Ophidiiformes is an order of ray-finned fish that includes the cusk-eels, pearlfishes, viviparous brotulas, and others. Members of this order have small heads and long slender bodies. They have either smooth scales or no scales, a long dorsal fin and an anal fin that typically runs into the caudal fin. They mostly come from the tropics and subtropics, and live in both freshwater and marine habitats, including abyssal depths. They have adopted a range of feeding methods and lifestyles, including parasitism. The majority are egg-laying, but some are viviparous.

The viviparous brotulas form a family, the Bythitidae, of ophidiiform fishes. They are known as viviparous brotulas as they generally bear live young, although there are indications that some species do not. They are generally infrequently seen, somewhat tadpole-like in overall shape and mostly about 5–10 cm (2–4 in) in length, but some species grow far larger and may surpass 60 cm (2 ft).
Fiordichthys is a genus of viviparous brotula native to the southwest Pacific Ocean.
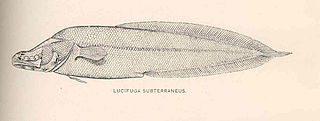
Lucifuga is a genus of viviparous brotulas. Most of the species are native to caves and sinkholes in Cuba and the Bahamas; L. inopinata from deep water off the Galápagos Islands is the only exception. The four species rated by the IUCN are all considered vulnerable. The largest species in the genus reaches about 15 cm (5.9 in) in length.

Ogilbia is a genus of viviparous brotulas. The generic name honours the Australian naturalist James Douglas Ogilby (1853-1925), for his contribution to the knowledge of the fishes of Australia.

Saccogaster is a genus of viviparous brotulas. They are found in the western Atlantic and Indo-Pacific.
Bellottia is a genus of viviparous brotulas which is found in the subtropical waters of the North Atlantic, the Mediterranean Sea and the Indo-Pacific.
Bythites is a genus of viviparous brotulas found in the Atlantic Ocean.
Cataetyx is a genus of viviparous brotulas.
Diplacanthopoma is a genus of viviparous brotulas.
Gunterichthys is a genus of viviparous brotula.

Hephthocara is a small genus of Indo-Pacific viviparous brotula.
Eurypleuron is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
Onuxodon is an Indo-Pacific genus of pearlfishes from the family Carapidae. The generic name is derived from the Greek onyx meaning "claw" and odon meaning "tooth", referring to the sharp fang like teeth of Onuxodon parvibrachium. Species in this genus are distributed from South Africa to Hawaii. They live commensally with molluscs. The three currently recognized species are:
Pyramodon is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
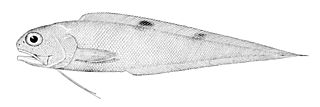
Neobythites is a genus of cusk-eels.
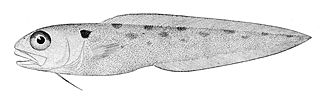
Otophidium is a genus of cusk-eels, part of the subfamily Ophidiinae in the family Ophidiidae. They are found in the western Atlantic and eastern Pacific.
Grammonus waikiki, or the Waikiki viviparous brotula, is a species of viviparous brotula found in the Hawaiian Islands where it occurs at depths of around 3–18 metres (9.8–59.1 ft).

Bythitinae is a subfamily of viviparous brotulas, one of the two subfamilies in the family Bythitidae. This subfamily is characterised by having the dorsal, caudal and anal fins combined. They are mostly found in temperate to tropical seas, from reefs to the benthopelagic zone, but some species from the North Atlantic Ocean occur in into Arctic waters.
Onuxodon fowleri is a species of pearlfish first described by Smith, 1955. Onuxodon fowleri is part of the genus Onuxodon and the subfamily Carapinae. No subspecies are listed in the Catalog of Life.






