
An echinoderm is any deuterostomal animal of the phylum Echinodermata, which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larvae, as adults echinoderms are recognisable by their usually five-pointed radial symmetry, and are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,600 living species, making it the second-largest group of deuterostomes after the chordates, as well as the largest marine-only phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian.

Sea urchins or urchins are typically spiny, globular animals, echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal to 5,000 metres. Their tests are round and spiny, typically from 3 to 10 cm across. Sea urchins move slowly, crawling with their tube feet, and sometimes pushing themselves with their spines. They feed primarily on algae but also eat slow-moving or sessile animals. Their predators include sea otters, starfish, wolf eels, and triggerfish.

Sand dollars are species of flat, burrowing sea urchins belonging to the order Clypeasteroida. Some species within the order, not quite as flat, are known as sea biscuits. Sand dollars can also be called "sand cakes" or "cake urchins".
The water vascular system is a hydraulic system used by echinoderms, such as sea stars and sea urchins, for locomotion, food and waste transportation, and respiration. The system is composed of canals connecting numerous tube feet. Echinoderms move by alternately contracting muscles that force water into the tube feet, causing them to extend and push against the ground, then relaxing to allow the feet to retract.

A pedicellaria is a small wrench- or claw-shaped appendage with movable jaws, called valves, commonly found on echinoderms, particularly in sea stars and sea urchins. Each pedicellaria is an effector organ with its own set of muscles, neuropils, and sensory receptors and is therefore capable of reflex responses to the environment. Pedicellariae are poorly understood but in some taxa, they are thought to keep the body surface clear of algae, encrusting organisms, and other debris in conjunction with the ciliated epidermis present in all echinoderms.

Kelp forests are underwater areas with a high density of kelp, which covers a large part of the world's coastlines. Smaller areas of anchored kelp are called kelp beds. They are recognized as one of the most productive and dynamic ecosystems on Earth. Although algal kelp forest combined with coral reefs only cover 0.1% of Earth's total surface, they account for 0.9% of global primary productivity. Kelp forests occur worldwide throughout temperate and polar coastal oceans. In 2007, kelp forests were also discovered in tropical waters near Ecuador.

In biology, a test is the hard shell of some spherical marine animals and protists, notably sea urchins and microorganisms such as testate foraminiferans, radiolarians, and testate amoebae. The term is also applied to the covering of scale insects. The related Latin term testa is used for the hard seed coat of plant seeds.

Lytechinus variegatus, commonly called the green sea urchin or the variegated sea urchin, is a species of sea urchin that can be found in the warm waters of the western Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea.

Echinus is a genus of sea urchins. Sea urchins are echinoderms that are typically spherical or flattened with a covering of spine-like structures. Sea urchins tend to be important members of their ecosystems by grazing on other organisms and stabilizing populations. In addition to this, sea urchins play a large role in different economies globally as the urchin themselves and their roe are sold for consumption. The same is true for the species within the genus Echinus.

The heart urchins or Spatangoida are an order of sea urchins.

The Atelostomata are a type of sea urchins. They are distinguished from other sea urchins by their irregular shape and the absence of a feeding lantern. The group includes the well known heart urchins, as well as some less familiar and extinct forms.

Toxopneustes pileolus, commonly known as the flower urchin, is a widespread and commonly encountered species of sea urchin from the Indo-West Pacific. It is considered highly dangerous, as it is capable of delivering extremely painful and medically significant stings when touched. It inhabits coral reefs, seagrass beds, and rocky or sandy environments at depths of up to 90 m (295 ft). It feeds on algae, bryozoans, and organic detritus.

Spatangus purpureus, commonly known as the purple heart urchin, is a species of sea urchin in the family Spatangidae. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, where it lives immersed in the sediment.

Lytechinus williamsi, the jewel urchin, is a sea urchin in the family Toxopneustidae. It occurs on shallow reefs off the coasts of Panama, Belize, the Florida Keys and Jamaica.
Ossicles are small calcareous elements embedded in the dermis of the body wall of echinoderms. They form part of the endoskeleton and provide rigidity and protection. They are found in different forms and arrangements in sea urchins, starfish, brittle stars, sea cucumbers, and crinoids. The ossicles and spines are the only parts of the animal likely to be fossilized after an echinoderm dies.

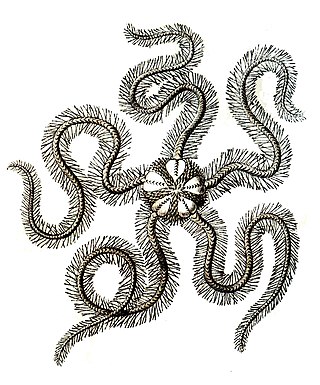
Luidia maculata is a species of starfish in the family Luidiidae in the order Paxillosida. It is native to the Indo-Pacific region. It is commonly known as the eight-armed sea star because, although the number of arms varies from five to nine, eight arms seems to be the most common.

Irregularia is an extant infraclass of sea urchins that first appeared in the Lower Jurassic.

Clypeaster reticulatus, the reticulated sea biscuit, is a species of sea urchin in the family Clypeasteridae. This species was first scientifically described in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus. It lives on the sandy seabed of shallow seas, semi-immersed in the sediment.

Echinocyamus pusillus, commonly known as the pea urchin or green urchin, is a species of sand dollar, a sea urchin in the family Fibulariidae, native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It buries itself in gravel or coarse sand at depths down to about 1,250 m (4,000 ft).

Luidia savignyi is a species of starfish belonging to the family Luidiidae. The species is found in the tropical and subtropical Indo-Pacific region. It is a large starfish and preys on other echinoderms.


















