
The wildcat is a species complex comprising two small wild cat species: the European wildcat and the African wildcat. The European wildcat inhabits forests in Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus, while the African wildcat inhabits semi-arid landscapes and steppes in Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Central Asia, into western India and western China. The wildcat species differ in fur pattern, tail, and size: the European wildcat has long fur and a bushy tail with a rounded tip; the smaller African wildcat is more faintly striped, has short sandy-gray fur and a tapering tail; the Asiatic wildcat is spotted.

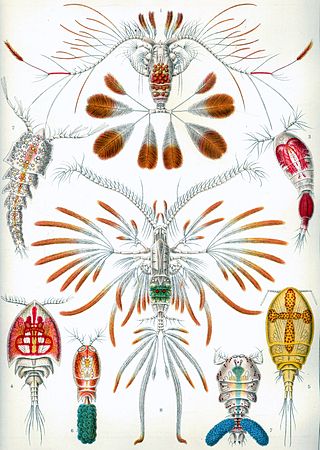
Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. There are 40 recognised families:

The steppe polecat, also known as the white or masked polecat, is a species of mustelid native to Central and Eastern Europe and Central Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List because of its wide distribution, occurrence in a number of protected areas, and tolerance to some degree of habitat modification. It is generally of a very light yellowish colour, with dark limbs and a dark mask across the face. Compared to its relative, the European polecat, the steppe polecat is larger in size and has a more powerfully built skull.

The beech marten, also known as the stone marten, house marten or white breasted marten, is a species of marten native to much of Europe and Central Asia, though it has established a feral population in North America. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List on account of its wide distribution, its large population, and its presence in a number of protected areas. It is superficially similar to the European pine marten, but differs from it by its smaller size and habitat preferences. While the pine marten is a forest specialist, the beech marten is a more generalist and adaptable species, occurring in a number of open and forest habitats.

The yellow-throated marten is a marten species native to Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List due to its wide distribution, evidently relatively stable population, occurrence in a number of protected areas, and lack of major threats.

George Stewardson Brady was a professor of natural history at the Hancock Museum in Newcastle-upon-Tyne who did important volumes on Copepoda and Ostracoda, including those from the Challenger expedition.

Göytəpə — is a city and the most populous municipality, except for the capital Cəlilabad, in the Jalilabad Rayon of Azerbaijan. It has a population of 15,500. Renamed in 1992, 'Göytəpə' in Azeri means "Blue Hill."
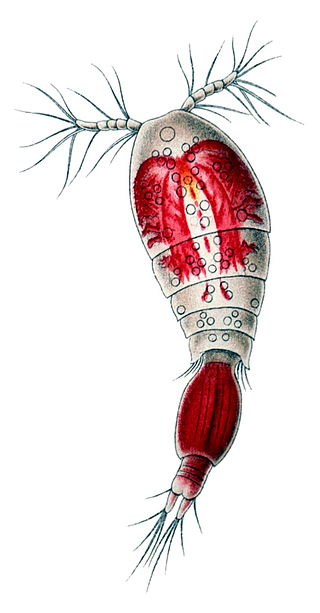
Oncaea is a genus of copepods. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Unlike other bioluminescent copepods, Oncaea have an internal (non-secreted) bioluminescence. Oncaea contains the following species:

The Asian badger, also known as the sand badger, is a species of badger native to Mongolia, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, the Korean Peninsula and Russia.

Wilhelm Giesbrecht (1854–1913) was a Prussian zoologist, specialising in copepods, during the "golden age of copepodology".
Centropagidae is a family of copepods in the order Calanoida. Its members are particularly known as plankton in coastal waters and in fresh water in Australia and southern South America. They are also found on subantarctic islands and in lakes in Antarctica.
Phaennidae is a family of planktonic copepods, found in pelagic or benthopelagic waters. It contains the following genera:

Euaugaptilus is a genus of copepods. The genus contains bioluminescent species.
Augaptilidae is a family of copepods.

Mormonillidae is a family of planktonic marine copepods, the only member of the order Mormonilloida. There are five known species in two genera:
Artotrogidae is a family of copepods in the order Siphonostomatoida.

The clade Multicrustacea constitutes the largest superclass of crustaceans, containing approximately four-fifths of all described crustacean species, including crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, barnacles, copepods, amphipods, mantis shrimp and others. The largest branch of multicrustacea is the class Malacostraca.
Aetideidae is a family of copepods belonging to the order Calanoida.
Clausocalanidae is a family of copepods belonging to the order Calanoida.
Hyalopontius is a genus of crustaceans belonging to the monotypic family Megapontiidae.













