Related Research Articles
In human genetics, the Mitochondrial Eve is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all living humans. In other words, she is defined as the most recent woman from whom all living humans descend in an unbroken line purely through their mothers and through the mothers of those mothers, back until all lines converge on one woman.

Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in Western Asia. The clade spread from there during the Neolithic, primarily into North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Socotra Archipelago, the Caucasus, Europe, Anatolia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia.

Haplogroup M is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. An enormous haplogroup spanning all the continents, the macro-haplogroup M, like its sibling the macro-haplogroup N, is a descendant of the haplogroup L3.
Haplogroup J is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. The clade derives from the haplogroup JT, which also gave rise to haplogroup T. Within the field of medical genetics, certain polymorphisms specific to haplogroup J have been associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.
Haplogroup T is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is believed to have originated around 25,100 years ago in the Near East.
Haplogroup V is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. The clade is believed to have originated over 14,000 years ago in Southern Europe.
Haplogroup U is a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup (mtDNA). The clade arose from haplogroup R, likely during the early Upper Paleolithic. Its various subclades are found widely distributed across Northern and Eastern Europe, Central, Western and South Asia, as well as North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the Canary Islands.

Haplogroup R is a widely distributed human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. Haplogroup R is associated with the peopling of Eurasia after about 70,000 years ago, and is distributed in modern populations throughout the world outside of sub-Saharan Africa.

Haplogroup N is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) clade. A macrohaplogroup, its descendant lineages are distributed across many continents. Like its sibling macrohaplogroup M, macrohaplogroup N is a descendant of the haplogroup L3.

In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup C is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.

Haplogroup L3 is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. The clade has played a pivotal role in the early dispersal of anatomically modern humans.
Haplogroup I is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is believed to have originated about 21,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) period in West Asia. The haplogroup is unusual in that it is now widely distributed geographically, but is common in only a few small areas of East Africa, West Asia and Europe. It is especially common among the El Molo and Rendille peoples of Kenya, various regions of Iran, the Lemko people of Slovakia, Poland and Ukraine, the island of Krk in Croatia, the department of Finistère in France and some parts of Scotland and Ireland.
Haplogroup P also known as P-F5850 or K2b2 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup in human genetics. P-F5850 is a branch of K2b, which is a branch of Haplogroup K2 (K-M526).

In human genetics, a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by differences in human mitochondrial DNA. Haplogroups are used to represent the major branch points on the mitochondrial phylogenetic tree. Understanding the evolutionary path of the female lineage has helped population geneticists trace the matrilineal inheritance of modern humans back to human origins in Africa and the subsequent spread around the globe.

In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup Y is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.
In human mitochondrial genetics, Haplogroup G is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.

Haplogroup N1a is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.
Haplogroup H is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. The clade is believed to have originated in Southwest Asia, near present day Syria, around 20,000 to 25,000 years ago. Mitochondrial haplogroup H is today predominantly found in Europe, and is believed to have evolved before the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). It first expanded in the northern Near East and Southern Caucasus, and later migrations from Iberia suggest that the clade reached Europe before the Last Glacial Maximum. The haplogroup has also spread to parts of Africa, Siberia and Inner Asia. Today, around 40% of all maternal lineages in Europe belong to haplogroup H.
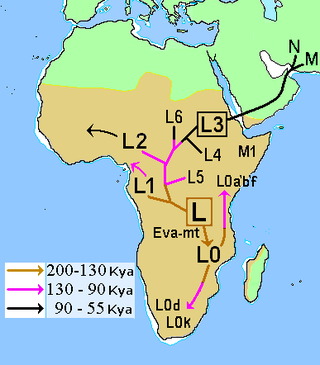
In human mitochondrial genetics, L is the mitochondrial DNA macro-haplogroup that is at the root of the anatomically modern human mtDNA phylogenetic tree. As such, it represents the most ancestral mitochondrial lineage of all currently living modern humans, also dubbed "Mitochondrial Eve".

The ancestry of modern Iberians is consistent with the geographical situation of the Iberian Peninsula in the South-west corner of Europe, showing characteristics that are largely typical in Southern and Western Europeans. As is the case for most of the rest of Southern Europe, the principal ancestral origin of modern Iberians are Early European Farmers who arrived during the Neolithic. The large predominance of Y-Chromosome Haplogroup R1b, common throughout Western Europe, is also testimony to a sizeable input from various waves of Western Steppe Herders that originated in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe during the Bronze Age.
References
- ↑ Maruszak A, Canter JA, Styczyńska M, Zekanowski C, Barcikowska M (November 2009). "Mitochondrial haplogroup H and Alzheimer's disease--is there a connection?". Neurobiology of Aging. 30 (11): 1749–55. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.01.004. PMID 18308428. S2CID 5067976.
- ↑ The genome of Homo sapiens
- ↑ Bermisheva M, Tambets K, Villems R, Khusnutdinova E (2002). "[Diversity of mitochondrial DNA haplotypes in ethnic populations of the Volga-Ural region of Russia]" (PDF). Molekuliarnaia Biologiia (in Russian). 36 (6): 990–1001. PMID 12500536.
- ↑ Simoni L, Calafell F, Pettener D, Bertranpetit J, Barbujani G (January 2000). "Geographic patterns of mtDNA diversity in Europe" (PDF). American Journal of Human Genetics. 66 (1): 262–78. doi:10.1086/302706. PMC 1288355 . PMID 10631156. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2008-12-08.
- ↑ Hendrickson SL, Hutcheson HB, Ruiz-Pesini E, et al. (November 2008). "Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups influence AIDS progression". AIDS. 22 (18): 2429–39. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e32831940bb. PMC 2699618 . PMID 19005266.
- ↑ van Oven M, Kayser M (February 2009). "Updated comprehensive phylogenetic tree of global human mitochondrial DNA variation". Human Mutation. 30 (2): E386–94. doi: 10.1002/humu.20921 . PMID 18853457. S2CID 27566749.
Phylogenetic tree of human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroups | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitochondrial Eve (L) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| L0 | L1–6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M | N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CZ | D | E | G | Q | O | A | S | R | I | W | X | Y | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C | Z | B | F | R0 | pre-JT | P | U | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HV | JT | K | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H | V | J | T | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||