
The enzyme urate oxidase (UO), uricase or factor-independent urate hydroxylase, absent in humans, catalyzes the oxidation of uric acid to 5-hydroxyisourate:

The Controlled Drugs and Substances Act is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals the Narcotic Control Act and Parts III and IV of the Food and Drugs Act, and establishes eight Schedules of controlled substances and two Classes of precursors. It provides that "The Governor in Council may, by order, amend any of Schedules I to VIII by adding to them or deleting from them any item or portion of an item, where the Governor in Council deems the amendment to be necessary in the public interest."

Urocanase is the enzyme that catalyzes the second step in the degradation of histidine, the hydration of urocanate into imidazolonepropionate.
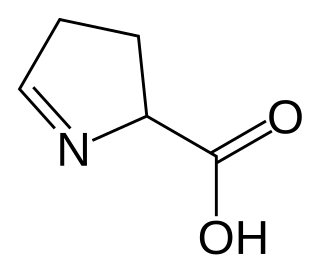
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid is a cyclic imino acid. Its conjugate base and anion is 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C). In solution, P5C is in spontaneous equilibrium with glutamate-5-semialdhyde (GSA).
In enzymology, a 3-hydroxy-4-oxoquinoline 2,4-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.47) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,6-dioxo-6-phenylhexa-3-enoate hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.6, systematic name = S-(2-hydroxyacyl)glutathione hydrolase) catalyzes the following reaction:
The enzyme hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.5) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme lipid-phosphate phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.76) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 1-pyrroline-4-hydroxy-2-carboxylate deaminase (EC 3.5.4.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 5-oxoprolinase (ATP-hydrolysing) (EC 3.5.2.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an allophanate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.54) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diaminohydroxyphosphoribosylaminopyrimidine deaminase (EC 3.5.4.26) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a GTP cyclohydrolase II (EC 3.5.4.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
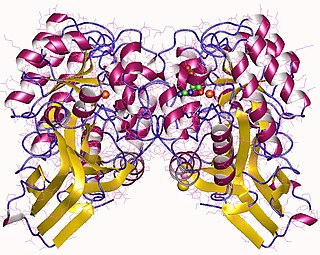
In enzymology, an imidazolonepropionase (EC 3.5.2.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
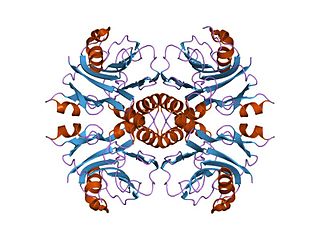
In enzymology, an IMP cyclohydrolase (EC 3.5.4.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mimosinase (EC 3.5.1.61) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoyl-L-amino-acid hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.87) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In molecular biology 2-oxo-4-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-ureidoimidazoline decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.n1 is an enzyme involved in purine catabolism. It catalyses the decarboxylation of 2-oxo-4-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-ureidoimidazoline (OHCU) into S(+)-allantoin. It is the third step of the conversion of uric acid to allantoin. Step one is catalysed by urate oxidase and step two is catalysed by hydroxyisourate hydrolase.
4-Hydroxy-7-methoxy-3-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-2-yl glucoside beta-D-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.182, DIMBOAGlc hydrolase, DIMBOA glucosidase) is an enzyme with systematic name (2R)-4-hydroxy-7-methoxy-3-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-2-yl beta-D-glucopyranoside beta-D-glucosidase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction






