Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

Condor is the common name for two species of New World vultures, each in a monotypic genus. The name derives from the Quechua kuntur. They are the largest flying land birds in the Western Hemisphere.

Cathartidae, known commonly as New World vultures or condors, are a family of birds of prey consisting of seven extant species in five genera. It includes five extant vultures and two extant condors found in warm and temperate areas of the Americas. They are known as "New World" vultures to distinguish them from Old World vultures, with which the Cathartidae does not form a single clade despite the two being similar in appearance and behavior as a result of convergent evolution.

Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae. The Sturnidae are named for the genus Sturnus, which in turn comes from the Latin word for starling, sturnus. The family contains 128 species which are divided into 36 genera. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas, as well as North America, Hawaii, and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common.

The Andean condor is a South American New World vulture and is the only member of the genus Vultur. It is found in the Andes mountains and adjacent Pacific coasts of western South America. With a maximum wingspan of 3.3 m and weight of 15 kg (33 lb), the Andean condor is one of the largest flying birds in the world, and is generally considered to be the largest bird of prey in the world.

Gryposaurus was a genus of duckbilled dinosaur that lived about 80 to 75 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous of North America. Named species of Gryposaurus are known from the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta, Canada, and two formations in the United States: the Lower Two Medicine Formation in Montana and the Kaiparowits Formation of Utah. A possible additional species from the Javelina Formation in Texas may extend the temporal range of the genus to 66 million years ago.

Ace Combat X: Skies of Deception is a 2006 combat flight simulation video game for the PlayStation Portable. It is the first installment of the Ace Combat franchise for the PlayStation Portable, and the second for a handheld game system.
Hercules in the Maze of the Minotaur is the fifth and final television movie in the syndicated fantasy series Hercules: The Legendary Journeys.

Aviculopecten is an extinct genus of bivalve mollusc that lived from the Early Devonian to the Late Triassic in Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America.

The wildlife of Chile is very diverse because of the country's slender and elongated shape, which spans a wide range of latitude, and altitude, ranging from the windswept coastline of the Pacific coast on the west to northern Andes to the sub-Antarctic, high Andes mountains in the east. There are many distinct ecosystems.

Anomia is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Anomiidae. They are commonly known as jingle shells because when a handful of them are shaken they make a jingling sound, though some are also known as saddle oysters.

Famatina is an Argentinian Department in La Rioja Province.

Uncites is an extinct genus of brachiopods in the family Uncitidae. This genus includes spire-bearing brachiopod with a rostrate ventral valve. A typical species is Uncites gryphus from the Middle Devonian in Germany.

Gypospirifer is an extinct genus of articulate brachiopod fossils belonging to the family Trigonotretidae. They were stationary epifaunal suspension feeders.
Pleistovultur is an extinct genus of large New World vulture from the Late Pleistocene or Early Holocene of South America. The type species P. nevesi was described based in a complete and well preserved right tibiotarsus from the Cuvieri cave deposits in Lagoa Santa region in Minas Gerais state, Brazil. It was larger than Sarcoramphus papa, but smaller than Vultur gryphus.
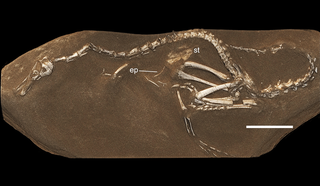
Halszkaraptorinae is a basal ("primitive") subfamily of Dromaeosauridae that includes the enigmatic genera Halszkaraptor, Natovenator, Mahakala, and Hulsanpes. Halszkaraptorines are definitively known only from Late Cretaceous strata in Asia, specifically in Mongolia. Following the recent discovery of Natovenator, a member of the subfamily, the group is believed to have a semiaquatic lifestyle.
Enoploides is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Thoracostomopsidae.












