| Heremites | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Heremites auratus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Scincidae |
| Subfamily: | Mabuyinae |
| Genus: | Heremites Gray, 1845 |
| Species | |
3 sp., see text | |
| Heremites | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Heremites auratus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Scincidae |
| Subfamily: | Mabuyinae |
| Genus: | Heremites Gray, 1845 |
| Species | |
3 sp., see text | |
The following 3 species, listed alphabetically by specific name, are recognized as being valid: [1]
Nota bene : A binomial authority in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a genus other than Heremites.

Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions.

Mabuya is a genus of long-tailed skinks, lizards in the family Scincidae. The genus is restricted to species from various Caribbean islands. Species in the genus Mabuya are primarily carnivorous, though many are omnivorous. The genus is viviparous, having a highly evolved placenta that resembles that of eutherian mammals. Formerly, many Old World species were placed here, as Mabuya was a kind of "wastebasket taxon". These Old World species are now placed in the genera Chioninia, Eutropis, and Trachylepis. Under the older classification, the New World species were referred to as "American mabuyas", and as of 2024 include the genera Alinea, Aspronema, Brasiliscincus, Capitellum, Copeoglossum, Maracaiba, Marisora, and Varzea.

The Andaman Islands grass skink is a species of skink found in the Andaman Islands of India.

The bronze grass skink, bronze mabuya or speckled forest skink, is a species of skink found in South and Southeast Asia. It is a common, but shy, ground-dwelling species that is active both day and night.

The bridled mabuya or bridled skink is a species of skink found in North Africa and Middle East. They grow up to 22 cm.

Trachylepis is a skink genus in the subfamily Mabuyinae found mainly in Africa. Its members were formerly included in the "wastebin taxon" Mabuya, and for some time in Euprepis. As defined today, Trachylepis contains the clade of Afro-Malagasy mabuyas. The genus also contains a species from the Brazilian island of Fernando de Noronha, T. atlantica, and may occur in mainland South America with Trachylepis tschudii and Trachylepis maculata, both poorly known and enigmatic. The ancestors of T. atlantica are believed to have rafted across the Atlantic from Africa during the last 9 million years.

Lygosominae is the largest subfamily of skinks in the family Scincidae. The subfamily can be divided into a number of genus groups. If the rarely used taxonomic rank of infrafamily is employed, the genus groups would be designated as such, but such a move would require a formal description according to the ICZN standards.

Eutropis is a genus of skinks belonging to the subfamily Mabuyinae. For long, this genus was included in the "wastebin taxon" Mabuya; it contains the Asian mabuyas. They often share their habitat with the related common skinks (Sphenomorphus), but they do not compete significantly as their ecological niches differ. This genus also contains the only member of the subfamily to occur in Australasia, the many-lined sun skink, whose wide range includes New Guinea.

The Noronha skink is a species of skink from the island of Fernando de Noronha off northeastern Brazil. It is covered with dark and light spots on the upperparts and is usually about 7 to 10 cm in length. The tail is long and muscular, but breaks off easily. Very common throughout Fernando de Noronha, it is an opportunistic feeder, eating both insects and plant material, including nectar from the Erythrina velutina tree, as well as other material ranging from cookie crumbs to eggs of its own species. Introduced predators such as feral cats prey on it and several parasitic worms infect it.
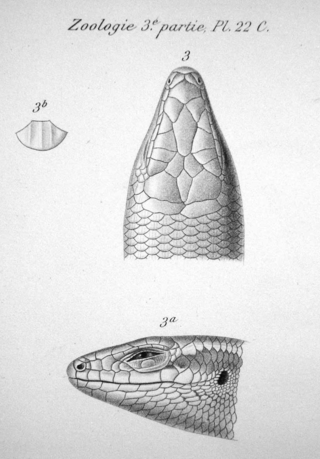
Trachylepis maculata, the spotted mabuya, is a species of skink in the genus Trachylepis recorded from Demerara in Guyana, northern South America. It is placed in the genus Trachylepis, which is otherwise mostly restricted to Africa, and its type locality may be in error. It is an unstriped, olive-brown, grayish animal, with dark spots all over the body. Its taxonomic history is complex due to confusion with Trachylepis atlantica from the Atlantic Ocean island of Fernando de Noronha and doubts regarding its type locality.
Trachylepis tschudii is an enigmatic skink, purportedly from Peru. First described in 1845 on the basis of a single specimen, it may be the same as the Noronha skink (T. atlantica) from Fernando de Noronha, off northeastern Brazil. T. tschudii represents one of two doubtful records of the otherwise African genus Trachylepis on mainland South America; the other is T. maculata from Guyana.

Heremites auratus, the Levant skink, golden grass mabuya, or golden grass skink, is a species of skink. It is found in Greece and Turkey, and possibly much more widely in Asia and even north-eastern Africa.

Mabuyinae is a subfamily of lizards, commonly known as skinks, within the family Scincidae. The genera in this subfamily were previously found to belong the Mabuya group in the large subfamily Lygosominae.

The golden grass mabuya or southern grass skink is a species of skink found in the Middle East.
There are two species of skink named golden grass mabuya: