This is a glossary of medical terms related to communications disorders which are conditions that could have the potential to negatively impact the level at which an individual can hear, understand, and respond to others.

A hearing test provides an evaluation of the sensitivity of a person's sense of hearing and is most often performed by an audiologist using an audiometer. An audiometer is used to determine a person's hearing sensitivity at different frequencies. There are other hearing tests as well, e.g., Weber test and Rinne test.

Conductive hearing loss (CHL) occurs when there is a problem transferring sound waves anywhere along the pathway through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). If a conductive hearing loss occurs in conjunction with a sensorineural hearing loss, it is referred to as a mixed hearing loss. Depending upon the severity and nature of the conductive loss, this type of hearing impairment can often be treated with surgical intervention or pharmaceuticals to partially or, in some cases, fully restore hearing acuity to within normal range. However, cases of permanent or chronic conductive hearing loss may require other treatment modalities such as hearing aid devices to improve detection of sound and speech perception.

Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear or sensory organ or the vestibulocochlear nerve. SNHL accounts for about 90% of reported hearing loss. SNHL is usually permanent and can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total. Various other descriptors can be used depending on the shape of the audiogram, such as high frequency, low frequency, U-shaped, notched, peaked, or flat.
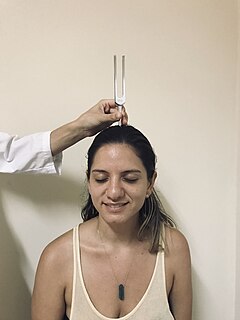
The Weber test is a screening test for hearing performed with a tuning fork. It can detect unilateral (one-sided) conductive hearing loss and unilateral sensorineural hearing loss. The test is named after Ernst Heinrich Weber (1795–1878). Conductive hearing ability is mediated by the middle ear composed of the ossicles: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. Sensorineural hearing ability is mediated by the inner ear composed of the cochlea with its internal basilar membrane and attached cochlear nerve. The outer ear consisting of the pinna, ear canal, and ear drum or tympanic membrane transmits sounds to the middle ear but does not contribute to the conduction or sensorineural hearing ability save for hearing transmissions limited by cerumen impaction.
The Rinne test is used primarily to evaluate loss of hearing in one ear. It compares perception of sounds transmitted by air conduction to those transmitted by bone conduction through the mastoid. Thus, one can quickly screen for the presence of conductive hearing loss.

Facial nerve paralysis is a common problem that involves the paralysis of any structures innervated by the facial nerve. The pathway of the facial nerve is long and relatively convoluted, so there are a number of causes that may result in facial nerve paralysis. The most common is Bell's palsy, a disease of unknown cause that may only be diagnosed by exclusion of identifiable serious causes.
Otology is a branch of medicine which studies normal and pathological anatomy and physiology of the ear as well as their diseases, diagnosis and treatment. Otologic surgery generally refers to surgery of the middle ear and mastoid related to chronic otitis media, such as tympanoplasty, or ear drum surgery, ossiculoplasty, or surgery of the hearing bones, and mastoidectomy. Otology also includes surgical treatment of conductive hearing loss, such as stapedectomy surgery for otosclerosis.
This is a shortened version of fifth chapter of the ICD-10: Mental and behavioural disorders. It covers ICD codes F00 to F99. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the sixth chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the nervous system. It covers ICD codes G00.0 to G99. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the eleventh chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the digestive system. It covers ICD codes K00.0 to K93. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the twelfth chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It covers ICD codes L00 to L99. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the thirteenth chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue. It covers ICD codes M00.0 to M99. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the fourteenth chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the genitourinary system. It covers ICD codes N00.0 to N99.9. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the sixteenth chapter of the ICD-10: Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period. It covers ICD codes P00.0 to P96.9. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
Hearing loss with craniofacial syndromes is a common occurrence. Many of these multianomaly disorders involve structural malformations of the outer or middle ear, making a significant hearing loss highly likely.
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) provided by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), for medical coding and reporting in the United States. The ICD-10-CM is a morbidity classification for classifying diagnoses and reason for visits in all American health care settings. The ICD-10-CM is based on the ICD-10, the statistical classification of disease published by the World Health Organization (WHO) which replaces ICD-9.
Amblyaudia is a term coined by Dr. Deborah Moncrieff to characterize a specific pattern of performance from dichotic listening tests. Dichotic listening tests are widely used to assess individuals for binaural integration, a type of auditory processing skill. During the tests, individuals are asked to identify different words presented simultaneously to the two ears. Normal listeners can identify the words fairly well and show a small difference between the two ears with one ear slightly dominant over the other. For the majority of listeners, this small difference is referred to as a "right-ear advantage" because their right ear performs slightly better than their left ear. But some normal individuals produce a "left-ear advantage" during dichotic tests and others perform at equal levels in the two ears. Amblyaudia is diagnosed when the scores from the two ears are significantly different with the individual's dominant ear score much higher than the score in the non-dominant ear Researchers interested in understanding the neurophysiological underpinnings of amblyaudia consider it to be a brain based hearing disorder that may be inherited or that may result from auditory deprivation during critical periods of brain development. Individuals with amblyaudia have normal hearing sensitivity but have difficulty hearing in noisy environments like restaurants or classrooms. Even in quiet environments, individuals with amblyaudia may fail to understand what they are hearing, especially if the information is new or complicated. Amblyaudia can be conceptualized as the auditory analog of the better known central visual disorder amblyopia. The term “lazy ear” has been used to describe amblyaudia although it is currently not known whether it stems from deficits in the auditory periphery or from other parts of the auditory system in the brain, or both. A characteristic of amblyaudia is suppression of activity in the non-dominant auditory pathway by activity in the dominant pathway which may be genetically determined and which could also be exacerbated by conditions throughout early development.
Bone-conduction auditory brainstem response or BCABR is a type of auditory evoked response that records neural response from EEG with stimulus transmitted through bone conduction.