
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.

The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.
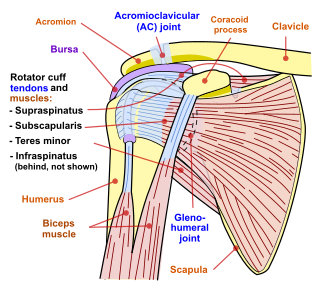
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.

Wrist drop, is a medical condition in which the wrist and the fingers cannot extend at the metacarpophalangeal joints. The wrist remains partially flexed due to an opposing action of flexor muscles of the forearm. As a result, the extensor muscles in the posterior compartment remain paralyzed.

The upper limb or upper extremity is the region in a vertebrate animal extending from the deltoid region up to and including the hand, including the arm, axilla and shoulder.
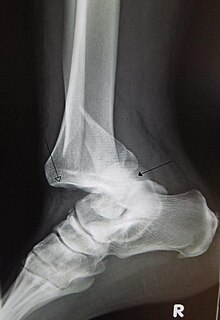
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma on the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any joint major or minor. The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.
A soft tissue injury (STI) is the damage of muscles, ligaments and tendons throughout the body. Common soft tissue injuries usually occur from a sprain, strain, a one off blow resulting in a contusion or overuse of a particular part of the body. Soft tissue injuries can result in pain, swelling, bruising and loss of function.
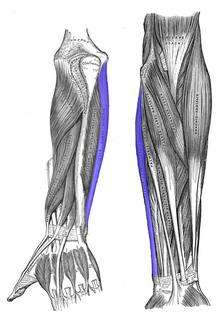
The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and adduct the hand.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball and socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves articulation between the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus.

A brachial plexus injury (BPI), also known as brachial plexus lesion, is an injury to the brachial plexus, the network of nerves that conducts signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm and hand. These nerves originate in the fifth, sixth, seventh and eighth cervical (C5–C8), and first thoracic (T1) spinal nerves, and innervate the muscles and skin of the chest, shoulder, arm and hand.
This is a shortened version of the thirteenth chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue. It covers ICD codes M00.0 to M99. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.

Radial neuropathy is a type of mononeuropathy which results from acute trauma to the radial nerve that extends the length of the arm. It is known as transient paresthesia when sensation is temporarily abnormal.

Jammed finger is a colloquialism referring to a variety of injuries to the joints of the fingers, resulting from axial loading beyond that which the ligaments can withstand. Common parts of the finger susceptible to this type of injury are ligaments, joints, and bones. The severity of the damage to the finger increases with the magnitude of the force exerted by the external object on the fingertip. Toes may become jammed as well, with similar results.

Musculoskeletal injury refers to damage of muscular or skeletal systems, which is usually due to a strenuous activity. In one study, roughly 25% of approximately 6300 adults received a musculoskeletal injury of some sort within 12 months—of which 83% were activity-related. Musculoskeletal injury spans into a large variety of medical specialties including orthopedic surgery, sports medicine, emergency medicine and rheumatology. Musculoskeletal injuries can affect any part of the human body including; bones, joints, cartilages, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and other soft tissues. Symptoms include mild to severe aches, low back pain, numbness, tingling, atrophy and weakness. These injuries are a result of repetitive motions and actions over a period of time. Tendons connect muscle to bone whereas ligaments connect bone to bone. Tendons and ligaments play an active role in maintain joint stability and controls the limits of joint movements, once injured tendons and ligaments detrimentally impact motor functions. Continuous exercise or movement of a musculoskeletal injury can result in chronic inflammation with progression to permanent damage or disability.

The elbow is the visible joint between the upper and lower parts of the arm. It includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the elbow pit, the lateral and medial epicondyles, and the elbow joint. The elbow joint is the synovial hinge joint between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body.
If your hands are hurt you should soak them in cold water for 5-10 minutes let them dry the cold water will numb the hands and stop the pain but if your hand hurting is serous then that here are other things you can do.