
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.

The tinfoil barb is a tropical Southeast Asian freshwater fish of the family Cyprinidae. This species was originally described as Barbus schwanenfeldii by Pieter Bleeker in 1853, and has also been placed in the genera Barbodes and Puntius. The specific epithet is frequently misspelled schwanefeldii.

The ticto barb or twospot barb is a species of subtropical freshwater fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae. It is a native of the upper Mekong, Salwen, Irrawaddy, Meklong and upper Charo Phraya basins in the countries of Nepal, India, Pakistan, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Thailand, and Sri Lanka. It has frequently been confused with the Odessa barb in the aquarium trade, but in that species the male is reddish-orange.

Puntigrus partipentazona, the Dwarf Tiger Barb, is a species of cyprinid fish native to Southeast Asia where it is found in the Mekong, Mae Klong, and Chao Phraya basins of Thailand, the Malay Peninsula, and coastal streams of southeast Thailand and Cambodia where it occurs in streams and impoundments with dense weed growth. It can also be found in the aquarium trade. It is frequently misidentified as the similar Puntigrus tetrazona.

The giant barb, Siamese Giant carp, or simply Siamese carp is the largest species of cyprinid in the world. These migratory fish are found only in the Mae Klong, Mekong, and Chao Phraya River basins in Indochina. Populations have declined drastically due to habitat loss and overfishing, and the giant barb is now considered critically endangered.
Hampala lopezi is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is found only in the Philippines.

Hampala is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae, the family which includes the carps, barbs and related fishes. The fishies in this genus are found in South-East Asia.

The Java barb, more commonly known as silver barb in aquaculture, is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Barbonymus.

Haplorchis taichui is a species of intestinal fluke in the family Heterophyidae. It is a human parasite.

The burnt-tailed barb, also known as Siamese bala-shark, is a possibly extinct freshwater fish species from the family Cyprinidae. It is or was endemic to the Mae Klong and Chao Phraya River basins in Thailand.
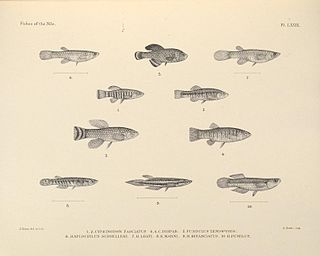
The Arabian toothcarp, known also as the Arabian toothcarp or mother-of-Pearl fish is a species of killifish belonging to the family Aphaniidae. It can be found from the shores of the Red Sea south to Ethiopia, the Gulf of Aden, the Arabian Sea and along the Persian Gulf east to Pakistan and India. It is also found in the Suez Canal, the northern coast of the Sinai Peninsula, and in one location on the Palestinian coast. The former recognized subspecies: A. d. richardsoni, the Dead Sea toothcarp endemic to the Dead Sea has now been raised to a full species as Aphaniops richardsoni.

The long-tailed shrew or rock shrew is a small shrew found in Atlantic Canada and the Northeastern United States.

Hampala macrolepidota, the hampala barb, is a relatively large southeast Asian species of cyprinid from the Mekong and Chao Phraya basins, as well as Peninsular Malaysia and the Greater Sundas. It prefers running rivers and streams, but can be seen in most freshwater habitats except torrents, small creeks and shallow swamps. This predatory species reaches up to 70 cm (2.3 ft) in length and it is common at half that size.
Hampala salweenensis is a southeast Asian species of cyprinid, endemic to the basin of the Salween in Thailand and Myanmar. It reaches a length of 30 cm.
The feathered river garfish, also known as the estuarine halfbeak, spoon-fin garfish, spoon-fin river garfish and viviparous half beak, is a species of marine, freshwater, brackish and reef-associated oceanodromous viviparous halfbeak found in Indo-Pacific regional countries, such as Kenya, Mozambique, Seychelles, Madagascar, New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Australia, New Caledonia, Fiji, Sri Lanka, India, Vanuatu, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore and Samoa.

Leptobarbus rubripinna, also known as the Sultan barb, is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish from the carp and minnow family, Cyprinidae which occurs in south-east Asia.

Hampala ampalong is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae, the family which includes the carps, barbs and related fishes. This species is found in Sumatra and western Borneo, and has a maximum total length of 15.5 centimetres (6.1 in).
Hampala bimaculata is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae, the family which includes the carps, barbs and related fishes. This species is found in Borneo and has a maximum total length of 50 centimetres (20 in).

Hampala sabana is a species of cyprinid in the genus Hampala that is native to Malaysia














