
Ophichthidae is a family of fish in the order Anguilliformes, commonly known as the snake eels. The term "Ophichthidae" comes from Greek ophis ("serpent") and ichthys ("fish"). Snake eels are also burrowing eels. They are named for their physical appearance, as they have long, cylindrical, snake-like bodies. This family is found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate waters. They inhabit a wide range of habitats, from coastal shallows and even rivers, to depths below 800 m (2,600 ft). Most species are bottom dwellers, hiding in mud or sand to capture their prey of crustaceans and small fish, but some are pelagic.

The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ophis meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses and others.

Heteroconger is a genus of marine congrid eels. These small, slender garden eels live in groups where each individual has its own burrow. Usually, only the head and front half of the body is visible. The greatest species richness is in the Indo-Pacific, but species are also found in the warmer parts of the Atlantic and the eastern Pacific. Its name relates to how a huge colony of the eels looks swaying in the current.
George Sprague Myers was an American ichthyologist who spent most of his career at Stanford University. He served as the editor of Stanford Ichthyological Bulletin as well as president of the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists. Myers was also head of the Division of Fishes at the United States National Museum, and held a position as an ichthyologist for the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. He was also an advisor in fisheries and ichthyology to the Brazilian Government.

Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders, 20 families, 164 genera, and about 1000 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage and are usually predators.
Scolecenchelys puhioilo is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker in 1979, originally under the genus Muraenichthys. The specific name puhioilo is derived from Hawaiian puhi oilo, which refers to "small eels about as large in diameter as a finger".
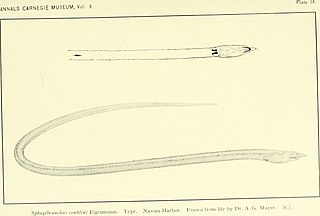
The surf eel, also known as the Finless snake eel in the United States, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Barton Warren Evermann and Millard Caleb Marsh in 1900, originally under the genus Sphagebranchus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, the Bahamas, Florida, USA; Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, northern South America, and St. Helena Island. It dwells at a maximum depth of 35 metres (115 ft), most often between 5 and 15 metres, and forms burrows in sand bottoms in surf areas, from which its common name is derived. Males can reach a maximum total length of 45 centimetres (18 in).
The smiling snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1882, originally under the genus Apterichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, Panama, Ecuador, and Mexico. It dwells at a maximum depth of 30 metres (98 ft), and inhabits sediments of sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 41 centimetres (16 in).
The Oriental worm-eel, also known as the Oriental snake eel, the Oriental sand-eel or the finny sand-eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John McClelland in 1844, originally under the genus Dalophis. It is a tropical, marine and freshwater-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific, including Somalia, South Africa, India, Papua New Guinea, Tahiti, French Polynesia, Indonesia, Oman, Palau, New Caledonia, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, Seychelles, and Vanuatu. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 3 metres, and forms burrows in sand and mud sediments in estuaries, rivers, and inshore turbid waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36 centimetres (14 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 25 centimetres (9.8 in).

The saddled snake-eel, also known commonly as the halfbanded snake-eel, the banded snake eel, or the culverin, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by George Tradescant Lay and Edward Turner Bennett in 1839, originally under the genus Ophisurus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and southeastern Atlantic Ocean, including East and South Africa, the Hawaiian Islands, the Marquesan Islands, the Mangaréva islands, Japan, and Australia. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 70 metres, most often around 0 to 10 metres, and inhabits lagoons and reefs, in which it forms burrows in beds of seagrass and sandy areas. Males can reach a maximum total length of 66 centimetres (2.17 ft).
The longfin spotted snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker and Richard Heinrich Rosenblatt in 1993. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from Mexico, Costa Rica and Panama, in the eastern central Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 44 to 64 metres, and inhabits sandy substrates. Males can reach a maximum total length of 51 centimetres.
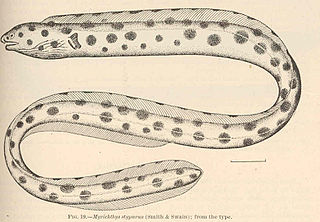
The magnificent snake eel, also known as the Hawaiian spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Conrad Abbott in 1860, originally under the genus Pisodonophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including the Hawaiian Islands, the Leeward Islands, Johnston Island, and Midway Atoll. It dwells at a depth range of 1 to 262 metres, and inhabits crevices, sand and rocks. Males can reach a maximum total length of 78 centimetres (31 in).

The goldspotted eel, also known as the goldspotted snake eel or the dark-spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1825, originally under the genus Muraenophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, southern Florida, USA; the Bahamas, Santa Catarina, and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 15 metres (49 ft), and inhabits rocky and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 110 centimetres (3.6 ft).

The highfin snake eel (Ophichthus altipennis, also known as the blackfin snake eel or the black-finned snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Microdonophis. It is a marine, tropical eel known from the eastern Indian Ocean and northwestern and western central Pacific Ocean, including Australia, French Polynesia, Indonesia, Japan, the Marshall Islands, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 40 m, and forms burrows in soft inshore sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 103 cm.

Ophichthus fowleri, also known as the Fowler's snake eel is a species of eel in the family Ophichthidae. It is a marine eel which is known from the eastern Central Pacific in Hawaii.
Ophichthus ophis, the spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, originally under the genus Muraena. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda and southern Florida, USA, Brazil, Lesser Antilles, Senegal, Angola, and the Mediterranean. It dwells at a depth range of 21 to 50 metres, usually at around 50 m, and lives in burrows on a permanent basis. Males can reach a maximum total length of 210 centimeters (83 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 100 centimeters (39 in).
The ornate snake eel, also known as the sea snake in St. Helena is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John Richardson in 1848, originally under the genus Ophisurus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Mauritania, St. Helena, and Ascension Island. It inhabits the continental shelf, where it forms burrows in sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 90 centimetres (35 in).

The punctuated snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1837, originally under the genus Ophisurus. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Nicaragua, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Peru, and Panama. It dwells at a depth range of 15 to 277 metres, and inhabits sand and mud sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 85 centimetres (33 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 60 centimetres (24 in).

The Pacific snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Muraenopsis. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including California, USA, Peru, the Gulf of California, Mexico, the Galapagos Islands, Colombia, Ecuador, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Honduras, Guatemala, Nicaragua, and Panama. It dwells at a maximum depth of 155 metres (509 ft), and forms burrows in mud and sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 115 centimetres (45 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 80 centimetres (31 in).
Herpetoichthys fossatus, the mustachioed snake-eel, is a species of eel in the family Ophichthidae. It is found in the Gulf of California.











