
The cicadas are a superfamily, the Cicadoidea, of insects in the order Hemiptera. They are in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, along with smaller jumping bugs such as leafhoppers and froghoppers. The superfamily is divided into two families, the Tettigarctidae, with two species in Australia, and the Cicadidae, with more than 3,000 species described from around the world; many species remain undescribed.
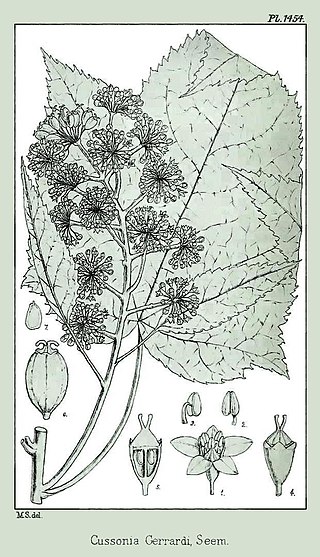
Seemannaralia gerrardii, commonly known as the wild-maple or mock carrot tree, is a species of flowering plant in the family Araliaceae. It is the sole member of genus Seemannaralia, and is endemic to South Africa, where it occurs in the Eastern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo and Mpumalanga provinces. It was originally included in genus Cussonia. Seemann- and gerrardii commemorate Berthold Seemann and William Gerrard respectively, while -aralia suggests the family or its type genus, Aralia.

Vachellia karroo, (synonym Acacia karroo} commonly known as the sweet thorn, common acacia, Karoo thorn, Cape gum or cockspur thorn, is a species of Vachellia, in the Mimosa sub-family of the Fabaceae or pea family, which is native to southern Africa from southern Angola east to Mozambique, and south to South Africa.

Gymnosporia is an Old World genus of plants, that comprise suffrutices, shrubs and trees. It was formerly considered congeneric with Maytenus, but more recent investigations separated it based on the presence of achyblasts and spines, alternate leaves or fascicles of leaves, an inflorescence that forms a dichasium, mostly unisexual flowers, and fruit forming a dehiscent capsule, with an aril on the seed. It is dioecious, with male and female flowers on separate plants.

Maytenus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Celastraceae. Members of the genus are distributed throughout Central and South America, Southeast Asia, Micronesia, and Australasia, the Indian Ocean and Africa. They grow in a very wide variety of climates, from tropical to subpolar. The traditional circumscription of Maytenus was paraphyletic, so many species have been transferred to Denhamia and Gymnosporia.
Gymnosporia dhofarensis is a species of plant in the family Celastraceae and is found in Oman and Yemen. It is an intricately branched spiny shrub or small tree with its leaves arranged alternately or clustered on short shoots. The flowers have white or cream petals and the fruit are purple or red. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Platypleura divisa is an African cicada first described by Ernst Friedrich Germar, entomologist and professor of mineralogy at Halle, who also studied beetles.

Platypleura is a genus of cicadas that occurs widely across Africa and southern Asia. Some of the South African species are remarkable for their endothermic thermoregulation that enables crepuscular signalling, an adaptation that reduces risk of predation and enables a greater range for their calls. In field experiments their maximum body temperature while calling at dusk, was measured at 22 °C above ambient temperature.

Ochna pulchra, also known as Lekkerbreek, is a small deciduous southern African tree up to 5 m, commonly found on deep sandy soil and rocky slopes, and belonging to the tropical family of Ochnaceae, which is widespread in Asia and Africa.

Newlands Forest is a conservancy area on the eastern slopes of Table Mountain, beside the suburb of Newlands, Cape Town, South Africa. It is owned and maintained by the Table Mountain National Parks Board, along with the City Parks Department of Cape Town, and includes a Fire Station, Nursery and Reservoir.

Aleeta curvicosta is a species of cicada, one of Australia's most familiar insects. Native to the continent's eastern coastline, it was described in 1834 by Ernst Friedrich Germar. The floury baker is the only described species in the genus Aleeta.

Maytenus oleoides, commonly known as the mountain maytenus or rock false candlewood, is a dense, medium-sized tree that grows throughout the western half of South Africa. It is known as klipkershout in Afrikaans.

Euclea crispa, commonly known as the blue guarri, is an Afrotropical plant species of the family Ebenaceae. The hardy and evergreen plants may form a dense stand of shrubs, or grow to tree size. It is widespread and common in the interior regions of southern Africa, and occurs northward to the tropics. Though some are present near the South African south and east coasts, they generally occur at middle to high altitudes. It is readily recognizable from its much-branched structure and dull bluish foliage colour. Those bearing lanceolate leaves may however resemble the Wild olive, another common species of the interior plateaus.

Marie Prins is a South African botanist.

Pycna semiclara, known as the Whining Forest Cicada, is a South African forest-dwelling platypleurine cicada.

Gymnosporia nemorosa is a spiny, somewhat sprawling evergreen shrub or small tree with drooping branches growing to some 5 m tall and found along forest edges in Mpumalanga, Eswatini, KwaZulu-Natal south to the Garden Route in the Southern Cape. In Maputaland the species adopts the form of a geoxylic suffrutex or ‘underground’ tree, with shoots sprouting from its woody, underground axis.

Megatibicen dealbatus, commonly called the plains cicada, is a species of annual cicada. Dealbatus is Latin for "whitewashed".

Gymnosporia thompsonii is a species of plant in the bittersweet family Celastraceae. It is endemic to the Mariana and Caroline Islands, where it grows as a many-stemmed understory shrub or small tree in karst forests. Its wood is used for fuel and its leaves are used medicinally.

Gymnosporia buxifolia is a species of plant in the bittersweet family (Celastraceae) native to southern Africa. It is commonly known as the pioneer spike-thorn or common spike-thorn. It ranges from Angola and Mozambique to South Africa.




















