
Cracker butterflies are a Neotropical group of medium-sized brush-footed butterfly species of the genus Hamadryas. They acquired their common name due to the unusual way that males produce a "cracking" sound as part of their territorial displays. The most comprehensive work about their ecology and behavior is that of Julian Monge Najera et al. (1998). The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1806.

Agrias is a genus of Neotropical charaxine nymphalid butterflies found in South and Central America.

Hamadryas amphinome, the red cracker, is a species of cracker butterfly in the family Nymphalidae, native to regions of North and South America.

Hamadryas arinome, the turquoise cracker, is a species of cracker butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. The species was first described by Hippolyte Lucas in 1853. It is found from Mexico south to the Amazon basin.

Hamadryas laodamia, the starry night cracker or starry cracker, is a species of cracker butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It can be found from Mexico to the Amazon basin, but is most common in lowland forest in the Caribbean area.

Hamadryas feronia, the blue cracker or variable cracker, is a species of cracker butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in the southern parts of North America and South America and southwards Brazil.

Parides erithalion, the variable cattleheart, is a North and South American butterfly in the family Papilionidae. The species was first described by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1836.

Papilio androgeus, the Androgeus swallowtail, queen page, or queen swallowtail, is a Neotropical butterfly of the family Papilionidae. It is found from Mexico to Argentina with a small population in southern Florida.

Papilio menatius is a butterfly of the family Papilionidae.

Myscelia cyaniris, the blue wave, blue-banded purplewing, tropical blue wave, whitened bluewing, or royal blue, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae.

Dismorphia crisia, the crisia mimic white or cloud forest mimic-white, is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1782. It is found from northern Central America to Bolivia and the Amazon basin.

Eurytides agesilaus, the short-lined kite swallowtail, is a medium-sized species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae.

Adelpha lycorias, the pink-banded sister, is a species of butterfly of the family Nymphalidae.

Hamadryas februa, the graycracker, is a species of cracker butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found from Argentina north through tropical America to Mexico. Rare strays can be found up to the lower Rio Grande Valley in southern Texas. The habitat consists of subtropical forests, forest edges and cultivated areas with trees.

Marpesia zerynthia, the waiter daggerwing, is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. Primarily found in Mesoamerica, it can also be observed in regions slightly north and south of this area.

Mimoides pausanias, the Pausanias swallowtail or bluish mimic-swallowtail, is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae.
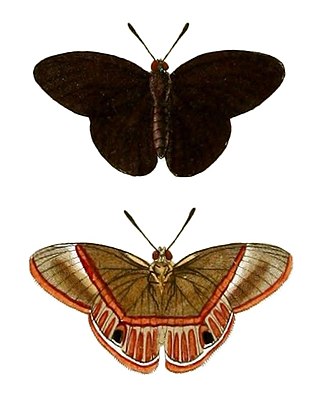
Euselasia is a genus of butterflies in the family Riodinidae. They are present only in the Neotropical realm. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819.
Dalechampia triphylla is a vine in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is native to tropical South America.

Hamadryas glauconome, the pale cracker or glaucous cracker, is a species of cracker butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1864 and is found in Mexico, Central America and south to Peru. It has been recorded as an unexpected vagrant in the United States in southern Florida, Arizona and Texas.

Marpesia berania, the amber daggerwing, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. The species was first described by William Chapman Hewitson in 1852. They are a brightly colored, Neotropical butterfly with a unique wing shape, found in Central and northern South America. The amber daggerwing exhibits several interesting characteristics varying from their unusual behavior to their physical traits that make them so distinct.


















