail quoll, the spotted quoll, the spotted-tail dasyure, native cat or the tiger cat, is a carnivorous marsupial of the quoll genus Dasyurus native to Australia. With males and females weighing around 3.5 and 1.8 kg, respectively, it is the world's second-largest extant carnivorous marsupial, behind the Tasmanian devil. Two subspecies are recognised; the nominate is found in wet forests of southeastern Australia and Tasmania, and a northern subspecies, D. m. gracilis, is found in a small area of northern Queensland and is endangered.

The Parastacidae are the family of freshwater crayfish found in the Southern Hemisphere. The family is a classic Gondwana-distributed taxon, with extant members in South America, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand, and New Guinea, and extinct taxa also in Antarctica.

The climbing galaxias or kōaro is a fish of the family Galaxiidae found in Australia, New Zealand, and nearby islands. The name climbing galaxias is used in Australia, and koaro or kōaro in New Zealand. Further vernacular names include short-finned galaxias, broad-finned galaxias, Cox's mountain galaxias, and Pieman galaxias.

The common yabby is an Australian freshwater crustacean in the Parastacidae family. It is listed as a vulnerable species of crayfish by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), though wild yabby populations remain strong, and have expanded into new habitats created by reservoirs and farm dams.

Handfish are any anglerfish within the family Brachionichthyidae, a group which comprises five genera and 14 extant species. These benthic marine fish are unusual in the way they propel themselves by walking on the sea floor rather than swimming.

Paranephrops planifrons is a species of southern crawfish in the family Parastacidae. It is found in New Zealand. P. planifrons is one of two indigenous species of freshwater crayfish found in New Zealand. They are more commonly found in the North Island and the West Coast of the South Island while the P. zealandicus is found in the east and south of the South Island. Both species of Paranephrops are important resources to the indigenous Māori, particularly in the Te Arawa and Lake Taupō regions.

Engaeus is a genus of freshwater crayfish found in Australia, the burrowing crayfishes. Fifteen of the 35 species in the genus occur in Tasmania, where they are known as the Tasmanian land crayfishes. The behaviour of these crayfish is notable as they live in burrows and construct large "chimneys" at the opening.

Euastacus is a genus of freshwater crayfish known as "spiny crayfish". They are found in the south-east of the Australian mainland, along with another genus of crayfish, Cherax. Both genera are members of the family Parastacidae, a family of freshwater crayfish restricted to the Southern Hemisphere.
The large forest bat is a common vesper bat found in southeast Australia, Tasmania, and Lord Howe Island.

Callitris rhomboidea, commonly known as the Oyster Bay pine, Tasmanian cypress pine, Port Jackson pine, Illawarra mountain pine, or dune cypress pine, is a species of conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to Australia, occurring in South Australia, Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania. It has become naturalized near Auckland, New Zealand and can be found on the island of Taillefer Rocks in Tasmania.
Carinascincus palfreymani, known commonly as the Pedra Branca skink, as well as the Palfreyman's window-eyed skink, the Pedra Branca cool-skink, or the red-throated skink, is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia, and is restricted to the windswept Pedra Branca, an island off southern Tasmania of only 2.5 ha, where it is dependent on the seabird colonies. It is the only lizard species found on the island.

Geocrinia laevis, the smooth frog, southern smooth froglet, smooth froglet, or Tasmanian smooth frog, is a species of frog in the family Myobatrachidae. It is endemic to Australia and found in Tasmania, southwestern Victoria, and the extreme southeast of South Australia.

Astacoides is a genus of freshwater crayfish endemic to Madagascar. The first specimens were brought to Europe in 1839, and seven species are now recognised, most of which are considered as threatened on the IUCN Red List. They are large and slow-growing, and are threatened by habitat loss, overexploitation by local people and by spread of introduced non-indigenous marbled crayfish. They are only found in a relatively small part of the island, mostly in undisturbed upland areas. They belong to the Gondwana-distributed family Parastacidae, but their nearest relatives live in Australasia, there being no native crayfish in mainland Africa or India.
Engaeus spinicaudatus, the Scottsdale burrowing crayfish, is a species of crayfish in the family Parastacidae. This species is only found in Tasmania, Australia. It is a medium-size burrowing crayfish with an adult carapace length of about 25 millimeters. It usually brown or purplish in color. The species is primarily found in wet buttongrass and healthy plains, but also occurs in surface seepages, floodplains of creeks and wet areas converted to pasture.

Sagmariasus verreauxi is a species of spiny lobster that lives around northern New Zealand, the Kermadec Islands the Chatham Islands and Australia from Queensland to Tasmania. It is probably the longest decapod crustacean in the world, alongside the American lobster Homarus americanus, growing to lengths of up to 60 centimetres (24 in).

Gymnoschoenus sphaerocephalus, commonly known as buttongrass, is a species of tussock-forming sedge from southeastern Australia. It forms part of a unique habitat in Tasmania.
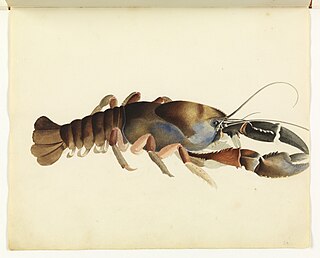
Astacopsis is a genus of crayfish endemic to the island of Tasmania. There are three extant species, Astacopsis gouldi, Astacopsis franklinii, and Astacopsis tricornis. All are threatened by illegal harvesting, and A. gouldi is protected by law. A. franklinii is found in the eastern half of the island, with A. tricornis taking its place in the west. A. gouldi is found only in rivers draining into the Bass Strait, except for the Tamar River.

Pterostylis falcata, commonly known as the sickle greenhood, is a species of orchid endemic to south-eastern Australia. It has a rosette of bright green leaves at the base of the plant and a single green and white, sickle-shaped flower. It is widespread and often common in Victoria but also occurs further north and west, and in Tasmania
Geocharax falcata is a species of crayfish in the Geocharax genus. It was first described in 1941. It is endemic to Victoria, Australia, and is listed as vunerable by the IUCN.
















