
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species. Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and then sometimes called carrs. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat.

Cladium is a genus of large sedges, with a nearly worldwide distribution in tropical and temperate regions. These are plants characterized by long, narrow (grass-like) leaves having sharp, often serrated (sawtooth-like) margins, and flowering stems 1–3 m tall bearing a much-branched inflorescence. Like many plants found in wet habitats, it has deeply buried rhizomes that can produce tall shoots with dense canopies.

Phalaris arundinacea, or reed canary grass, is a tall, perennial bunchgrass that commonly forms extensive single-species stands along the margins of lakes and streams and in wet open areas, with a wide distribution in Europe, Asia, northern Africa and North America. Other common names for the plant include gardener's-garters in English, alpiste roseau in French, rohrglanzgras in German, kusa-yoshi in Japanese, caniço-malhado in Portuguese, and hierba cinta and pasto cinto in Spanish.

The Big Thicket is the name given to a somewhat imprecise region of a heavily-forested area of Southeast Texas in the United States. This area represents a portion of the mixed pine-hardwood forests of southeast US. The National Park Service established the Big Thicket National Preserve (BTNP) within the region in 1974 and it is recognized as a biosphere reserve by UNESCO. Although the diversity of animals in the area is high, with over 500 vertebrates, it is the complex mosaic of ecosystems and plant diversity that is particularly remarkable. Biologists have identified at least eight, and up to eleven, ecosystems in the Big Thicket area. More than 160 species of trees and shrubs, 800 herbs and vines, and 340 types of grasses are known to occur in the Big Thicket, and estimates as high as over 1000 flowering plant species and 200 trees and shrubs have been made, plus ferns, carnivorous plants, and more. The Big Thicket has historically been the most dense forest region in what is now Texas.

Cynodon is a genus of plants in the grass family. It is native to warm temperate to tropical regions of the Old World, as well as being cultivated and naturalized in the New World and on many oceanic islands.

Eriophorum angustifolium, commonly known as common cottongrass or common cottonsedge, is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. Native to North America, North Asia, and Northern Europe, it grows on peat or acidic soils, in open wetland, heath or moorland. It begins to flower in April or May and, after fertilisation in early summer, the small, unremarkable brown and green flowers develop distinctive white bristle-like seed-heads that resemble tufts of cotton; combined with its ecological suitability to bog, these characteristics give rise to the plant's alternative name, bog cotton.

Brassica juncea, commonly brown mustard, Chinese mustard, Indian mustard, leaf mustard, Oriental mustard and vegetable mustard, is a species of mustard plant.

The University of Wisconsin–Madison Arboretum is a teaching and research facility of the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the site of historic research in ecological restoration. In addition to its 1,260 acres (5 km2) in Madison, Wisconsin, the Arboretum also manages 520 acres (210 ha) of remnant forests and prairies throughout Wisconsin. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2021, in recognition for its role as a pioneer in the field of ecological restoration.

Johnson grass or Johnsongrass, Sorghum halepense, is a plant in the grass family, Poaceae, native to Asia and northern Africa. The plant has been introduced to all continents except Antarctica, and most larger islands and archipelagos. It reproduces by rhizomes and seeds.

Hypoxis hirsuta is an ornamental plant in the family Hypoxidaceae. Sometimes this plant is placed in the family Amaryllidaceae or the family Liliaceae. The species is native to the United States, Canada, and the State of Tamaulipas in northeastern Mexico.

Hypoxis is a genus of flowering plants of the family Hypoxidaceae. The genus has an "almost cosmopolitan" distribution, occurring in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Australia. Europe lacks native species. Most species are in the Southern Hemisphere, especially in southern Africa. Common names for the genus include star-grass, star lily, yellow stars, African potato, and stars. The genus is the largest of the Hypoxidaceae and has its centre of variation in South Africa, where it occurs in open undisturbed grasslands. The name Hypoxis was taken over by Linnaeus in 1759 from a name coined by Paul Reneaulme in 1611 for a superficially similar species of Gagea and meaning "a little sour", referring to the taste of that plant's leaves.

Hypoxis hemerocallidea, the African star grass or African potato, is a medicinal plant in the Hypoxidaceae family. It is native to southern Africa from South Africa as far north as Mozambique and Zimbabwe. This plant is the best known member of this genus.

Microstegium vimineum, commonly known as Japanese stiltgrass, packing grass, or Nepalese browntop, is an annual grass that is common in a wide variety of habitats and is well adapted to low light levels.

The round-tailed muskrat is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae, sometimes called the Florida water rat. The species is monotypic in the genus Neofiber. It is found only in the southeastern United States, where its natural habitat is swamps.

Cirsium lecontei, often called the Le Conte's thistle, is a North American plant species native to the southeastern United States. It is a perennial, or sometimes biennial, species of the tribe Cardueae within the family Asteraceae. It grows along the coastal plain from Louisiana to North Carolina.

Psathyrostachys juncea is a species of grass known by the common name Russian wildrye. It was formerly classified as Elymus junceus. It is native to Russia and China, and has been introduced to other parts of the world, such as Canada and the United States. Psathyrostachys juncea is a great source of food for grazing animals, as it has high nutrition value in its dense basal leaves, even in the late summer and autumn seasons. This species can grow and prosper in many harsh environments, making it an ideal candidate for improvement as it can grow in areas were farming is difficult. This species is a drought-resistant forage plant and can survive during the cool seasons. It is also a cross-pollinator and is self-sterile. This means that P. juncea cannot self-fertilize; it must find another plant of the same species with which to exchange gametes. Self-sterilization increases the genetic diversity of a species.
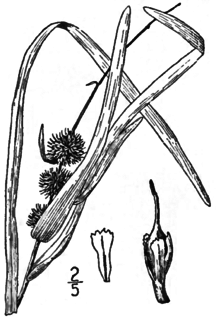
Sparganium americanum, American bur-reed, is a perennial plant found in the United States of America and Canada. Though this species resembles a grass, it is a type of bur-reed. This species is important for conservation purposes because it has the ability to remove nitrogen and phosphorus runoff from water, like many other wetland species. By doing this it protects waterways from excess nitrogen which can cause eutrophication. This increased nitrogen is especially a problem during the farmers’ growing season. During this same time frame the S. americanum is growing and taking up nitrogen.

Polygala nana, commonly known as candyroot or low bachelors' buttons, is a small herbaceous plant native to the southeastern United States. The root has a sweet liquorice flavor when it is chewed, but it is usually hidden underground until the plant flowers. The seeds of candyroot are dispersed by ants.

Eriocaulon aquaticum is a species of flowering plant in the family Eriocaulaceae.



















