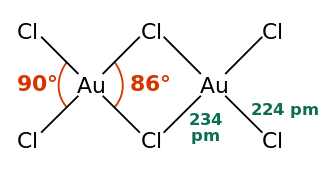Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula FeCl3(H2O)x. Also called ferric chloride, these compounds are some of the most important and commonplace compounds of iron. They are available both in anhydrous and in hydrated forms, which are both hygroscopic. They feature iron in its +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous derivative is a Lewis acid, while all forms are mild oxidizing agents. It is used as a water cleaner and as an etchant for metals.

Copper(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuSO4. It forms hydrates CuSO4·nH2O, where n can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (n = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate, while its anhydrous form is white. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper, and Roman vitriol. It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The Cu(II)(H2O)4 centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains.

Zinc chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula ZnCl2·nH2O, with n ranging from 0 to 4.5, forming hydrates. Zinc chloride, anhydrous and its hydrates, are colorless or white crystalline solids, and are highly soluble in water. Five hydrates of zinc chloride are known, as well as four polymorphs of anhydrous zinc chloride.

In chemistry, hypochlorite, or chloroxide is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite. The Cl-O distance in ClO− is 1.69 Å.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms a hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour.

Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. It is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.
Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.

Acetyl chloride is an acyl chloride derived from acetic acid. It belongs to the class of organic compounds called acid halides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid. Its formula is commonly abbreviated to AcCl.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and the hemipentahydrate CdCl2•2.5H2O.
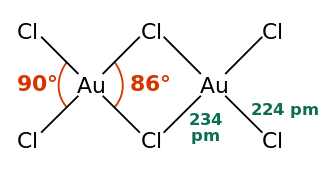
Gold(III) chloride, traditionally called auric chloride, is an inorganic compound of gold and chlorine with the molecular formula Au2Cl6. The "III" in the name indicates that the gold has an oxidation state of +3, typical for many gold compounds. It has two forms, the monohydrate (AuCl3·H2O) and the anhydrous form, which are both hygroscopic and light-sensitive solids. This compound is a dimer of AuCl3. This compound has a few uses, such as an oxidizing agent and for catalyzing various organic reactions.

Terbium(III,IV) oxide, occasionally called tetraterbium heptaoxide, has the formula Tb4O7, though some texts refer to it as TbO1.75. There is some debate as to whether it is a discrete compound, or simply one phase in an interstitial oxide system. Tb4O7 is one of the main commercial terbium compounds, and the only such product containing at least some Tb(IV) (terbium in the +4 oxidation state), along with the more stable Tb(III). It is produced by heating the metal oxalate, and it is used in the preparation of other terbium compounds. It is also used in Electronics and Data Storage, Green Energy Technologies, Medical Imaging and Diagnosis, and Chemical Processes. Terbium forms three other major oxides: Tb2O3, TbO2, and Tb6O11.
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran (THF) by replacement of the methylene group (CH2) at the 2-position with an oxygen atom. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals.

Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine compound with the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It is a haloacetic acid, with all three of the acetyl group's hydrogen atoms replaced by fluorine atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a vinegar-like odor. TFA is a stronger acid than acetic acid, having an acid ionisation constant, Ka, that is approximately 34,000 times higher, as the highly electronegative fluorine atoms and consequent electron-withdrawing nature of the trifluoromethyl group weakens the oxygen-hydrogen bond (allowing for greater acidity) and stabilises the anionic conjugate base. TFA is commonly used in organic chemistry for various purposes.

Cobalt(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula (CoF2). It is a pink crystalline solid compound which is antiferromagnetic at low temperatures (TN=37.7 K) The formula is given for both the red tetragonal crystal, (CoF2), and the tetrahydrate red orthogonal crystal, (CoF2·4H2O). CoF2 is used in oxygen-sensitive fields, namely metal production. In low concentrations, it has public health uses. CoF2 is sparingly soluble in water. The compound can be dissolved in warm mineral acid, and will decompose in boiling water. Yet the hydrate is water-soluble, especially the di-hydrate CoF2·2H2O and tri-hydrate CoF2·3H2O forms of the compound. The hydrate will also decompose with heat.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2. It is an amber oily liquid.
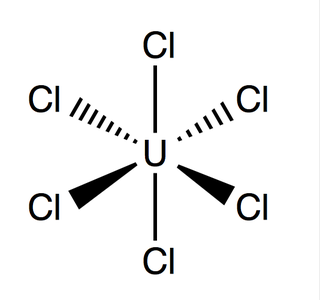
Uranium hexachloride is an inorganic chemical compound of uranium in the +6 oxidation state. UCl6 is a metal halide composed of uranium and chlorine. It is a multi-luminescent dark green crystalline solid with a vapor pressure between 1-3 mmHg at 373.15 K. UCl6 is stable in a vacuum, dry air, nitrogen and helium at room temperature. It is soluble in carbon tetrachloride. Compared to the other uranium halides, little is known about UCl6.

1,1,1,2,2,3,3-Heptachloropropane is a compound of chlorine, hydrogen, and carbon. Its linear formula is C2Cl5CHCl2.

Neodymium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and neodymium the formula NdBr3. The anhydrous compound is an off-white to pale green solid at room temperature, with an orthorhombic PuBr3-type crystal structure. The material is hygroscopic and forms a hexahydrate in water (NdBr3· 6H2O), similar to the related neodymium(III) chloride.