
Spiriferida is an order of extinct articulate brachiopod fossils which are known for their long hinge-line, which is often the widest part of the shell. In some genera it is greatly elongated, giving them a wing-like appearance. They often have a deep fold down the center of the shell. The feature that gives the spiriferids their name ("spiral-bearers") is the internal support for the lophophore; this brachidium, which is often preserved in fossils, is a thin ribbon of calcite that is typically coiled tightly within the shell.

Craniata is a class of brachiopods originating in the Cambrian period and still extant today. It is the only class within the subphylum Craniiformea, one of three major subphyla of brachiopods alongside linguliforms and rhynchonelliforms. Craniata is divided into three orders: the extinct Craniopsida and Trimerellida, and the living Craniida, which provides most information on their biology. Living members of the class have shells which are composed of calcite, though some extinct forms my have aragonite shells. The shells are inarticulate and are usually rounded in outline. There is no pedicle; the rear edge of the body cavity is a smooth and flat wall perforated by the anus. This class of brachiopods has an unsupported lophophore with only a single row of tentacles. In the absence of a pedicle, the shell is usually attached directly to a hard substrate. Many craniiforms are encrusting animals which attach directly to the shell of another animal, usually another brachiopod. The plicae from the host brachiopod will then appear within the shell of the craniiform.

The taxonomic order Rhynchonellida is one of the two main groups of living articulate brachiopods, the other being the order Terebratulida. They are recognized by their strongly ribbed wedge-shaped or nut-like shells, and the very short hinge line.

Orthida is an extinct order of brachiopods which appeared during the Early Cambrian period and became very diverse by the Ordovician, living in shallow-shelf seas. Orthids are the oldest member of the subphylum Rhynchonelliformea, and is the order from which all other brachiopods of this group stem. Physically they are usually strophic, with well-developed interareas. They also commonly have radiating ribs, sulcus, and fold structures. Typically one valve, often the brachial valve, is flatter than the other. The interior structure of the brachial valves are usually simple. In shape they are sub-circular to elliptical, with typically biconvex valves.

The Craniidae are a family of brachiopods, the only surviving members of the subphylum Craniiformea. They are the only members of the order Craniida, the monotypic suborder Craniidina, and the superfamily Cranioidea; consequently, the latter two taxa are at present redundant and rarely used.There are three living genera within Craniidae: Neoancistrocrania, Novocrania, and Valdiviathyris. As adults, craniids either live freely on the ocean floor or, more commonly, cement themselves onto a hard object with all or part of the ventral valve.

The taxonomy of commonly fossilized invertebrates combines both traditional and modern paleozoological terminology. This article compiles various invertebrate taxa in the fossil record, ranging from protists to arthropods. This includes groups that are significant in paleontological contexts, abundant in the fossil record, or have a high proportion of extinct species. Special notations are explained below:

Atrypa is a genus of brachiopod with round to short egg-shaped shells covered with many fine radial ridges. Growth lines form perpendicular to the costae and are spaced approximately 2 to 3 times further apart than the costae.. The pedunculate valve is slightly convex, but oftentimes levels out or becomes slightly concave toward the anterior margin. The brachial valve is highly convex. Neither valve contains an interarea. Atrypa had a large geographic range and occurred from the late Lower Silurian (Telychian) to the early Upper Devonian (Frasnian). Other sources expand the range from the Late Ordovician to Carboniferous, approximately from 449 to 336 Ma. A proposed new species, A. harrisi, was found in the trilobite-rich Floresta Formation in Boyacá, Colombia.

Strophomenida is an extinct order of articulate brachiopods which lived from the lower Ordovician period to the mid Carboniferous period. Strophomenida is part of the extinct class Strophomenata, and was the largest known order of brachiopods, encompassing over 400 genera. Some of the largest and heaviest known brachiopod species belong to this class. Strophomenids were among the most diverse and abundant brachiopods during the Ordovician, but their diversity was strongly impacted at the Late Ordovician mass extinction. Survivors rediversified into new morphologies in the Silurian, only to be impacted once again at the Late Devonian mass extinction. However, they still survived till the end of the Permian.

Brachiopods, phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a stalk-like pedicle projects from an opening near the hinge of one of the valves, known as the pedicle or ventral valve. The pedicle, when present, keeps the animal anchored to the seabed but clear of sediment which would obstruct the opening.
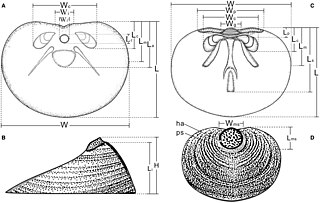
Acrotretides (Acrotretida) are an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. Acrotretida contains 8 families within the sole superfamily Acrotretoidea. They lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Middle Devonian, rapidly diversifying during the middle Cambrian. In the upper Cambrian, linguliforms reached the apex of their diversity: acrotretides and their relatives the lingulides together comprised nearly 70% of brachiopod genera at this time. Though acrotretides continued to diversify during the Ordovician, their proportional dominance declined, as rhynchonelliforms took on a larger role in brachiopod faunas.

Rhynchonelliformea is a major subphylum and clade of brachiopods. It is roughly equivalent to the former class Articulata, which was used previously in brachiopod taxonomy up until the 1990s. These so-called articulated brachiopods have many anatomical differences relative to "inarticulate" brachiopods of the subphyla Linguliformea and Craniformea. Articulates have hard calcium carbonate shells with tongue-and-groove hinge articulations and separate sets of simple opening and closing muscles.

Pentamerida is an order of biconvex, impunctate shelled, articulate brachiopods that are found in marine sedimentary rocks that range from the Middle Cambrian through the Devonian.

Athyridida is an order of Paleozoic brachiopods included in the Rhynchonellata, which makes up part of the articulate brachiopods.

Athyris is a brachiopod genus with a subequally biconvex shell that is generally wider than long and a range that extends from the Silurian into the Triassic. Athyris is the type genus for the Athyrididae, which belongs to the articulate order Athyridida. R.C. Moore (1952) gives a shorter range, from the Mid Devonian to the Lower Mississippian.

Paterinata is an extinct class of linguliform brachiopods which lived from the lower Cambrian ("Tommotian") to the Upper Ordovician (Hirnantian). It contains the single order Paterinida and the subfamily Paterinoidea. Despite being some of the earliest brachiopods to appear in the fossil record, paterinides stayed as a relatively subdued and low-diversity group even as other brachiopods diversified later in the Cambrian and Ordovician. Paterinides are notable for their high degree of convergent evolution with rhynchonelliform (articulate) brachiopods, which have a similar set of muscles and hinge-adjacent structures.

Trimerellida is an extinct order of craniate brachiopods, containing the sole superfamily Trimerelloidea and the families Adensuidae, Trimerellidae, and Ussuniidae. Trimerellidae was a widespread family of warm-water brachiopods ranging from the Middle Ordovician to the late Silurian (Ludlow). Adensuidae and Ussuniidae are monogeneric families restricted to the Ordovician of Kazakhstan. Most individuals were free-living, though some clustered into large congregations similar to modern oyster reefs.

Kutorginates (Kutorginata) are an extinct class of early rhynchonelliform ("articulate") brachiopods. The class contains only a single order, Kutorginida (kutorginides). Kutorginides were among the earliest rhynchonelliforms, restricted to the lower-middle part of the Cambrian Period.

The orthotetides (Orthotetida) are an extinct order of brachiopods in the class Strophomenata. Though not particularly diverse or abundant relative to strophomenides (Strophomenida) or productides (Productida), orthotetides were nevertheless the longest-lasting order of strophomenates, surviving from the Middle Ordovician (“Llanvirn”) up until the Late Permian. Externally, many orthotetides are difficult to distinguish from strophomenides. Most fundamental differences between the two orders are internal: orthotetides have more elaborate cardinal processes and a greater diversity of shell microstructure.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2019.

Atrypida is an extinct order of rhynchonelliform brachiopods. They first appeared in middle Ordovician and survived the Ordovician-Silurian extinction, becoming the dominant brachiopods of the Silurian alongside the order Pentamerida. They would survive into the Late Devonian before going extinct at the end of the Frasnian.



















