
Franz Steindachner was an Austrian zoologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. He published over 200 papers on fishes and over 50 papers on reptiles and amphibians. Steindachner described hundreds of new species of fish and dozens of new amphibians and reptiles. At least seven species of reptile have been named after him.

The Mormyridae, sometimes called "elephantfish", are a superfamily of weakly electric fish in the order Osteoglossiformes native to Africa. It is by far the largest family in the order, with around 200 species. Members of the family can be popular, if challenging, aquarium species. These fish have a large brain size and unusually high intelligence.

The blunt-jawed elephantnose or wormjawed mormyrid is a species of elephantfish. It is found in rivers in West and Middle Africa. It is brown or black with a long elephant-like snout with the mouth located near the tip. Its diet consists of worms, fish, and insects.

Gnathonemus is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Mormyridae, the elephantfishes. The fishes in this genus are found in subsaharan Africa.

Marcusenius is a genus of the elephantfish group native to Africa. Its members are highly diverse in size, with the smallest species reaching less than 15 cm (6 in) and the largest more than 1 m (3.3 ft).

Mormyrus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Mormyridae. They are weakly electric, enabling them to navigate, to find their prey, and to communicate with other electric fish.
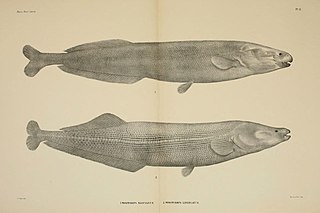
Mormyrops is a genus of weakly electric fish in the family Mormyridae from freshwater in Africa. They are characterized by an elongate head measuring twice as long as high, and no teeth on the palate or the tongue. The genus includes the largest member of the mormyrid family, the cornish jack at up to 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length.

The subfamily Mormyrinae contains all but one of the genera of the African freshwater fish family Mormyridae in the order Osteoglossiformes. They are often called elephantfish due to a long protrusion below their mouths used to detect buried invertebrates that is suggestive of a tusk or trunk. They can also be called tapirfish.

Boulengeromyrus is a monospecific genus of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Mormyridae, the elephantfishes. The only species in the genus is Knoepffler's elephantfish. It occurs only in the Ivindo River and the Ntem River basins of Gabon and Cameroon. It reaches a maximum length of about 41 cm (16 in).
Brienomyrus is a genus of small elephantfish in the family Mormyridae from Africa. Usually available in the pet trade, these fish are commercially referred to as baby whales or baby whalefish.

Campylomormyrus is a genus of elephantfish in the family Mormyridae.

Cyphomyrus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Mormyridae, the freshwater elephantfishes.

Heteromormyrus is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Mormyridae, the elephantfishes. These fishes are found in southern and central Africa in Angola, Namibia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and, maybe, Zimbabwe.

Ivindomyrus is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Mormyridae, the elephantfishes. These fishes are found in rivers in Middle Africa.

Myomyrus is a genus of elephantfish in the family Mormyridae. Its members reach about 25–30 cm (10–12 in) in length and are restricted to the Congo River Basin in Africa.

Paramormyrops is a genus of elephantfish in the family Mormyridae from Africa.
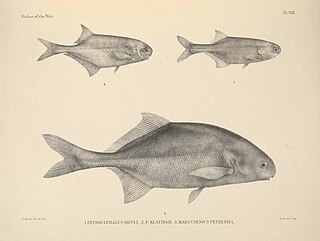
Petrocephalus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Mormyridae. All the fish species of this genus are endemic to Africa.

Stomatorhinus is a genus of small elephantfish in the family Mormyridae.

Cryptomyrus is a genus of mormyrid fish native to Gabon.

The Mormyroidea are a superfamily of fresh water fishes endemic to Africa that, together with the families Hiodontidae, Osteoglossidae, Pantodontidae and Notopteridae, represents one of the main groups of living Osteoglossiformes. They stand out for their use of weak electric fields, which they use to orient themselves, reproduce, feed, and communicate.




















