
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms. Allenes are classified as cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene, which is itself also called allene. A group of the structure R2C=C=CR− is called allenyl, while a substituent attached to an allene is referred to as an allenic substituent. In analogy to allylic and propargylic, a substituent attached to a saturated carbon α to an allene is referred to as an allenylic substituent. While allenes have two consecutive ('cumulated') double bonds, compounds with three or more cumulated double bonds are called cumulenes.

Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group bonded to a hydroxy group. Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.
The Ferrier rearrangement is an organic reaction that involves a nucleophilic substitution reaction combined with an allylic shift in a glycal. It was discovered by the carbohydrate chemist Robert J. Ferrier.

In organic chemistry, a sulfone is a organosulfur compound containing a sulfonyl functional group attached to two carbon atoms. The central hexavalent sulfur atom is double-bonded to each of two oxygen atoms and has a single bond to each of two carbon atoms, usually in two separate hydrocarbon substituents.
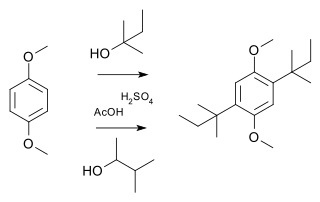
A Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement is a class of carbocation 1,2-rearrangement reactions in which a hydrogen, alkyl or aryl group migrates from one carbon to a neighboring carbon. They can be described as cationic [1,2]-sigmatropic rearrangements, proceeding suprafacially and with stereochemical retention. As such, a Wagner–Meerwein shift is a thermally allowed pericyclic process with the Woodward-Hoffmann symbol [ω0s + σ2s]. They are usually facile, and in many cases, they can take place at temperatures as low as –120 °C. The reaction is named after the Russian chemist Yegor Yegorovich Vagner; he had German origin and published in German journals as Georg Wagner; and Hans Meerwein.

Benzidine (trivial name), also called 1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine (systematic name), is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4NH2)2. It is an aromatic amine. It is a component of a test for cyanide. Related derivatives are used in the production of dyes. Benzidine has been linked to bladder and pancreatic cancer.

In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation describes a carbonium ionic derivative of norbornane. A salt of the 2-norbornyl cation was crystallized and characterized by X-ray crystallography confirmed the non-classical structure.
The Gabriel–Colman rearrangement is the chemical reaction of a saccharin or phthalimido ester with a strong base, such as an alkoxide, to form substituted isoquinolines. First described in 1900 by chemists Siegmund Gabriel and James Colman, this rearrangement, a ring expansion, is seen to be general if there is an enolizable hydrogen on the group attached to the nitrogen, since it is necessary for the nitrogen to abstract a hydrogen to form the carbanion that will close the ring. As shown in the case of the general example below, X is either CO or SO2.
Bullvalene is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H10. The molecule has a cage-like structure formed by the fusion of one cyclopropane and three cyclohepta-1,4-diene rings. Bullvalene is unusual as an organic molecule due to the C−C and C=C bonds forming and breaking rapidly on the NMR timescale; this property makes it a fluxional molecule.
The McLafferty rearrangement is a reaction observed in mass spectrometry during the fragmentation or dissociation of organic molecules. It is sometimes found that a molecule containing a keto-group undergoes β-cleavage, with the gain of the γ-hydrogen atom, as first reported by Anthony Nicholson working in the Division of Chemical Physics at the CSIRO in Australia. This rearrangement may take place by a radical or ionic mechanism. This reaction occurs secondary to the Cormas-Grisius electrophilic benzene addition reaction, a multi-step benzene-derivative reaction. The Cormas-Grisius electrophilic benzene addition reaction's validity is highly contested by scholars in the field, and its practical usage has yet to be elucidated.

The Hayashi rearrangement is the chemical reaction of ortho-benzoylbenzoic acids catalyzed by sulfuric acid or phosphorus pentoxide.
The Chichibabin pyridine synthesis is a method for synthesizing pyridine rings. The reaction involves the condensation reaction of aldehydes, ketones, α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds, or any combination of the above, with ammonia. It was reported by Aleksei Chichibabin in 1924. Methyl-substituted pyridines, which show widespread uses among multiple fields of applied chemistry, are prepared by this methodology.

Oripavine is an opioid and the major metabolite of thebaine. It is the parent compound from which a series of semi-synthetic opioids are derived, which includes the compounds etorphine and buprenorphine. Although its analgesic potency is comparable to morphine, it is not used clinically due to its severe toxicity and low therapeutic index. Due to its use in manufacture of strong opioids, oripavine is a controlled substance in some jurisdictions.

Pinacolone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) is an important ketone in organic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid with a slight peppermint or camphor odor. It is a precursor to triazolylpinacolone in the synthesis of the fungicide triadimefon and in synthesis of the herbicide metribuzin. The molecule is an unsymmetrical ketone. The α-methyl group can participate in condensation reactions. The carbonyl group can undergo the usual reactions. It is a Schedule 3 compound under the Chemical Weapons Convention 1993, due to being related to pinacolyl alcohol, which is used in the production of soman. It is also a controlled export in Australia Group member states.
The Stieglitz rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry which is named after the American chemist Julius Stieglitz (1867–1937) and was first investigated by him and Paul Nicholas Leech in 1913. It describes the 1,2-rearrangement of trityl amine derivatives to triaryl imines. It is comparable to a Beckmann rearrangement which also involves a substitution at a nitrogen atom through a carbon to nitrogen shift. As an example, triaryl hydroxylamines can undergo a Stieglitz rearrangement by dehydration and the shift of a phenyl group after activation with phosphorus pentachloride to yield the respective triaryl imine, a Schiff base.
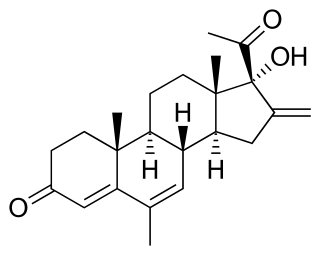
Melengestrol is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group and an antineoplastic drug which was never marketed. An acylated derivative, melengestrol acetate, is used as a growth promoter in animals.

Basketane is a polycyclic alkane with the chemical formula C10H12. The name is taken from its structural similarity to a basket shape. Basketane was first synthesized in 1966, independently by Masamune and Dauben and Whalen. A patent application published in 1988 used basketane, which is a hydrocarbon, as a source material in doping thin diamond layers because of the molecule's high vapor pressure, carbon ring structure, and fewer hydrogen-to-carbon bond ratio.
The Newman–Kwart rearrangement is a type of rearrangement reaction in which the aryl group of an O-aryl thiocarbamate, ArOC(=S)NMe2, migrates from the oxygen atom to the sulfur atom, forming an S-aryl thiocarbamate, ArSC(=O)NMe2. The reaction is named after its discoverers, Melvin Spencer Newman and Harold Kwart. The reaction is a manifestation of the double bond rule. The Newman–Kwart reaction represents a useful synthetic tool for the preparation of thiophenol derivatives.
The Mislow–Evans rearrangement is a name reaction in organic chemistry. It is named after Kurt Mislow who reported the prototypical reaction in 1966, and David A. Evans who published further developments. The reaction allows the formation of allylic alcohols from allylic sulfoxides in a 2,3-sigmatropic rearrangement.

Robert John Ferrier FRSNZ, FNZIC, was an organic chemist who discovered two chemical reactions, the Ferrier rearrangement and the Ferrier carbocyclization. Originally from Edinburgh, he moved to Wellington, New Zealand, in 1970.













