
Crates of Thebes was a Greek Cynic philosopher, the principal pupil of Diogenes of Sinope and the husband of Hipparchia of Maroneia who lived in the same manner as him. Crates gave away his money to live a life of poverty on the streets of Athens. Respected by the people of Athens, he is remembered for being the teacher of Zeno of Citium, the founder of Stoicism. Various fragments of Crates' teachings survive, including his description of the ideal Cynic state.
Grayling or Greyling may refer to:

The grayling or rock grayling is a species in the brush-footed butterfly family Nymphalidae. Although found all over Europe, the grayling mostly inhabits coastal areas, with inland populations declining significantly in recent years. The grayling lives in dry and warm habitats with easy access to the sun, which helps them with body temperature regulation.

Hipparchia of Maroneia was a Cynic philosopher, and wife of Crates of Thebes. She was the sister of Metrokles, the cynic philosopher. She was born in Maroneia, but her family moved to Athens, where Hipparchia came into contact with Crates, the most famous Cynic philosopher in Greece at that time. She fell in love with him, and, despite the disapproval of her parents, she married him. She went on to live a life of Cynic poverty on the streets of Athens with her husband.

Hipparchia is a genus of butterflies within the family Nymphalidae. The genus was erected by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1807.
Theodorus "the Atheist", of Cyrene, was a Greek philosopher of the Cyrenaic school. He lived in both Greece and Alexandria, before ending his days in his native city of Cyrene. As a Cyrenaic philosopher, he taught that the goal of life was to obtain joy and avoid grief, and that the former resulted from knowledge, and the latter from ignorance. However, his principal claim to fame was his alleged atheism. He was usually designated by ancient writers ho atheos, "the atheist."

Hipparchia fagi, the woodland grayling, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae.

Hipparchia statilinus, the tree grayling, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae.

Hipparchia hansii is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is endemic to the North African region, mainly Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and western Libya. Its natural habitats are dense soil, grazed and rocky slopes, and ridges. It prefers to stay in the shade. This is one of the last butterflies that flies in the season.

Hipparchia syriaca is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Greece especially on the island of Samos, Turkey, Bulgaria, Albania, North Macedonia, Caucasus and Transcaucasia. It is found on the edges of foothills and mountain forests up to 2,000 m
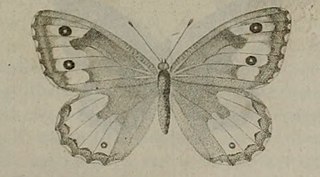
Hipparchia aristaeus, the southern grayling, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It was described by Franco Andrea Bonelli in 1826. It is found in North Africa, southern Europe and Asia Minor. The habitat consists of hot dry rocky areas.

Hipparchia genava, the lesser rock grayling, is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae.










