
Chitons are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora, formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.

Elephas is one of two surviving genera in the family of elephants, Elephantidae, with one surviving species, the Asian elephant, Elephas maximus.
Lorica is a genus of chitons in the family Schizochitonidae.
Septemchiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Septemchiton became extinct during the Ordovician period.
Calceochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Calceochiton became extinct during the Ordovician period.
Olingechiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Olingechiton became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous period.
Gotlandochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran mollusc. Gotlandochiton became extinct during the Silurian period.
Ivoechiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Ivoechiton became extinct during the Cretaceous period.
Pterochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs.
Cymatochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Cymatochiton became extinct during the Permian period.
Pterygochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Pterygochiton became extinct during the Carboniferous period.
Trachypleura is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Trachypleura became extinct during the Triassic period.
Acutichiton is among the most primitive genera of Neoloricate chitons. Acutichiton became extinct during the Carboniferous period. Articulated specimens are known.
Glyptochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran mollusc. Glyptochiton became extinct during the Carboniferous period.
Heterochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran mollusc. Heterochiton became extinct during the Jurassic period.
Oochiton is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. Oochiton became extinct during the Miocene period.
Polysacos is an extinct genus of multiplacophorans (chitons) known from articulated Carboniferous fossils; its seventeen shell plates are arranged in three rows, with seven iterated units. It demonstrates that multiplacophora are related to modern polyplacophora. It was fringed with a ring of hollow spines resembling those of the Ordovician Echinochiton.
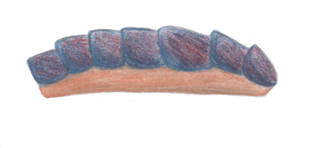
Kulindroplax perissokomos is a Silurian mollusk, known from a single fossil from the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte fauna of England. It lived during the Homerian Age. It is considered a basal aplacophoran. Unlike all modern aplacophorans, which are shell-less, Kulindroplax has a chiton-like shell, and it is considered a transitional fossil in the evolution of molluscs.
Phthipodochiton is an extinct genus of molluscs, known from several fossils from the upper Ordovician fauna of the Lady Burn Starfish beds of Girvan, Scotland. It shows a mixture of aplacophoran body plan and polyplacophoran-like valves, and it is an informative fossil in the evolution of aculiferan mollusks.

Megalochelys is an extinct genus of cryptodiran tortoises that lived from the Miocene to Pleistocene, across Asia and possibly Eastern Europe. They are noted for their giant size, which is among the largest of any known testudine, with a maximum carapace length over 2 m in M. atlas.



