
The Canadian Space Agency is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the Canadian Space Agency Act.
The David Florida Laboratory is the Canadian Space Agency's spacecraft assembly, integration and testing centre, in Shirleys Bay, just west of central Ottawa. It is operated by the Canadian Space Agency and rented out to Canadian and foreign aerospace and telecommunications companies and organizations for qualifying space bound equipment such as communication or scientific satellites, or components made to be placed on satellites or installed in a space station. The laboratory was named to honour C. David Florida, a leading Canadian pioneer in space research.

Cascade, Smallsat and Ionospheric Polar Explorer (CASSIOPE), is a Canadian Space Agency (CSA) multi-mission satellite operated by the University of Calgary. The mission development and operations from launch to February 2018 was funded through CSA and the Technology Partnerships Canada program. In February 2018 CASSIOPE became part of the European Space Agency's Swarm constellation through the Third Party Mission Program, known as Swarm Echo, or Swarm-E. It was launched September 29, 2013, on the first flight of the SpaceX Falcon 9 v1.1 launch vehicle. CASSIOPE is the first Canadian hybrid satellite to carry a dual mission in the fields of telecommunications and scientific research. The main objectives are to gather information to better understand the science of space weather, while verifying high-speed communications concepts through the use of advanced space technologies.

IMAGE was a NASA Medium Explorer mission that studied the global response of the Earth's magnetosphere to changes in the solar wind. It was believed lost but as of August 2018 might be recoverable. It was launched 25 March 2000, at 20:34:43.929 UTC, by a Delta II launch vehicle from Vandenberg Air Force Base on a two-year mission. Almost six years later, it unexpectedly ceased operations in December 2005 during its extended mission and was declared lost. The spacecraft was part of NASA's Sun-Earth Connections Program, and its data has been used in over 400 research articles published in peer-reviewed journals. It had special cameras that provided various breakthroughs in understanding the dynamics of plasma around the Earth. The principal investigator was Jim Burch of the Southwest Research Institute.
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd, or SSTL, is a company involved in the manufacture and operation of small satellites. A spin-off company of the University of Surrey, it is presently wholly owned by Airbus Defence and Space.

NOAA-19, known as NOAA-N' before launch, is the last of the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) series of weather satellites. NOAA-19 was launched on 6 February 2009. NOAA-19 is in an afternoon Sun-synchronous orbit and is intended to replace NOAA-18 as the prime afternoon spacecraft.
SPAR Aerospace was a Canadian aerospace company. It produced equipment for the Canadian Space Agency to be used in cooperation with NASA's Space Shuttle program, most notably the Canadarm, a remote manipulator system.
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services.
The Canadian Advanced Nanospace eXperiment (CanX) program is a Canadian CubeSat nanosatellite program operated by the University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies, Space Flight Laboratory (UTIAS/SFL). The program's objectives are to involve graduate students in the process of spaceflight development, and to provide low-cost access to space for scientific research and the testing of nanoscale devices. The CanX projects include CanX-1, CanX-2, the BRIght Target Explorer (BRITE), and CanX-4&5.

The Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) is the latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites. JPSS will provide the global environmental data used in numerical weather prediction models for forecasts, and scientific data used for climate monitoring. JPSS will aid in fulfilling the mission of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an agency of the Department of Commerce. Data and imagery obtained from the JPSS will increase timeliness and accuracy of public warnings and forecasts of climate and weather events, thus reducing the potential loss of human life and property and advancing the national economy. The JPSS is developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), who is responsible for operation of JPSS. Three to five satellites are planned for the JPSS constellation of satellites. JPSS satellites will be flown, and the scientific data from JPSS will be processed, by the JPSS – Common Ground System (JPSS-CGS).

GOES-16, formerly known as GOES-R before reaching geostationary orbit, is the first of the GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) operated by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). GOES-16 serves as the operational geostationary weather satellite in the GOES East position at 75.2°W, providing a view centered on the Americas. GOES-16 provides high spatial and temporal resolution imagery of the Earth through 16 spectral bands at visible and infrared wavelengths using its Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI). GOES-16's Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) is the first operational lightning mapper flown in geostationary orbit. The spacecraft also includes four other scientific instruments for monitoring space weather and the Sun.
Teledyne e2v is a manufacturer with its headquarters in England, that designs, develops and manufactures systems and components in healthcare, life sciences, space, transportation, defence and security and industrial markets. The company was previously known as English Electric Valve Company and for a short time Marconi Applied Technologies. e2v was acquired by US company Teledyne Technologies in March 2017.
Sapphire is a Canadian space surveillance satellite which was launched in 2013. Sapphire was commissioned and integrated by MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates (MDA) based on an SSTL-150 bus produced by Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL) and an optical payload produced by COM DEV International.
Dr. Robert E. Huffman (1931–2008) was an American space scientist and author. He specialized in ultraviolet spectroscopy in the earth's upper atmosphere. Working for the United States Air Force, Dr. Huffman managed the Horizon Ultraviolet Program (HUP) experiments on two Space Shuttle flights: Columbia and Discovery.

exactEarth Ltd is a Canadian company that specializes in data services that deliver real-time global location-based maritime vessel tracking information utilizing patented satellite AIS detection technology.
Haiyang is a series of marine remote sensing satellites developed and operated by the People's Republic of China since 2002. The name "Haiyang" translates to "ocean" in English. As of October 2022, eight satellites have been launched with ten more planned. Built by the state-owned aerospace contractor China Academy of Space Technology (CAST), Haiyang satellites carry a variety of ocean-imaging sensor payloads and are operated by the National Satellite Ocean Application Service (NSOAS), a subordinate agency of the State Oceanic Administration (SOA). Haiyang satellites are launched from Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center (TSLC) into Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO) aboard Long March-series rockets.
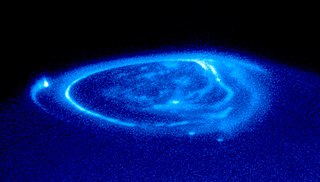
UVS, known as the Ultraviolet Spectrograph or Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrometer is the name of an instrument on the Juno orbiter for Jupiter. The instrument is an imaging spectrometer that observes the ultraviolet range of light wavelengths, which is shorter wavelengths than visible light but longer than X-rays. Specifically, it is focused on making remote observations of the aurora, detecting the emissions of gases such as hydrogen in the far-ultraviolet. UVS will observes light from as short a wavelength as 70 nm up to 200 nm, which is in the extreme and far ultraviolet range of light. The source of aurora emissions of Jupiter is one of the goals of the instrument. UVS is one of many instruments on Juno, but it is in particular designed to operate in conjunction with JADE, which observes high-energy particles. With both instruments operating together, both the UV emissions and high-energy particles at the same place and time can be synthesized. This supports the Goal of determining the source of the Jovian magnetic field. There has been a problem understanding the Jovian aurora, ever since Chandra determined X-rays were coming not from, as it was thought Io's orbit but from the polar regions. Every 45 minutes an X-ray hot-spot pulsates, corroborated by a similar previous detection in radio emissions by Galileo and Cassini spacecraft. One theory is that its related to the solar wind. The mystery is not that there are X-rays coming Jupiter, which has been known for decades, as detected by previous X-ray observatories, but rather why with the Chandra observation, that pulse was coming from the north polar region.

NOAA-21, designated JPSS-2 prior to launch, is the second satellite in National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s latest series of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites, known as the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS). Launched on November 10, 2022, along with LOFTID, NOAA-21 now operates in the same orbit as NOAA-20 and Suomi NPP. It travels in a polar orbit, crossing the equator approximately 14 times a daily, and provides complete global coverage twice a day.

EQUULEUS is a nanosatellite of the 6U CubeSat format that will measure the distribution of plasma that surrounds the Earth (plasmasphere) to help scientists understand the radiation environment in that region. It will also demonstrate low-thrust trajectory control techniques, such as multiple lunar flybys, within the Earth-Moon region using water steam as propellant. The spacecraft was designed and developed jointly by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the University of Tokyo.

NOAA-20, designated JPSS-1 prior to launch, is the first of the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites called the Joint Polar Satellite System. NOAA-20 was launched on 18 November 2017 and joined the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite in the same orbit. NOAA-20 operates about 50 minutes behind Suomi NPP, allowing important overlap in observational coverage. Circling the Earth from pole-to-pole, it crosses the equator about 14 times daily, providing full global coverage twice a day. This gives meteorologists information on "atmospheric temperature and moisture, clouds, sea-surface temperature, ocean color, sea ice cover, volcanic ash, and fire detection" so as to enhance weather forecasting including hurricane tracking, post-hurricane recovery by detailing storm damage and mapping of power outages.











