
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and 88% of its population. The archipelagic country consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.

The British Virgin Islands (BVI), officially the Virgin Islands, are a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean, to the east of Puerto Rico and the US Virgin Islands and north-west of Anguilla. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles and part of the West Indies.

The CaymanIslands is a self-governing British Overseas Territory, and the largest by population. The 264-square-kilometre (102-square-mile) territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located south of Cuba and north-east of Honduras, between Jamaica and Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. The capital city is George Town on Grand Cayman, which is the most populous of the three islands.

Hawaii is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. It is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics. It also hosts 10 out of 14 climates - the highest for any country subdivision - and is one of two U.S. states with a tropical climate.

Kiribati, officially the Republic of Kiribati, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the central Pacific Ocean. Its permanent population is over 119,000 as of the 2020 census, with more than half living on Tarawa atoll. The state comprises 32 atolls and one remote raised coral island, Banaba. Its total land area is 811 km2 (313 sq mi) dispersed over 3,441,810 km2 (1,328,890 sq mi) of ocean.

Long Island is a populous island east of Manhattan in southeastern New York state, constituting a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land area. The island extends from New York Harbor 118 miles (190 km) eastward into the North Atlantic Ocean with a maximum north–south width of 23 miles (37 km). With a land area of 1,401 square miles (3,630 km2), it is the largest island in the contiguous United States.

Oceania is a geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Australia is regarded as an island or a continental landmass within that continent. Spanning the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, at the centre of the water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about 9,000,000 square kilometres (3,500,000 sq mi) and a population of around 44.4 million as of 2022. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the second-least populated after Antarctica.

Puerto Rico, officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a self-governing Caribbean archipelago and island organized as an unincorporated territory of the United States under the designation of commonwealth. Located about 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Miami, Florida, between the Dominican Republic in the Greater Antilles and the U.S. Virgin Islands in the Lesser Antilles, it consists of the eponymous main island and numerous smaller islands, including Vieques, Culebra, and Mona. With approximately 3.2 million residents, it is divided into 78 municipalities, of which the most populous is the capital municipality of San Juan. Spanish and English are the official languages of the executive branch of government, though Spanish predominates.

The Pitcairn Islands, officially Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, are a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four islands—Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno—are scattered across several hundred kilometres of ocean and have a combined land area of about 47 square kilometres. Henderson Island accounts for 86% of the land area, but only Pitcairn Island is inhabited. The inhabited islands nearest to the Pitcairn Islands are Mangareva, 688 km to the west, as well as Easter Island, 1,929 km to the east.

Rhode Island is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Island Sound; and shares a small maritime border with New York, east of Long Island. Rhode Island is the smallest U.S. state by area and the seventh-least populous, with slightly fewer than 1.1 million residents as of 2020; but it has grown at every decennial count since 1790 and is the second-most densely populated state, after New Jersey. The state takes its name from the eponymous island, though nearly all its land area is on the mainland. Providence is its capital and most populous city.
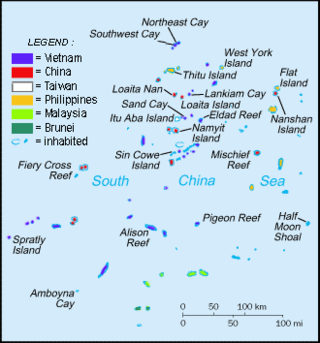
The Spratly Islands are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea. Composed of islands, islets, cays, and more than 100 reefs, sometimes grouped in submerged old atolls, the archipelago lies off the coasts of the Philippines, Malaysia, and southern Vietnam. Named after the 19th-century British whaling captain Richard Spratly who sighted Spratly Island in 1843, the islands contain less than 2 km2 of naturally occurring land area, which is spread over an area of more than 425,000 km2 (164,000 sq mi).

The Statue of Liberty is a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor, within New York City. The copper-clad statue, a gift to the United States from the people of France, was designed by French sculptor Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi and its metal framework was built by Gustave Eiffel. The statue was dedicated on October 28, 1886.

Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest of the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain, and the seventh largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.

Curaçao, officially the Country of Curaçao, is a Lesser Antilles island in the southern Caribbean Sea, specifically the Dutch Caribbean region, about 65 km (40 mi) north of Venezuela. It is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands.

Island Records is a Jamaican multinational record label owned by Universal Music Group. It was founded in 1959 by Chris Blackwell, Graeme Goodall, and Leslie Kong in Jamaica, and was eventually sold to PolyGram in 1989. Island and A&M Records, another label recently acquired by PolyGram, were both at the time the largest independent record labels in history, with Island having exerted a major influence on the progressive music scene in the United Kingdom in the early 1970s. Island Records operates four international divisions: Island US, Island UK, Island Australia, and Island France. Current key people include Island US president Darcus Beese, and MD Jon Turner. Partially due to its significant legacy, Island remains one of UMG's pre-eminent record labels.

Rikers Island is a 413-acre (167.14-hectare) prison island in the East River in the Bronx that contains New York City's largest jail.

The Falkland Islands is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about 300 mi (480 km) east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 mi (1,210 km) from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of 4,700 sq mi (12,000 km2), comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, but the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital and largest settlement is Stanley on East Falkland.

New York, also called New York State, is a state in the Northeastern United States. One of the Mid-Atlantic states, it borders the Atlantic Ocean, New England, Canada, and the Great Lakes. With almost 19.6 million residents, it is the fourth-most populous state in the United States and eighth-most densely populated as of 2023. New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area, with a total area of 54,556 square miles (141,300 km2).

The Faroe or Faeroe Islands, or simply the Faroes, are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. The official language of the country is Faroese, which is closely related to and partially mutually intelligible with Icelandic.



















