
Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3. It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances.

Terpenes are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n > 1. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes are further classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), as examples. The terpene alpha-pinene, is a major component of the common solvent, turpentine.
Mesitylene or 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene is a derivative of benzene with three methyl substituents positioned symmetrically around the ring. The other two isomeric trimethylbenzenes are 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (pseudocumene) and 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene (hemimellitene). All three compounds have the formula C6H3(CH3)3, which is commonly abbreviated C6H3Me3. Mesitylene is a colorless liquid with sweet aromatic odor. It is a component of coal tar, which is its traditional source. It is a precursor to diverse fine chemicals. The mesityl group (Mes) is a substituent with the formula C6H2Me3 and is found in various other compounds.
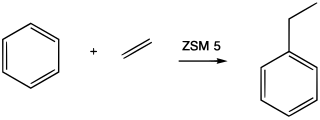
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene. Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character.

In organic chemistry, a cyanohydrin or hydroxynitrile is a functional group found in organic compounds in which a cyano and a hydroxy group are attached to the same carbon atom. The general formula is R2C(OH)CN, where R is H, alkyl, or aryl. Cyanohydrins are industrially important precursors to carboxylic acids and some amino acids. Cyanohydrins can be formed by the cyanohydrin reaction, which involves treating a ketone or an aldehyde with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of excess amounts of sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst:
Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CONH2. It is the simplest amide, and it is derived from acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent. The related compound N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA) is more widely used, but it is not prepared from acetamide. Acetamide can be considered an intermediate between acetone, which has two methyl (CH3) groups either side of the carbonyl (CO), and urea which has two amide (NH2) groups in those locations. Acetamide is also a naturally occurring mineral with the IMA symbol: Ace.

Geraniol is a monoterpenoid and an alcohol. It is the primary component of citronella oil and is a primary component of rose oil, palmarosa oil. It is a colorless oil, although commercial samples can appear yellow. It has low solubility in water, but it is soluble in common organic solvents. The functional group derived from geraniol is called geranyl.

Linalool refers to two enantiomers of a naturally occurring terpene alcohol found in many flowers and spice plants. Linalool has multiple commercial applications, the majority of which are based on its pleasant scent. A colorless oil, linalool is classified as an acyclic monoterpenoid. In plants, it is a metabolite, a volatile oil component, an antimicrobial agent, and an aroma compound. Linalool has uses in manufacturing of soaps, fragrances, food additives as flavors, household products, and insecticides. Esters of linalool are referred to as linalyl, e.g. linalyl pyrophosphate, an isomer of geranyl pyrophosphate.

Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COCH2COCH3. It is a colorless liquid, classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3C(O)CH=(OH)CH3. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. It is a colorless liquid that is a precursor to acetylacetonate anion, a bidentate ligand. It is also a building block for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds.

Acetone, is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CO. It is the simplest and smallest ketone. It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.

Sulfamic acid, also known as amidosulfonic acid, amidosulfuric acid, aminosulfonic acid, sulphamic acid and sulfamidic acid, is a molecular compound with the formula H3NSO3. This colourless, water-soluble compound finds many applications. Sulfamic acid melts at 205 °C before decomposing at higher temperatures to water, sulfur trioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen.

Myrcene, or β-myrcene, is a monoterpene. A colorless oil, it occurs widely in essential oils. It is produced mainly semi-synthetically from Myrcia, from which it gets its name. It is an intermediate in the production of several fragrances. α-Myrcene is the name for the isomer 2-methyl-6-methylene-1,7-octadiene, which has not been found in nature.
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), also known as farnesyl diphosphate (FDP), is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids such as sterols and carotenoids. It is also used in the synthesis of CoQ, as well as dehydrodolichol diphosphate.

Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and often have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be cyclic or contain rings, including many unique combinations. Biochemical modifications such as oxidation or rearrangement produce the related sesquiterpenoids.
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen functionality or missing a methyl group, are called monoterpenoids. Monoterpenes and monoterpenoids are diverse. They have relevance to the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, agricultural, and food industries.

Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) is an organic compound with the formula OC(OCH3)2. It is a colourless, flammable liquid. It is classified as a carbonate ester. This compound has found use as a methylating agent and more recently as a solvent that is exempt from the restrictions placed on most volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the US. Dimethyl carbonate is often considered to be a green reagent.
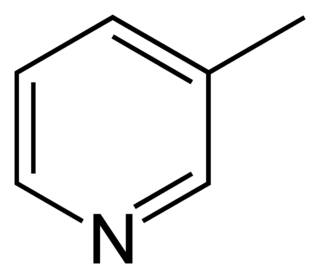
3-Methylpyridine or 3-picoline, is an organic compound with formula 3-CH3C5H4N. It is one of three positional isomers of methylpyridine, whose structures vary according to where the methyl group is attached around the pyridine ring. This colorless liquid is a precursor to pyridine derivatives that have applications in the pharmaceutical and agricultural industries. Like pyridine, 3-methylpyridine is a colorless liquid with a strong odor and is classified as a weak base.

2-Methyl-1-butanol is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2OH. It is one of several isomers of amyl alcohol. A colorless liquid, it occurs naturally in trace amounts and has attracted some attention as a potential biofuel, exploiting its hydrophobic (gasoline-like) and branched structure. It is chiral.

Wine is a complex mixture of chemical compounds in a hydro-alcoholic solution with a pH around 4. The chemistry of wine and its resultant quality depend on achieving a balance between three aspects of the berries used to make the wine: their sugar content, acidity and the presence of secondary compounds. Vines store sugar in grapes through photosynthesis, and acids break down as grapes ripen. Secondary compounds are also stored in the course of the season. Anthocyanins give grapes a red color and protection against ultraviolet light. Tannins add bitterness and astringency which acts to defend vines against pests and grazing animals.
In organic chemistry, alkynylation is an addition reaction in which a terminal alkyne is added to a carbonyl group to form an α-alkynyl alcohol.

















