Mieszko I was Duke of Poland from 960 until his death in 992 and the founder of the first unified Polish state, the Civitas Schinesghe. A member of the Piast dynasty, he was the first Christian ruler of Poland and continued the policies of both his father Siemomysł and grandfather Lestek, who initiated a process of unification among the Polish tribes and the creation of statehood.

The Sorbian languages are the Upper Sorbian language and Lower Sorbian language, two closely related and partially mutually intelligible languages spoken by the Sorbs, a West Slavic ethno-cultural minority in the Lusatia region of Eastern Germany. They are classified under the West Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages and are therefore closely related to the other two West Slavic subgroups: Lechitic and Czech–Slovak. Historically, the languages have also been known as Wendish or Lusatian. Their collective ISO 639-2 code is wen.

The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor. Today Belarusians, Russians and Ukrainians are the existent East Slavic nations. Rusyns can also be considered as a separate nation, although they are often considered a subgroup of the Ukrainian people.

Kuyavia, also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western, central, and south-eastern.

The Drevlians, Derevlians or Derevlianians were a tribe of East Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries, which inhabited the territories of Polesia and right-bank Ukraine, west of the eastern Polans and along the lower reaches of the rivers Teteriv, Uzh, Ubort, and Stsviha. To the west, the Drevlians' territories reached the Sluch River, where the Volhynians and Buzhans lived. To the north, the Drevlians' neighbors were the Dregoviches.

The Polans or Polians, also known as Polanians, Polianians, and Eastern Polans, were an East Slavic tribe between the 6th and the 9th century, which inhabited both sides of the Dnieper river from Liubech to Rodnia and also down the lower streams of the rivers Ros', Sula, Stuhna, Teteriv, Irpin', Desna and Pripyat.
The Polans, also known as Polanians or Western Polans, were a West Slavic and Lechitic tribe, inhabiting the Warta River basin of the contemporary Greater Poland region starting in the 6th century. They were one of the main tribes in Central Europe and were closely related to the Vistulans, Masovians, Czechs and Slovaks. According to Zygmunt Gloger, their name was derived from the word "pole" meaning "field", thus denoting them as "men of the fields".
Siemomysł or Ziemomysł was the third |duke of the Polans and the father of Poland's first Christian ruler, Mieszko I. A member of the Piast dynasty, he was listed by Gallus Anonymous in his Gesta principum Polonorum as the son of Lestek, the second known duke of the Polans. According to Gallus' account and historical research, Siemomysł has been credited with leaving the lands of the Polans, Goplans and Masovians to his son Mieszko I, who further expanded them during his reign.

Prince Popiel ІІ was a legendary 9th-century ruler of two proto-Polish tribes, the Goplans and West Polans. He was the last member of the Popielids, a mythical dynasty before the Piasts. According to the chroniclers Gallus Anonymus, Jan Długosz, and Marcin Kromer, as a consequence of his bad rule he was deposed, besieged by his subjects, and eaten alive by mice in a tower in Kruszwica.
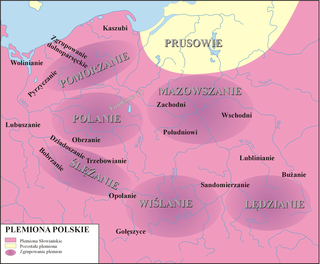
"Polish tribes" is a term used sometimes to describe the tribes of West Slavic Lechites that lived from around the mid-6th century in the territories that became Polish with the creation of the Polish state by the Piast dynasty. The territory on which they lived became a part of the first Polish state created by duke Mieszko I and expanded at the end of the 10th century, enlarged further by conquests of king Bolesław I at the beginning of the 11th century.

The Vistulans, or Vistulanians, were an early medieval Lechitic tribe inhabiting the western part of modern Lesser Poland.

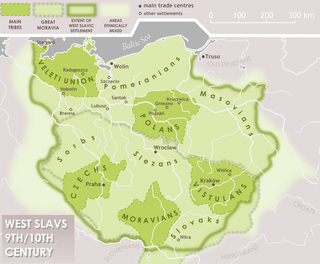
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic languages diversified into their historically attested forms over the 10th to 14th centuries.

The Popielids were a legendary ruling dynasty of either the Polans, Goplans or both tribes, founded by Leszko II. They supposedly ruled the lands of Poland prior to the start of the Piast dynasty. Two Polish families claim descent from the Popielids: the Pobog-Pobodze clan is a junior branch of the Popielid dynasty, rulers of Poland from the 7th through 9th centuries, before the era of Bolescic-Piast dynasty another junioral branch of the Popielid dynasty.

Lechites, also known as the Lechitic tribes, is a name given to certain West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and of Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians.

The Silesians were a tribe of West Slavs, specifically of the Lechitic/Polish group, inhabiting territories of Lower Silesia, near Ślęża mountain and Ślęza river, on both banks of the Oder, up to the area of modern city of Wrocław. They were the first permanent inhabitants of the site of Wrocław where they build a fort on Ostrów Tumski in the 9th century or earlier, which at the time was an island on the Oder.

OdoI was margrave in the Saxon Eastern March of the Holy Roman Empire from 965 until his death.
The most important phenomenon that took place within the lands of Poland in the Early Middle Ages, as well as other parts of Central Europe was the arrival and permanent settlement of the West Slavic or Lechitic peoples. The Slavic migrations to the area of contemporary Poland started in the second half of the 5th century AD, about a half century after these territories were vacated by Germanic tribes fleeing from the Huns. The first waves of the incoming Slavs settled the vicinity of the upper Vistula River and elsewhere in the lands of present southeastern Poland and southern Masovia. Coming from the east, from the upper and middle regions of the Dnieper River, the immigrants would have had come primarily from the western branch of the early Slavs known as Sclaveni, and since their arrival are classified as West Slavs and Lechites, who are the closest ancestors of Poles.[a]
The Wolinians were a Lechitic tribe in Early Middle Age Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Velunzani" with 70 civitates by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845. Associated with both the Veleti and the Pomeranians, they were based on the island of Wolin and the adjacent mainland. Compared to other tribes of these groups, the Wolinians' territory was relatively small but densely settled: in the 11th century, there was one settlement per four square kilometers. The Wolinians are described by Jan Maria Piskorski as the most powerful Pomeranian tribe. This position resulted from the multi-ethnic emporium at the site of the present-day town of Wolin (Wollin), then known as Jomsborg, Jumne, Julin or Vineta.
Rethra was, in the 10th to the 12th centuries, the main town and political center of the Slavic Redarians, one of the four major Lutician tribes, located most likely in present-day Mecklenburg. It was also a major worship center, devoted to the cult of the Slavic deity Radegast-Swarożyc.
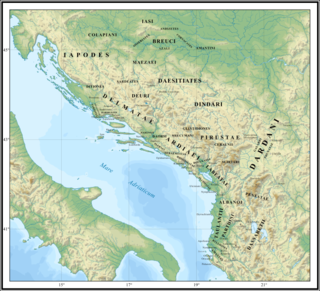
The Albanoi were an Illyrian tribe. They were possibly first mentioned by Hecataeus of Miletus under the name Abroi. Ptolemy is the first author who mentions them under the name Albanoi. Their central settlement was called Albanopolis (Ἀλβανόπολις) and was located roughly between the Mat and Shkumbin rivers, in central Albania. The archaeological site of Zgërdhesh has been identified as the likely location of Albanopolis. Stephanus of Byzantium who reproduced Hecataeus added an entry for another settlement named Arbon in Illyria whose inhabitants were called Arbonioi or Arbonites. Another Arbon was recorded by Polybius. John of Nikiû wrote in the 7th century CE about a people known as Arbanitai in the Greek translation of the manuscript.












