
Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.
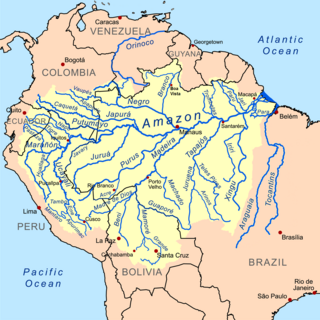
The Amazon Basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about 6,300,000 km2 (2,400,000 sq mi), or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana (France), Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.

The iridescent shark is a species of shark catfish native to the rivers of Southeast Asia. Despite its name, it is not a shark. It is found in the Mekong basin as well as the Chao Phraya River, and is heavily cultivated for food there.

Hypostomus plecostomus, also known as the suckermouth catfish or the common pleco, is a tropical fish belonging to the armored catfish family (Loricariidae), named for the armor-like longitudinal rows of scutes that cover the upper parts of the head and body. Although the name Hypostomus plecostomus is often used to refer to common plecostomus sold in aquarium shops, most are actually members of other genera.

Loricariidae is the largest family of catfish, with 92 genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South America. These fish are noted for the bony plates covering their bodies and their suckermouths. Several genera are sold as "plecos", notably the suckermouth catfish, Hypostomus plecostomus, and are popular as aquarium fish.

The walking catfish is a species of freshwater airbreathing catfish native to Southeast Asia. It is named for its ability to "walk" and wiggle across dry land, to find food or suitable environments. While truly, it does not walk as most bipeds or quadrupeds do, it has the ability to use its pectoral fins to keep it upright as it makes a wiggling motion with snakelike movements to traverse land. This fish normally lives in slow-moving and often stagnant waters in ponds, swamps, streams, and rivers, as well as in flooded rice paddies, or temporary pools that may dry up. When this happens, its "walking" skill allows the fish to move to other aquatic environments. Considerable taxonomic confusion surrounds this species and it has frequently been confused with other close relatives. One main distinction between the walking catfish and the native North American ictalurid catfish with which it sometimes is confused, is that the walking catfish lacks an adipose fin.

The blue catfish is the largest species of North American catfish, reaching a length of 165 cm (65 in) and a weight of 68 kg (150 lb). The typical length is about 25–46 in (64–117 cm). The fish can live to 20 years. The native distribution of blue catfish is primarily in the Mississippi River drainage, including the Missouri, Ohio, Tennessee, and Arkansas Rivers, The Des Moines River in South Central Iowa, and the Rio Grande, and south along the Gulf Coast to Belize and Guatemala. These large catfish have also been introduced in a number of reservoirs and rivers, notably the Santee Cooper lakes of Lake Marion and Lake Moultrie in South Carolina, the James River in Virginia, Powerton Lake in Pekin, Illinois, and Lake Springfield in Springfield, Illinois. This fish is also found in some lakes in Florida. The fish is considered an invasive pest in some areas, particularly the Chesapeake Bay. Blue catfish can tolerate brackish water, thus can colonize along inland waterways of coastal regions.

Clarias is a genus of catfishes of the family Clariidae, the airbreathing catfishes. The name is derived from the Greek chlaros, which means lively, in reference to the ability of the fish to live for a long time out of water.

The Ariidae or ariid catfish are a family of catfish that mainly live in marine waters with many freshwater and brackish water species. They are found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate zones. The family includes about 143 species.

Callichthys callichthys, the cascarudo, armored catfish, bubblenest catfish, hassar, or mailed catfish, is a subtropical freshwater fish belonging to the subfamily Callichthyinae of the family Callichthyidae.

Sturisoma is a genus of armored catfishes native to Central and South America.

Arius is a genus of catfishes of the family Ariidae. The genus Arius is distributed in brackish and fresh waters of Eastern Africa and south to Southeast Asia.

Clarias gariepinus or African sharptooth catfish is a species of catfish of the family Clariidae, the airbreathing catfishes.

Cavefish or cave fish is a generic term for fresh and brackish water fish adapted to life in caves and other underground habitats. Related terms are subterranean fish, troglomorphic fish, troglobitic fish, stygobitic fish, phreatic fish and hypogean fish.

Hemiarius is a genus of sea catfishes found in the coastal waters, estuaries, and rivers from South Asia through New Guinea and Australia to Oceania. Four described species are in this genus:
The Bressou sea catfish, also called the marine catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840, originally under the genus Arius. It inhabits tropical marine, brackish and freshwater on the Atlantic coast of South America, ranging from Guyana to Brazil. It reaches a maximum total length of 50 cm (20 in), but more commonly reaches a TL of 30 cm (12 in).
Chinchaysuyoa labiata is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was first described under the genus Arius as Arius labiatus in 1898. Another fish species, Hexanematichthys henni, was described by Homer Glenn Fisher and Carl H. Eigenmann in 1922 but is now considered to be a junior synonym for A. labiatus. A study in 2019 found that A. labiatus was distinct from any other catfish species in the region, and thus constructed the genus Chinchaysuyoa for it and the recently discovered species C. ortegai. It is endemic to freshwater bodies in Ecuador.

The Sagor catfish, also called the Sagor sea catfish, the Sunda sea-catfish, the Marine catfish or the Dusky catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton in 1822, originally under the genus Pimelodus. It inhabits estuaries and freshwater bodies in numerous areas of the Indo-Western Pacific ocean. It reaches a maximum total length of 45 cm (18 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 30 cm (12 in).
Chinchaysuyoa ortegai is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It is endemic to freshwater bodies in northern Peru. Specimens of this species were formerly classified as Hexanematichthys henni until they were found to actually represent a new species in the genus Chinchaysuyoa.















