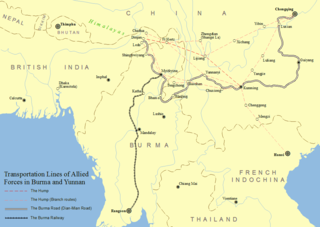
Operation Matterhorn was a military operation of the United States Army Air Forces in World War II for the strategic bombing of Japanese forces by B-29 Superfortresses based in India and China. Targets included Japan itself, and Japanese bases in China and South East Asia. The name comes from the Matterhorn, a mountain traditionally considered particularly difficult to climb.

The XX Bomber Command is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with Twentieth Air Force, based on Okinawa. It was inactivated on 16 July 1945.

The Twentieth Air Force is a numbered air force of the United States Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC). It is headquartered at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming.

The 58th Air Division is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, based at Wright Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio. It was inactivated on 1 February 1959.

The 444th Air Expeditionary Wing is a provisional unit of the United States Air Force assigned to Air Combat Command to activate or inactivate as needed. It was last activated in 2003.

The 468th Bombardment Group was a World War II United States Army Air Forces combat organization. It was inactivated on 31 March 1946. The unit served primarily in the Pacific Ocean theater and China Burma India Theater of World War II as part of Twentieth Air Force. The 468th Bomb Group's aircraft engaged in very heavy bombardment B-29 Superfortress operations against Japan. After its reassignment to the Mariana Islands in 1945, its aircraft were identified by a "I" and a triangle painted on the tail.

Lakeland Army Airfield, was a World War II United States Army Air Force located 5.3 miles southwest of Lakeland, Florida. From 1960 to 2017 it was Lakeland Linder Regional Airport. In 2017 it was renamed Lakeland Linder International Airport.

Dinjan Airfield was a World War II airfield, located in Dinjan, approximately seven miles northeast of Chabua, in the state of Assam, India.

Chakulia Airport is an airport in India. It is located southwest of Chakulia, a town and a notified area in Purbi Singhbhum district in the state of Jharkhand.

Charra Airfield is an abandoned airfield in India, located 5 miles (8.0 km) ExNE of Purulia, in West Bengal.

Piardoba Airfield is an abandoned airfield in India, located 6.6 miles (10.7 km) S of Bishnupur, West Bengal, Bankura District in the state of West Bengal, India.

Xinjin Airport is an airport in Xinjin County, in the southwestern part of the Chengdu prefecture-level city in Sichuan province of China. The airfield is located approximately 2 km east of the Xinjin County seat, just east of the China National Highway 108. A former military airfield, it is now used by Civil Aviation Flight University of China for pilot training.

Qionglai Air Base is a People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) located west of the city of Chengdu, the capital of the province of Sichuan in Southwestern China. More precisely, the facility is located approximately 3 km southwest of Wangsi Town and 2 km northeast of Sangyuan Town, just to the east of 318 National Road. This entire area is located in the northwestern part of the Sichuan Basin, not far from the foothills of the great Qionglai Mountains.

Pengshan Air Base is a People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) air base, located approximately 1 km east of Gongyi Town, in Pengshan County, Sichuan province, Southwestern China.

Brooksville Army Airfield, was a United States Army Air Forces airfield constructed during World War II, located 7.2 miles (11.6 km) southwest of Brooksville, Florida.

Chengdu Fenghuangshan Airport is military air base in Chengdu, Sichuan province, China. During World War II it was a United States Army Air Forces airfield. It is located approximately 10 miles south of Chengdu.

The 679th Bombardment Squadron is a disbanded unit of the United States Army Air Forces (AAF). It was last assigned to the 444th Bombardment Group at Dudhkundi Airfield, India where it was disbanded on 12 October 1944.

The 677th Bombardment Squadron is an inactive unit of the United States Army Air Forces it was last assigned to the 444th Bombardment Group at Davis-Monthan Field, Arizona.

The 676th Bombardment Squadron is an inactive unit of the United States Army Air Forces it was last assigned to the 444th Bombardment Group at Davis-Monthan Field, Arizona.