
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. The electrons that are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to the ETC involves four multi-subunit large enzymes complexes and two mobile electron carriers. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane.

The coenzyme Q : cytochrome c – oxidoreductase, sometimes called the cytochrome bc1 complex, and at other times complex III, is the third complex in the electron transport chain, playing a critical role in biochemical generation of ATP. Complex III is a multisubunit transmembrane protein encoded by both the mitochondrial and the nuclear genomes. Complex III is present in the mitochondria of all animals and all aerobic eukaryotes and the inner membranes of most eubacteria. Mutations in Complex III cause exercise intolerance as well as multisystem disorders. The bc1 complex contains 11 subunits, 3 respiratory subunits, 2 core proteins and 6 low-molecular weight proteins.
Iron–sulfur proteins are proteins characterized by the presence of iron–sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers in variable oxidation states. Iron–sulfur clusters are found in a variety of metalloproteins, such as the ferredoxins, as well as NADH dehydrogenase, hydrogenases, coenzyme Q – cytochrome c reductase, succinate – coenzyme Q reductase and nitrogenase. Iron–sulfur clusters are best known for their role in the oxidation-reduction reactions of electron transport in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Both Complex I and Complex II of oxidative phosphorylation have multiple Fe–S clusters. They have many other functions including catalysis as illustrated by aconitase, generation of radicals as illustrated by SAM-dependent enzymes, and as sulfur donors in the biosynthesis of lipoic acid and biotin. Additionally, some Fe–S proteins regulate gene expression. Fe–S proteins are vulnerable to attack by biogenic nitric oxide, forming dinitrosyl iron complexes. In most Fe–S proteins, the terminal ligands on Fe are thiolate, but exceptions exist.
A hydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyses the reversible oxidation of molecular hydrogen (H2), as shown below:

Cupriavidus necator is a Gram-negative soil bacterium of the class Betaproteobacteria.
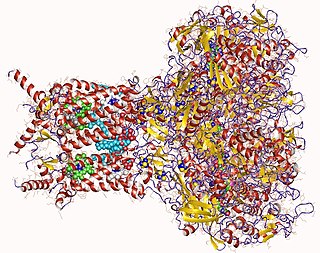
Formate dehydrogenases are a set of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide, donating the electrons to a second substrate, such as NAD+ in formate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (EC 1.17.1.9) or to a cytochrome in formate:ferricytochrome-b1 oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.2.1). This family of enzymes has attracted attention as inspiration or guidance on methods for the carbon dioxide fixation, relevant to global warming.

Electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers electrons from electron-transferring flavoprotein in the mitochondrial matrix, to the ubiquinone pool in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is part of the electron transport chain. The enzyme is found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes and contains a flavin and FE-S cluster. In humans, it is encoded by the ETFDH gene. Deficiency in ETF dehydrogenase causes the human genetic disease multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.
In enzymology, a 4-methoxybenzoate monooxygenase (O-demethylating) (EC 1.14.99.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (R)-pantolactone dehydrogenase (flavin) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phenylacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.17.5.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The 5,10-methenyltetrahydromethanopterin hydrogenase, the so-called iron-sulfur cluster-free hydrogenase, is an enzyme found in methanogenic archea such as Methanothermobacter marburgensis. It was discovered and first characterized by the Thauer group at the Max Planck Institute in Marburg. Hydrogenases are enzymes that either reduce protons or oxidize molecular dihydrogen.
In enzymology, a coenzyme F420 hydrogenase (EC 1.12.98.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cytochrome-c3 hydrogenase (EC 1.12.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, the hydrogenase maturation protease family is a family of aspartic endopeptidases belonging to MEROPS family A31.
[NiFe] hydrogenase is a type of hydrogenase, which is an oxidative enzyme that reversibly converts molecular hydrogen in prokaryotes including Bacteria and Archaea. The catalytic site on the enzyme provides simple hydrogen-metabolizing microorganisms a redox mechanism by which to store and utilize energy via the reaction

Fumarate reductase (quinol) (EC 1.3.5.4, QFR,FRD, menaquinol-fumarate oxidoreductase, quinol:fumarate reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name succinate:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction:

NADH:ubiquinone reductase (non-electrogenic) (EC 1.6.5.9, NDH-2, ubiquinone reductase, coenzyme Q reductase, dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-ubiquinone reductase, NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase, NADH-coenzyme Q reductase, NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase, NADH-CoQ reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Nitrate reductase (quinone) (EC 1.7.5.1, nitrate reductase A, nitrate reductase Z, quinol/nitrate oxidoreductase, quinol-nitrate oxidoreductase, quinol:nitrate oxidoreductase, NarA, NarZ, NarGHI) is an enzyme with systematic name nitrite:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Nitric oxide reductase (menaquinol) (EC 1.7.5.2) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Sulfide:quinone reductase is an enzyme with systematic name sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction









