
Glycine is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG. Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to the "flexibility" caused by such a small R group. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction.

A dipeptide is an organic compound derived from two amino acids. The constituent amino acids can be the same or different. When different, two isomers of the dipeptide are possible, depending on the sequence. Several dipeptides are physiologically important, and some are both physiologically and commercially significant. A well known dipeptide is aspartame, an artificial sweetener.

In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base. An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid.

Diazomethane is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether. The compound is a popular methylating agent in the laboratory, but it is too hazardous to be employed on an industrial scale without special precautions. Use of diazomethane has been significantly reduced by the introduction of the safer and equivalent reagent trimethylsilyldiazomethane.
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed acetate esters or simply acetates. Deacetylation is the opposite reaction, the removal of an acetyl group from a chemical compound.
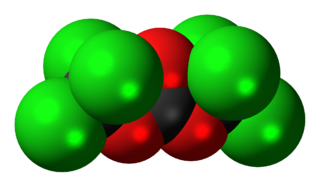
Triphosgene (bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate (BTC)) is a chemical compound with the formula OC(OCCl3)2. It is used as a solid substitute for phosgene, which is a gas and diphosgene, which is a liquid. Triphosgene is stable up to 200 °C. Triphosgene is used in a variety of halogenation reactions.

Trimethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name it has the formula Al2(CH3)6 (abbreviated as Al2Me6 or TMA), as it exists as a dimer. This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industrially important compound, closely related to triethylaluminium.
The Bouveault–Blanc reduction is a chemical reaction in which an ester is reduced to primary alcohols using absolute ethanol and sodium metal. It was first reported by Louis Bouveault and Gustave Louis Blanc in 1903. Bouveault and Blanc demonstrated the reduction of ethyl oleate and n-butyl oleate to oleyl alcohol. Modified versions of which were subsequently refined and published in Organic Syntheses.
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile, and the activated carbon, serves as a nucleophile. Classical coupling agents are phenols and naphthols. Usually the diazonium reagent attacks at the para position of the coupling agent. When the para position is occupied, coupling occurs at a ortho position, albeit at a slower rate.

The Knorr pyrrole synthesis is a widely used chemical reaction that synthesizes substituted pyrroles (3). The method involves the reaction of an α-amino-ketone (1) and a compound containing an electron-withdrawing group α to a carbonyl group (2).

Cyanamide is an organic compound with the formula CN2H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug. The molecule features a nitrile group attached to an amino group. Derivatives of this compound are also referred to as cyanamides, the most common being calcium cyanamide (CaCN2).

o-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. OPD is a white compound although samples appear darker owing to oxidation by air. It is isomeric with m-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine.

Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCHN2. It is classified as a diazo compound. Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is commercially available as solutions in hexanes, DCM, and ether. It is a specialized reagent used in organic chemistry as a methylating agent for carboxylic acids. It is a safer replacement for diazomethane, which is a sensitive explosive gas, whereas trimethylsilyldiazomethane is a relatively stable liquid and thus easier to handle.
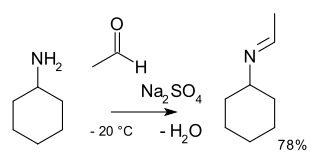
In organic chemistry, alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution is the organic reaction of carbonyl compounds with amines to imines. The reaction name is based on the IUPAC Nomenclature for Transformations. The reaction is acid catalyzed and the reaction type is nucleophilic addition of the amine to the carbonyl compound followed by transfer of a proton from nitrogen to oxygen to a stable hemiaminal or carbinolamine. With primary amines, water is lost in an elimination reaction to an imine. With aryl amines, especially stable Schiff bases are formed.
The Schotten–Baumann reaction is a method to synthesize amides from amines and acid chlorides:

Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic compound with the formula [(CH3)3O]+[BF4]−. This salt is a strong methylating agent, being a synthetic equivalent of CH+3. It is a white solid that rapidly decomposes upon exposure to atmospheric moisture, although it is robust enough to be weighed quickly without inert atmosphere protection. Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is a closely related compound.

Phenylglycine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a non-proteinogenic alpha amino acid related to alanine, but with a phenyl group in place of the methyl group. It is a white solid. The compound exhibits some biological activity.
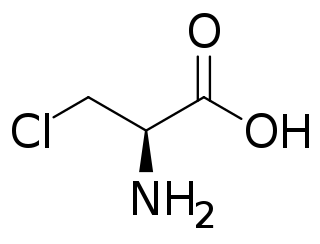
Chloroalanine (3-chloroalanine) is an unnatural amino acid with the formula ClCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a white, water-soluble solid. The compound is usually derived from chlorination of serine. The compound is used in the synthesis of other amino acids by replacement of the chloride. Protected forms of the related iodoalanine are also known.

Tris(o-tolyl)phosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H4CH3)3. It is a white, water-insoluble solid that is soluble in organic solvents. In solution it slowly converts to the phosphine oxide. As a phosphine ligand, it has a wide cone angle of 194°. Consequently, it tends to cyclometalate when treated with metal halides and metal acetates. Complexes of this ligand are common in homogeneous catalysis.

Diethyl acetamidomalonate (DEAM) is a derivative of malonic acid diethyl ester. Formally, it is derived through the acetylation of ester from the unstable aminomalonic acid. DEAM serves as a starting material for racemates including both, natural and unnatural α-amino acids or hydroxycarboxylic acids. It is also usable as a precursor in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly in the cases of active ingredients like fingolimod, which is used to treat multiple sclerosis.

















