| Hyperpituitarism | |
|---|---|
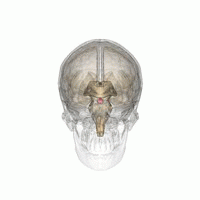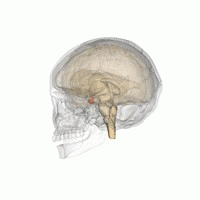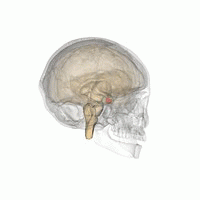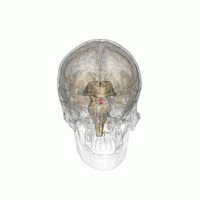 | |
| Pituitary gland | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
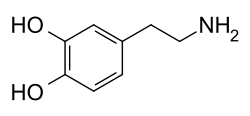
| Symptoms | Hirsutism [1] |
| Causes | From a pituitary microadenoma. [2] |
| Diagnostic method | MRI [2] |
| Treatment | Dopamine agonists [2] |
Hyperpituitarism is a condition due to the primary hypersecretion of pituitary hormones; [3] [ medical citation needed ] it typically results from a pituitary adenoma. In children with hyperpituitarism, disruption of growth regulation is rare, either because of hormone hypersecretion or because of manifestations caused by local compression of the adenoma. [2]