
The grey pug is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is found throughout the Palearctic region. It is also found in North America. Since it does not place any special demands on climatic conditions, special caterpillar food plants, geological subsoil or the like it is a typical species of almost any Hochstaudenflur, where it occurs in the herb layer, in bushes and even on deciduous trees. It can be found on forest edges and hedgerows, on heath, in rocky places and wetlands, parks and gardens, as well as in villages and town centres.

The scalloped hazel is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Carl Alexander Clerck in 1759.

The scalloped oak is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Rabdophaga rosaria is a gall midge which forms Camellia galls or terminal rosette gall on willow species. It was first described by Hermann Loew in 1850.

Eriophyes tiliae is a mite that forms the lime nail gall or bugle gall. It develops in a chemically induced gall; an erect, oblique or curved distortion rising up from the upper surface of the leaves of the lime (linden) trees, such as the large-leaved lime tree Tilia platyphyllos, the common lime tree Tilia × europaea, etc.

The nettle pouch gall develops in leaf veins, leaf petioles, flower stalks and sometimes the stem of Urtica dioica. This structure is caused by the gall midge Dasineura urticae, sometimes misspelled Dasyneura urticae. Obsolete synonyms are Perrisia urticae and Cecidomyia urticae.

Dasineura crataegi, the hawthorn button-top gall-midge, is a dipteran gall-midge. It causes the hawthorn button-top gall, which develops in the terminal shoots of common hawthorn, Crataegus monogyna Jacq., Midland hawthorn C laevigata (Poir.) DC and their hybrid, C × media Bechst. Synonyms are Perrisia crataegi and Cecidomyia crataegi.

Chrysomela populi is a species of broad-shouldered leaf beetle belonging to the family Chrysomelidae, subfamily Chrysomelinae.

Aceria fraxinivora, also known as the cauliflower gall mite and the ash key gall, causes the growths, known as galls, found on the hanging seeds or "keys" of the ash (Fraxinus) species.
Orseolia oryzae, also called the Asian rice gall midge, is a species of small fly in the family Cecidomyiidae. It is a major insect pest of rice. The damage to the crop is done by the larvae which form galls commonly known as "silver shoots" or "onion shoots". The rice plant is stunted and the seed heads fail to develop.

A gnat is any of many species of tiny flying insects in the dipterid suborder Nematocera, especially those in the families Mycetophilidae, Anisopodidae and Sciaridae. Most often they fly in large numbers, called clouds. "Gnat" is a loose descriptive category rather than a phylogenetic or other technical term, so there is no scientific consensus on what constitutes a gnat. Some entomologists consider only non-biting flies to be gnats. Certain universities and institutes also distinguish eye gnats: the Smithsonian Institution describes them as "non-biting flies, no bigger than a few grains of salt, ... attracted to fluids secreted by your eyes".
Rabdophaga strobilina is a gall midge which forms galls on the buds of some species of willow. It was first described by Hermann Loew in 1850.

Rabdophaga salicis is a gall midge which forms galls on sallows. It was first described by Franz von Paula Schrank in 1803.

Iteomyia major is a gall midge which forms galls on willows. It was first described by Jean-Jacques Kieffer in 1889.

Iteomyia capreae is a gall midge which forms galls on willows. It was first described by Johannes Winnertz in 1853.

Euura proxima is a species of sawfly belonging to the family Tenthredinidae. The larvae feed on the leaves of willows, creating galls. It was described by Jean Guillaume Audinet-Serville in 1823. The species was placed in the genus Euura in 2014 and was previously known as Nematus proximus and Pontania proxima.

Polystepha pilulae, the oak leaf gall midge, is a species of gall midge in the family Cecidomyiidae. It is found in eastern North America.

Dasineura fraxini is a gall midge which forms galls on the leaves and petioles of ash. It was first described by Johann Jacob Bremi-Wolf in 1847.
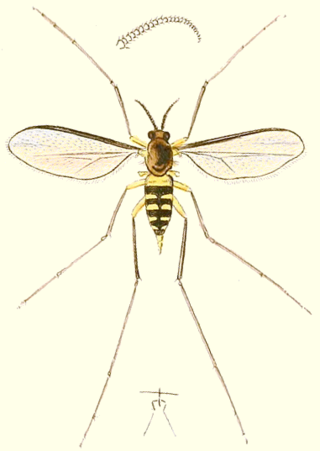
Lasioptera rubi is a species of gall midge in the family Cecidomyiidae and is found in Europe. It was first described in 1803 by the German priest, botanist and entomologist, Franz von Paula Schrank. The larvae feed within the tissue of brambles, creating abnormal plant growths known as galls.


















