Tieling is one of 14 prefecture-level cities in Liaoning province of the People's Republic of China. Tieling is a city where coal mining is an important industry.

Xiangshui County is a coastal county under the administration of Yancheng, Jiangsu province, China. The northernmost county-level division of Yancheng, it borders the prefecture-level cities of Lianyungang to the northwest and Huai'an to the southwest. The county was founded in April 1966.

Qiaokou District forms part of the urban core of and is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China, situated on the northern (left) bank of the Han River. Along with Dongxihu, it is the only district of Wuhan to not have any shoreline along the Yangtze River, and it borders Dongxihu to the north, Jianghan to the east, and Hanyang to the south across the Han River. 'Qiaokou' is used as an example of the usage of the rarely used character 礄/硚 in the Contemporary Chinese Dictionary. It is said that the character 'qiao' refers to stone bridges constructed over the Han River in the Late Qing. The district is part of the historical Hankou.

Hanchuan is a county-level city in east-central Hubei province, People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of Xiaogan prefecture-level city.

Jianghua is an autonomous county of Yao people in the Province of Hunan, China, it is under the administration of Yongzhou Prefecture-level City.

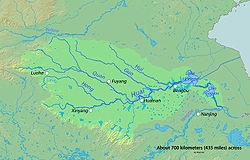
The history of canals in China connecting its major rivers and centers of agriculture and population extends from the legendary exploits of Yu the Great in his attempts control the flooding of the Yellow River to the present infrastructure projects of the People's Republic of China. From the Spring and Autumn period onward, the canals of China were used for army transportation and supply, as well as colonization of new territories. From the Qin to the Qing, China's canal network was also essential to imperial taxation-in-kind. Control of shipbuilding and internal tariffs were also administered along the canals.
Xili Reservoir is a reservoir located in Xili Subdistrict, Nanshan District, in the southwest of Shenzhen.

The Eastern Zhejiang Canal is located in Zhejiang province, China. Its west end is in Xixing Street, Binjiang District, Hangzhou City, crossing Cao'e River and Shaoxing City to its east end, the Yong River estuary in Ningbo City. The canal is 239 kilometres (149 mi) long. Early canal construction took place in the Shanyin old canal in Shaoxing City, during the Spring and Autumn period. In the third century AD, an official named He Xun supervised the construction of Xixing Canal, establishing the complete Eastern Zhejiang Canal.

The Quan River is a major river in Henan province of China. It is the largest tributary of the Ying River which is a part of the Huai River watershed system. Its total length is about 241 km, 120 km of which in the upstream section is also called Fen River. It flows into the Ying River in Anhui province.

The 2017 China floods began in early June 2017. More than 14.9017 million people in 10 provinces and municipalities and regions were affected, especially the southern and central provinces and regions of Guangxi, Guangdong, Hunan, Hubei, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Anhui, Zhejiang, Shandong, Shaanxi, Yunnan, Sichuan, Gansu and Henan. Hunan was the hardest hit. A total of 18,100 houses were destroyed, and more than 9,821-square-metre (105,710 sq ft) of crops were inundated.

Rulin Town is a town and the seat of Chengbu Miao Autonomous County in Hunan, China. The town has an area of 311 km2 (120 sq mi) with a population of 64,364. As of the 2015 census it had a population of 75,900. It is surrounded by Maoping Town on the north, Dankou Town on the west, Lanrong Township on the east, and Tingping Township on the south.

Mangshi River also called Mangshi Large River, is a river in western Yunnan, mainly in the territory of Mangshi City. It is the largest tributary river of Shweli River in China, which is a tributary river of Irrawaddy. The source of Mangshi River is at Longxin Township in Longling County, Baoshan, and the upper also called Bawan River. Mangshi River flow through the west fields of Mangshi city, and it flow in Shweli River at Gazhong Village in Zhefang Town. It is the mother river of Mangshi. The length of Mangshi River is 117.1 km, and the basin size is 1,881 km², about 61.3% of area of Mangshi City.

Lipu River, also known as Changtan River and Xiuren River, is a tributary of the Li River in northern Guangxi, China. It is 121 kilometres (75 mi) long and drains an area of 2,038 square kilometres (787 sq mi). The river rises in Mount Dayao in Zhongliang Township, Jinxiu Yao Autonomous County, and flows generally north through the towns of Xiuren and Licheng of Lipu, past the town of Pingle County, where it flows into the Li River from the west.

Maling River is a river in northern Lipu, in Guangxi, China. It is 69 square kilometres (27 sq mi) long and is a tributary of the Lipu River, draining an area of 600 square kilometres (230 sq mi). It rises in northwestern Lipu, and flows generally southeast, passing through the towns of Hualong, Shuangjiang and Maling and joining the Lipu River in the town of Dongchang.

The Rong River, commonly referred to as the South River, formerly known as the Jieyang River is located in Guangdong Province of the People's Republic of China and is the second longest river on the eastern coast of Guangdong. It is named for the many Banyan trees (róngshù) in the city of Jieyang. It rises in the southern foothills of Phoenix Mountain in Luhe County and flows northeast through the towns of Dongkeng and Shuichun, in Jiexi County the towns of Wuyun, Hepo, Daxi, and Qiankeng, in Puning the town of Lihu, then again in Jiexi the towns of Mianhu and Fengjiang, Jieyang city, and finally empties into the South China Sea at Shantou. The river is 196 km long with a drainage basin area of 4650 km2 and an average annual discharge of 6.1 billion m3. Typhoons, flooding, waterlogging, and droughts are all common along the Rong River basin.

Namwan River is a river in China and Myanmar. Namwan River rises in the mountain called Ganya Liangzi at the northern section of Longchuan County, Yunnan. It through the Longchuan county, as the major irrigation water source of the fields in the basin. And entering the valley at the southwest of Zhangfeng, the county town of Longchuan. Then it became the boundary between Myanmar and China until it entering Shweli River at Nongdao, Ruili.