
The bongo is a large, mostly nocturnal, forest-dwelling antelope, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes and long slightly spiralled horns. It is the only tragelaphid in which both sexes have horns. Bongos have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. They are the third-largest antelope in the world.

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit.

The hirola, also called the Hunter's hartebeest or Hunter's antelope, is a critically endangered antelope species found on the border between Kenya and Somalia. It was first described by the big game hunter and zoologist H.C.V. Hunter in 1888. It is the only living member of the genus Beatragus, though other species are known from the fossil record. The global hirola population is estimated at 300–500 animals and there are none in captivity. According to a document produced by the International Union for Conservation of Nature "the loss of the hirola would be the first extinction of a mammalian genus on mainland Africa in modern human history".

The hartebeest, also known as kongoni or kaama, is an African antelope. It is the only member of the genus Alcelaphus. Eight subspecies have been described, including two sometimes considered to be independent species. A large antelope, the hartebeest stands just over 1 m at the shoulder, and has a typical head-and-body length of 200 to 250 cm. The weight ranges from 100 to 200 kg. It has a particularly elongated forehead and oddly-shaped horns, a short neck, and pointed ears. Its legs, which often have black markings, are unusually long. The coat is generally short and shiny. Coat colour varies by the subspecies, from the sandy brown of the western hartebeest to the chocolate brown of the Swayne's hartebeest. Both sexes of all subspecies have horns, with those of females being more slender. Horns can reach lengths of 45–70 cm (18–28 in). Apart from its long face, the large chest and the sharply sloping back differentiate the hartebeest from other antelopes. A conspicuous hump over the shoulders is due to the long dorsal processes of the vertebrae in this region.

The conservation status of a group of organisms indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status exist and are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels as well as for consumer use.

The Harvey's red duiker is one of 19 species of duiker found in Tanzania and scattered through Kenya, southern Somalia and possibly central Ethiopia.
A rare species is a group of organisms that are very uncommon, scarce, or infrequently encountered. This designation may be applied to either a plant or animal taxon, and is distinct from the term endangered or threatened. Designation of a rare species may be made by an official body, such as a national government, state, or province. The term more commonly appears without reference to specific criteria. The International Union for Conservation of Nature does not normally make such designations, but may use the term in scientific discussion.

The mountain reedbuck is an antelope found in mountainous areas of much of sub-Saharan Africa.

Guioa is a genus of about 78 rainforest tree species known to science, which constitute part of the plant family Sapindaceae. They have a wide distribution, ranging from throughout Malesia, in Burma, Cambodia, Vietnam, Thailand, Malay Peninsula, Borneo, Sumatra, Philippines, Java, Flores, Timor, Sulawesi, Moluccas, New Guinea, further southwards through the east coast of Queensland and New South Wales, Australia and further eastwards to the Pacific Islands, including Tonga, New Caledonia, Fiji and Samoa.

Hildegarde's tomb bat is a species of sac-winged bat in the family Emballonuridae. It is found near the coast in Kenya and Tanzania where it feeds in tropical dry forests and roosts in caves. It is a diurnal species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as "endangered". The specific name hildegardeae was given in honour of anthropologist Hildegarde Beatrice Hinde.
The Amani sunbird is a species of bird in the family Nectariniidae. It is found in Kenya and Tanzania. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and subtropical or tropical moist montane forests. The male Amani sunbird has a white and dark-green feathered body while the female Amani sunbird has a yellow and grey plumage. Breeding season takes place from May to June and from September to December. The regular diet of the Amani sunbird consists of spiders, caterpillars and other flying insects. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The Tana River mangabey is a highly endangered species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. Some authorities have included the taxa agilis and sanjei as subspecies of this species, while others award these full species status.

The Tana River red colobus, also called the eastern red colobus, is a highly endangered species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is endemic to a narrow zone of gallery forest near the Tana River in southeastern Kenya.

Ctenochromis pectoralis, the Pangani haplo, is a species of fish in the family Cichlidae. It was originally characterized in the Pangani River of Tanzania, and may also be present in Kenya. It is listed as extinct by IUCN as a result of a 1996 evaluation, but this appears to be incorrect. A more recent IUCN publication stated that this species is not endangered in any way.

Helicia is a genus of 110 species of trees and shrubs, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. They grow naturally in rainforests throughout tropical South and Southeast Asia, including India, Sri Lanka, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia to New Guinea and as far south as New South Wales.
Rothmannia macrosiphon is a species of plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in Kenya and Tanzania.
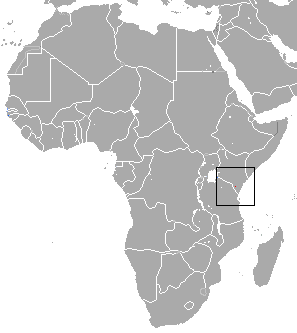
The Taita shrew is an extant species of white-toothed shrew from two localities in the Taita Hills mountain range in the Taita-Taveta District of southwestern Kenya. Given the continuing decline in the quality of this habitat, and the limitations in its range, the IUCN recognises the shrew as an endangered species.

Aloe dorotheae is a critically endangered succulent plant in the family Asphodelaceae. It is native to Tanzania.

Aloe volkensii is a species of plant widely distributed in East Africa.

Endangered species as classified by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), are species which have been categorized as very likely to become extinct in their known native ranges in the near future. On the IUCN Red List, endangered is the second-most severe conservation status for wild populations in the IUCN's schema after critically endangered. In 2012, the IUCN Red List featured 3,079 animal and 2,655 plant species as endangered worldwide. The figures for 1998 were 1,102 and 1,197 respectively.

















