
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 34 weeks, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies or premmies. Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be.

Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus.
HELLP syndrome is a complication of pregnancy; the acronym stands for hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. It usually begins during the last three months of pregnancy or shortly after childbirth. Symptoms may include feeling tired, retaining fluid, headache, nausea, upper right abdominal pain, blurry vision, nosebleeds, and seizures. Complications may include disseminated intravascular coagulation, placental abruption, and kidney failure.
Oligohydramnios is a medical condition in pregnancy characterized by a deficiency of amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds the fetus in the abdomen, in the amniotic sac. It is typically diagnosed by ultrasound when the amniotic fluid index (AFI) measures less than 5 cm or when the single deepest pocket (SDP) of amniotic fluid measures less than 2 cm. Amniotic fluid is necessary to allow for normal fetal movement, lung development, and cushioning from uterine compression. Low amniotic fluid can be attributed to a maternal, fetal, placental or idiopathic cause and can result in poor fetal outcomes including death. The prognosis of the fetus is dependent on the etiology, gestational age at diagnosis, and the severity of the oligohydramnios.
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method, if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization, or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using this measure of pregnancy is largely due to convenience: menstruation is usually noticed, while there is generally no convenient way to discern when fertilization or implantation occurred.
Bishop score, also Bishop's score or cervix score, is a pre-labor scoring system to assist in predicting whether induction of labor will be required. It has also been used to assess the likelihood of spontaneous preterm delivery. The Bishop score was developed by Professor Emeritus of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Dr. Edward Bishop, and was first published in August 1964.
Fetal fibronectin (fFN) is a fibronectin protein produced by fetal cells. It is found at the interface of the chorion and the decidua. Fetal fibronectin is found normally in vaginal fluid in early pregnancy prior to 22 weeks due to normal growth and development of tissues at the junction of the uterus and amniotic sac. It may also be found in vaginal fluid after 36 weeks as labor approaches. However, fFN should not be detected between 22 and 36 weeks.

Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labor. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis.

Fetal surgery also known as antenatal surgery, prenatal surgery, is a growing branch of maternal-fetal medicine that covers any of a broad range of surgical techniques that are used to treat congenital abnormalities in fetuses who are still in the pregnant uterus. There are three main types: open fetal surgery, which involves completely opening the uterus to operate on the fetus; minimally invasive fetoscopic surgery, which uses small incisions and is guided by fetoscopy and sonography; and percutaneous fetal therapy, which involves placing a catheter under continuous ultrasound guidance.
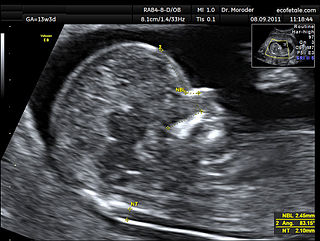
A nuchal scan or nuchal translucency (NT) scan/procedure is a sonographic prenatal screening scan (ultrasound) to detect chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus, though altered extracellular matrix composition and limited lymphatic drainage can also be detected.

A bicornuate uterus or bicornate uterus, is a type of mullerian anomaly in the human uterus, where there is a deep indentation at the fundus (top) of the uterus.

The arcuate uterus is a form of a uterine anomaly or variation where the uterine cavity displays a concave contour towards the fundus. Normally the uterine cavity is straight or convex towards the fundus on anterior-posterior imaging, but in the arcuate uterus the myometrium of the fundus dips into the cavity and may form a small septation. The distinction between an arcuate uterus and a septate uterus is not standardized.
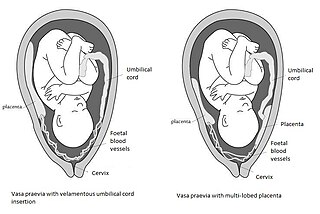
Vasa praevia is a condition in which fetal blood vessels cross or run near the internal opening of the uterus. These vessels are at risk of rupture when the supporting membranes rupture, as they are unsupported by the umbilical cord or placental tissue.

Kyprianos "Kypros" Nicolaides is a Greek Cypriot physician of British citizenship, Professor of Fetal Medicine at King's College Hospital, London. He is one of the pioneers of fetal medicine and his discoveries have revolutionised the field. He was elected to the US National Academy of Medicine in 2020 for 'improving the care of pregnant women worldwide with pioneering rigorous and creative approaches, and making seminal contributions to prenatal diagnosis and every major obstetrical disorder'. This is considered to be one of the highest honours in the fields of health and medicine and recognises individuals who have demonstrated outstanding professional achievement and commitment to service.
Stuart Campbell DSc FRCPEd FRCOG FACOG, was born in Glasgow, Scotland, and graduated from the medical school of Glasgow University. During his training he worked with Ian Donald, who had published some of the first papers on the use of ultrasound in obstetrics.

In enzymology, an amidase (EC 3.5.1.4, acylamidase, acylase (misleading), amidohydrolase (ambiguous), deaminase (ambiguous), fatty acylamidase, N-acetylaminohydrolase (ambiguous)) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide. In this way, the two substrates of this enzyme are an amide and H2O, whereas its two products are monocarboxylate and NH3.

Velamentous cord insertion is a complication of pregnancy where the umbilical cord is inserted in the fetal membranes. It is a major cause of antepartum hemorrhage that leads to loss of fetal blood and associated with high perinatal mortality. In normal pregnancies, the umbilical cord inserts into the middle of the placental mass and is completely encased by the amniotic sac. The vessels are hence normally protected by Wharton's jelly, which prevents rupture during pregnancy and labor. In velamentous cord insertion, the vessels of the umbilical cord are improperly inserted in the chorioamniotic membrane, and hence the vessels traverse between the amnion and the chorion towards the placenta. Without Wharton's jelly protecting the vessels, the exposed vessels are susceptible to compression and rupture.
Fetal echocardiography, or Fetal echocardiogram, is the name of the test used to diagnose cardiac conditions in the fetal stage. Cardiac defects are amongst the most common birth defects. Their diagnosis is important in the fetal stage as it might help provide an opportunity to plan and manage the baby as and when the baby is born. Not all pregnancies need to undergo fetal echo.

Monoamniotic twins are identical or semi-identical twins that share the same amniotic sac within their mother's uterus. Monoamniotic twins are always monochorionic and are usually termed Monoamniotic-Monochorionic twins. They share the placenta, but have two separate umbilical cords. Monoamniotic twins develop when an embryo does not split until after formation of the amniotic sac, at about 9–13 days after fertilization. Monoamniotic triplets or other monoamniotic multiples are possible, but extremely rare. Other obscure possibilities include multiples sets where monoamniotic twins are part of a larger gestation such as triplets, quadruplets, or more.
Placental alpha microglobulin-1 (PAMG-1) is a human protein that was first isolated in 1975 from amniotic fluid. PAMG-1 is an important biomarker for the detection of premature rupture of fetal membrane (PROM) The high concentration of PAMG-1 in amniotic fluid means it can be used to detect if this fluid is present in the cervico-vaginal discharge of pregnant women; the presence of PAMG-1 in the discharge suggests that amniotic fluid is present, and therefore suggests that PROM has occurred. PAMG-1 was originally referred to as specific alpha-1 globulin of placenta.












